本文主要是介绍图论09-桥和割点,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1 寻找桥的算法
- 2 桥的代码实现
- 3 寻找割点的算法
- 4 割点的代码实现
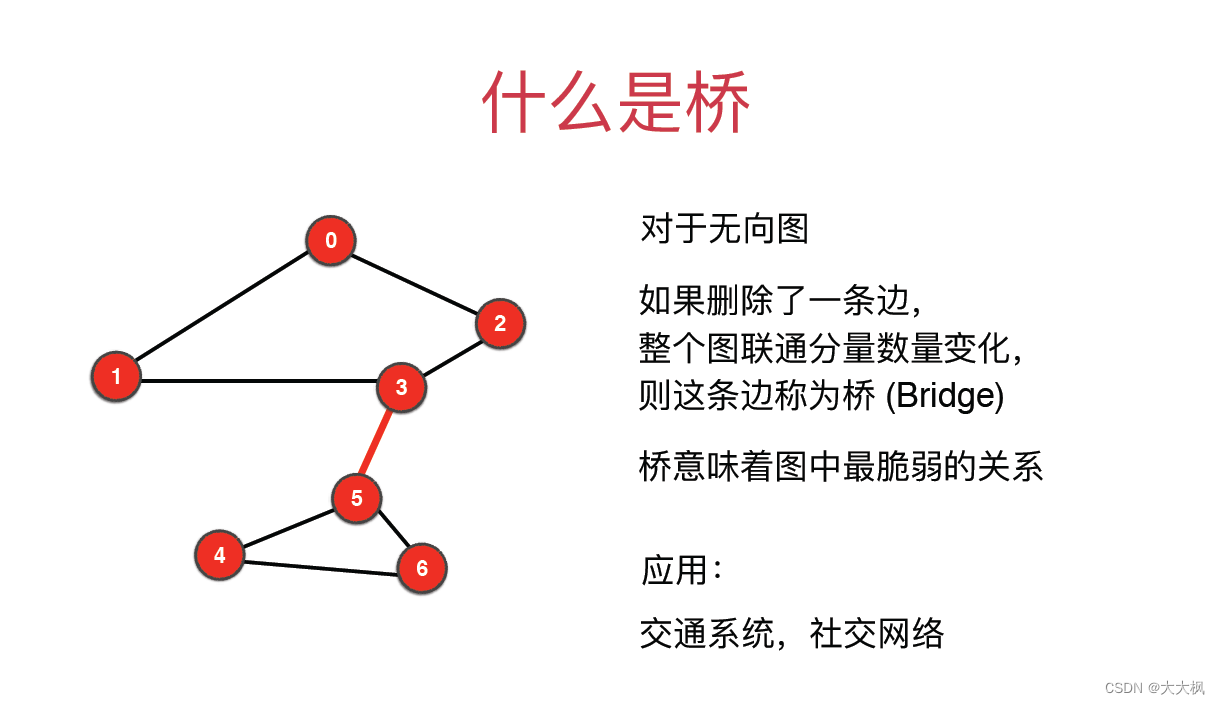
1 寻找桥的算法
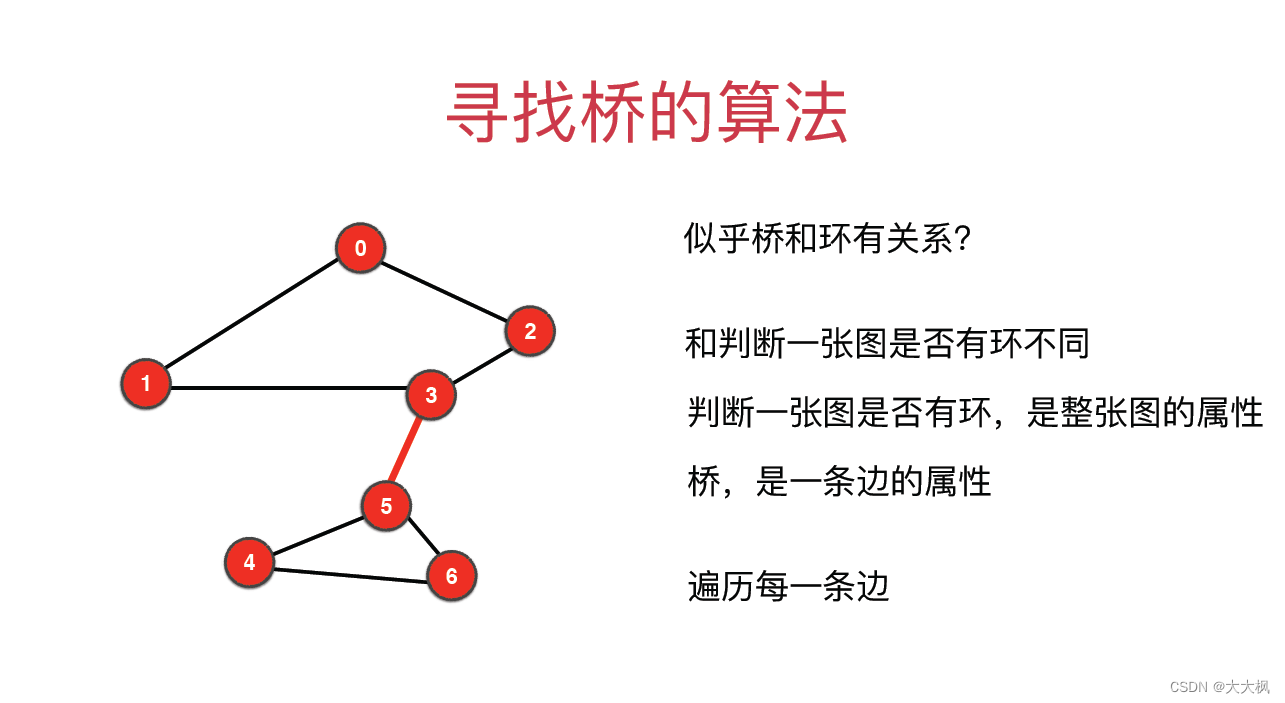
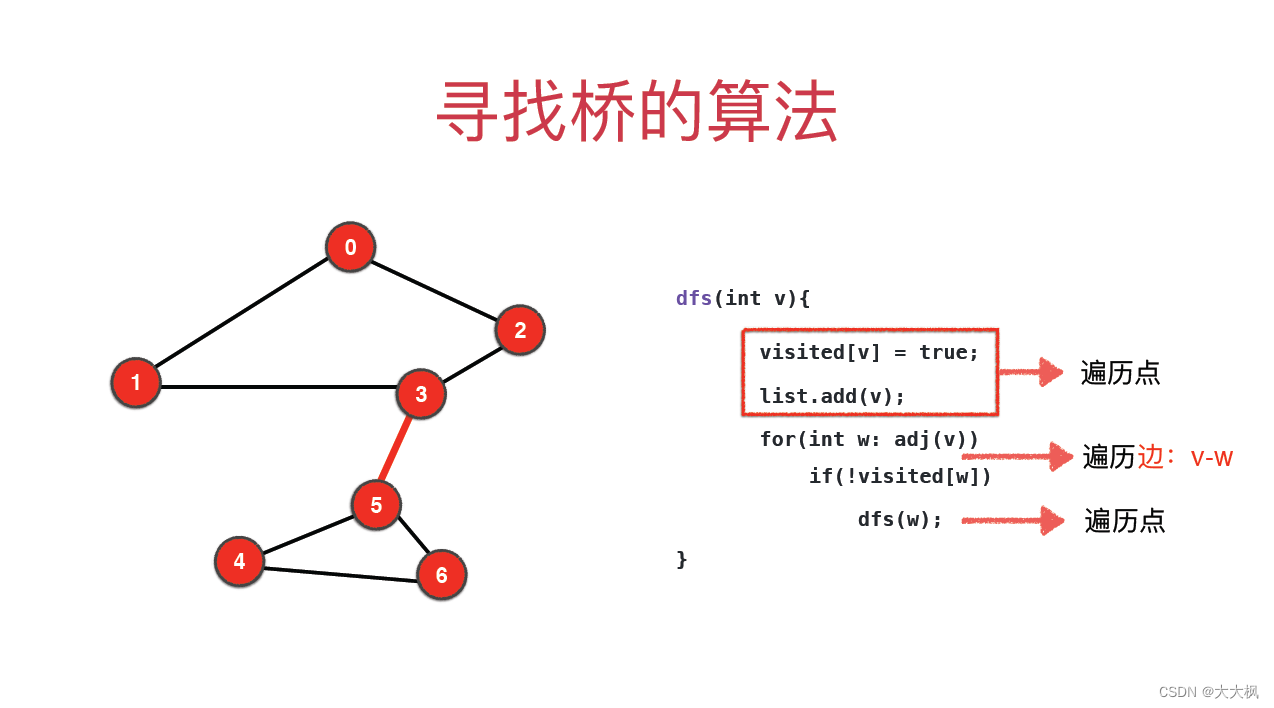
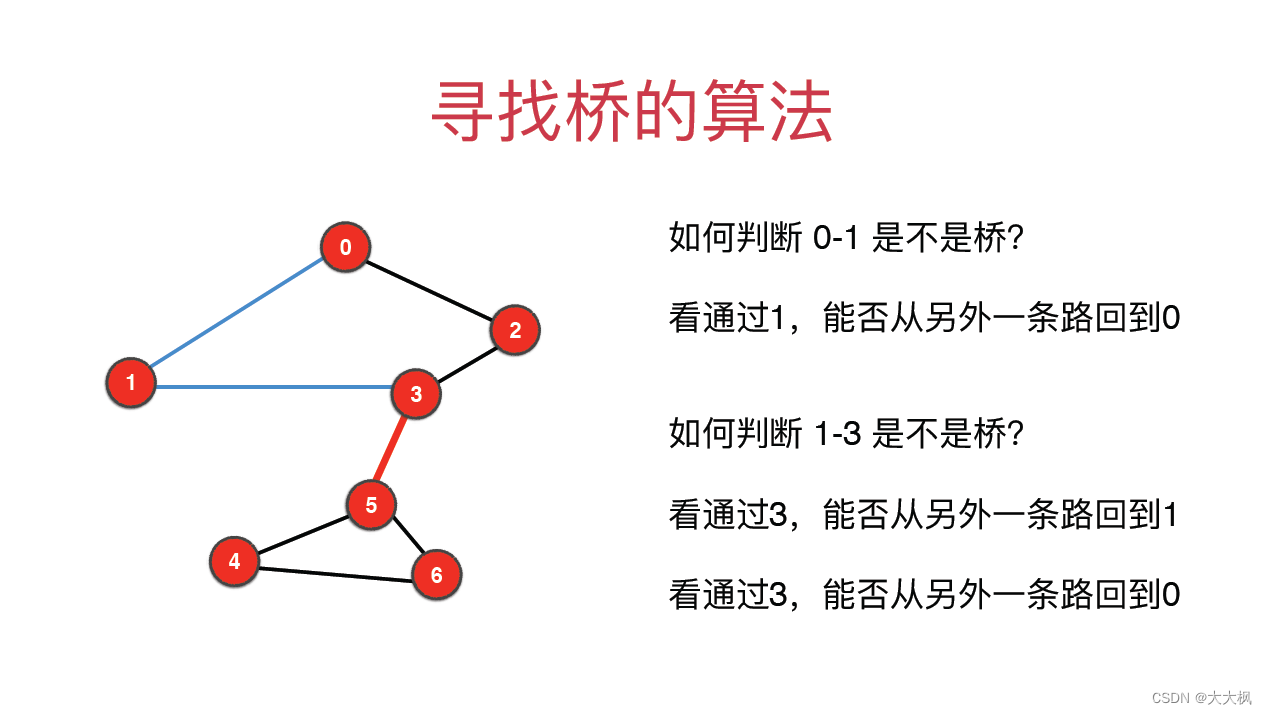
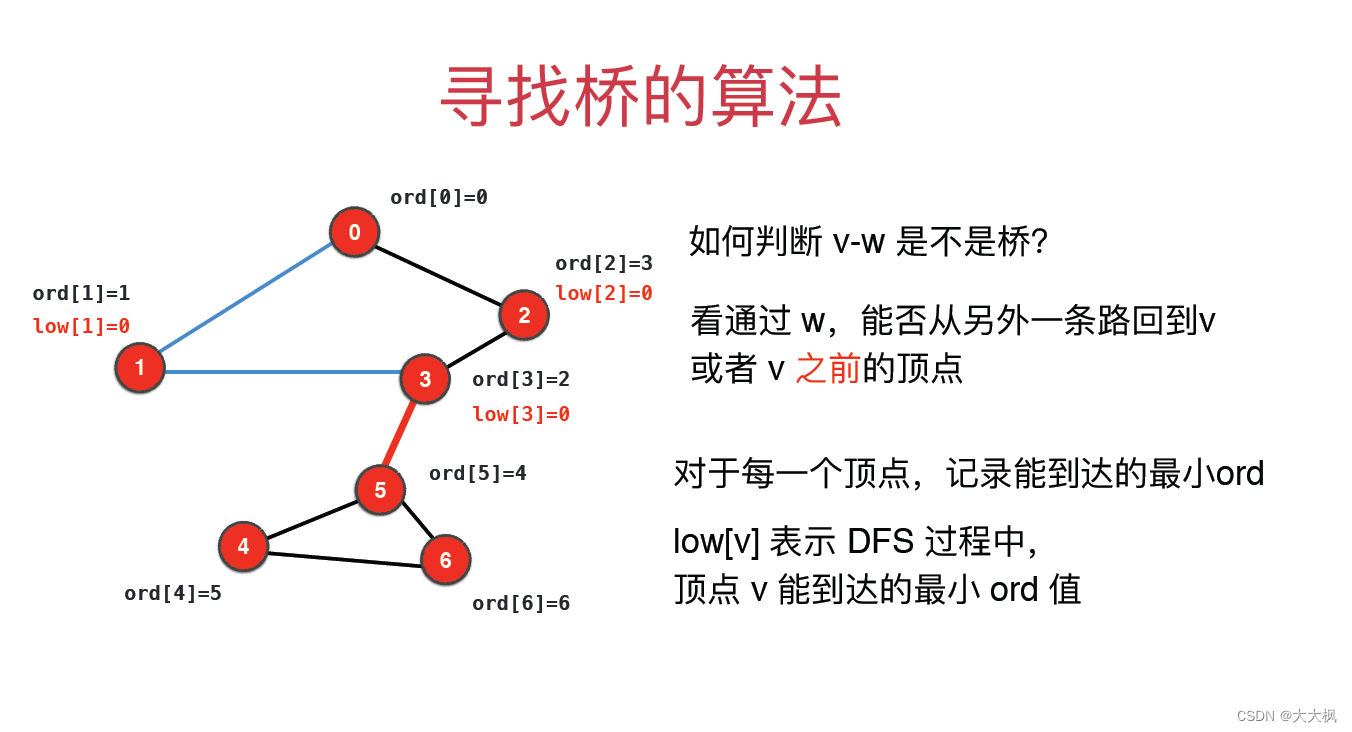
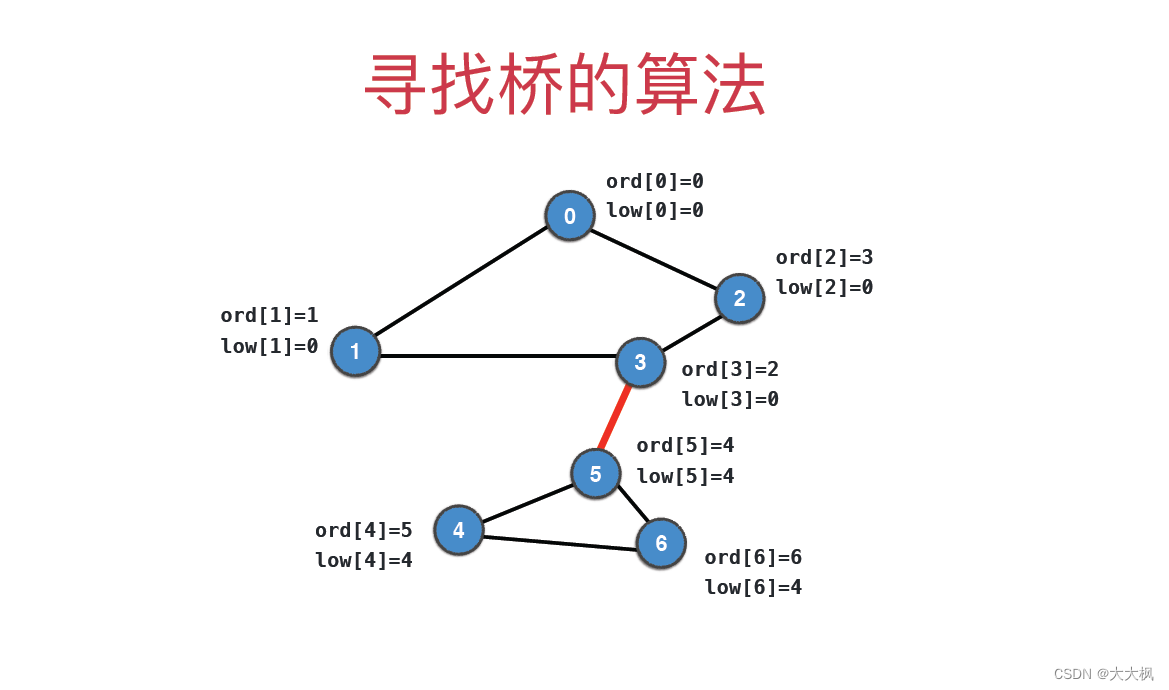
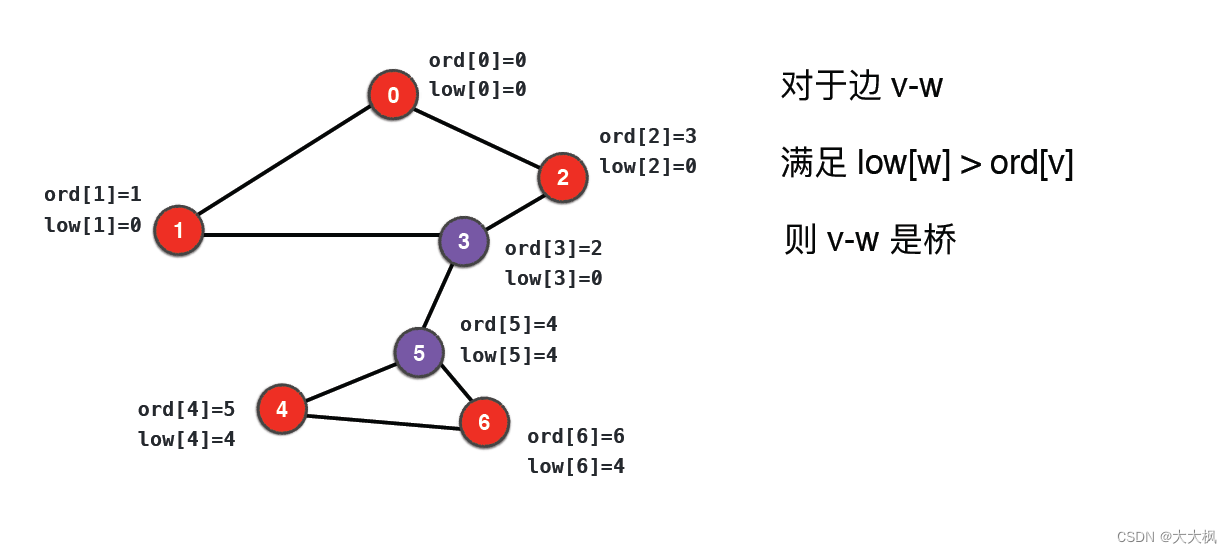
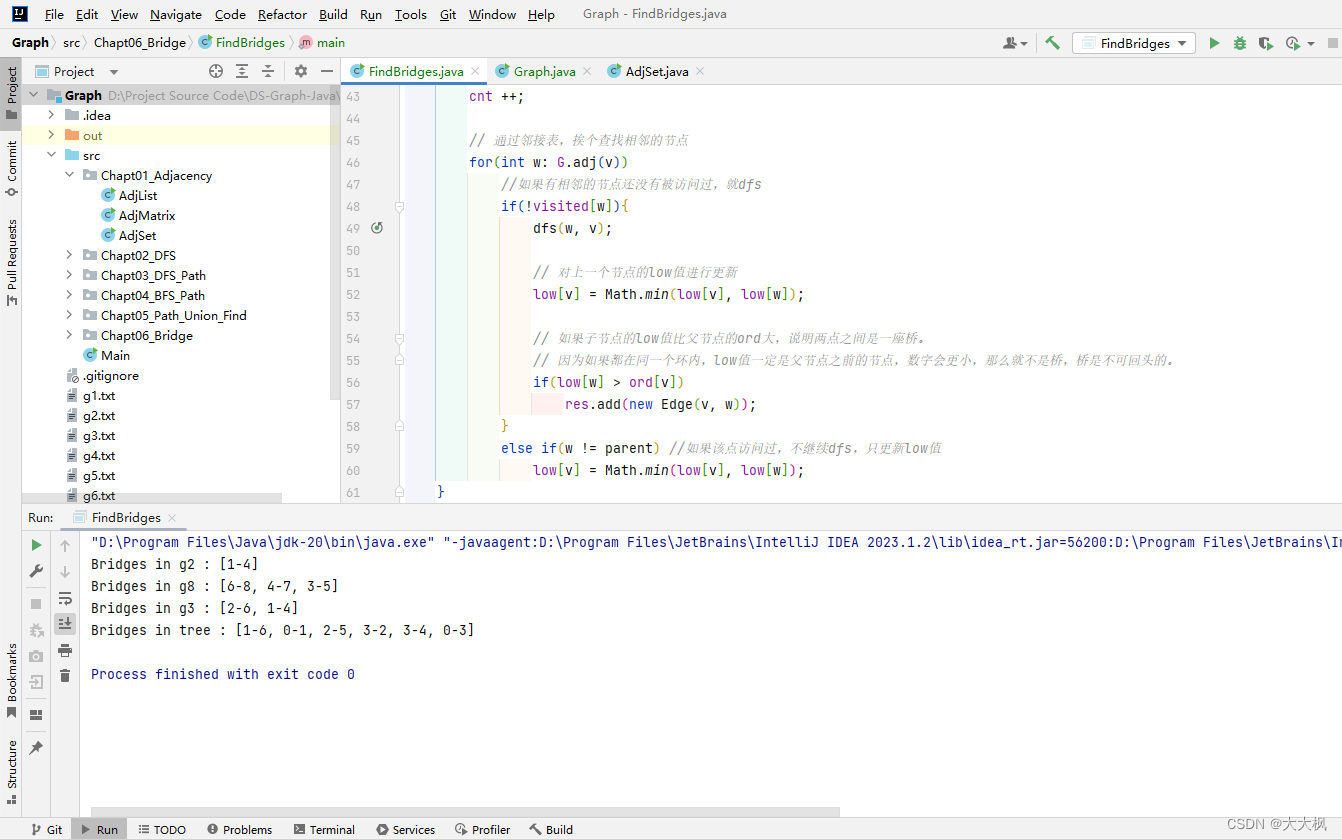
2 桥的代码实现
package Chapt06_Bridge;import java.util.ArrayList;public class FindBridges {private Graph G;private boolean[] visited;//ord数组记录访问的顺序private int ord[];//low数组记录该顶点可以访问到的ord[值]最小的[顶点]private int low[];//cnt用来记录步数,给order赋值private int cnt;// Edge类型的动态数组private ArrayList<Edge> res;public FindBridges(Graph G){this.G = G;visited = new boolean[G.V()];res = new ArrayList<>();ord = new int[G.V()];low = new int[G.V()];cnt = 0;for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)if(!visited[v])dfs(v, v);}private void dfs(int v, int parent){visited[v] = true;ord[v] = cnt;// 初始的时候,low的值就是访问的顺序值,在递归return的时候才进行更新low[v] = ord[v];cnt ++;// 通过邻接表,挨个查找相邻的节点for(int w: G.adj(v))//如果有相邻的节点还没有被访问过,就dfsif(!visited[w]){dfs(w, v);// 对上一个节点的low值进行更新low[v] = Math.min(low[v], low[w]);// 如果子节点的low值比父节点的ord大,说明两点之间是一座桥。// 因为如果都在同一个环内,low值一定是父节点之前的节点,数字会更小,那么就不是桥,桥是不可回头的。if(low[w] > ord[v])res.add(new Edge(v, w));}else if(w != parent) //如果该点访问过,不继续dfs,只更新low值low[v] = Math.min(low[v], low[w]);}public ArrayList<Edge> result(){return res;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g2.txt");FindBridges fb = new FindBridges(g);System.out.println("Bridges in g2 : " + fb.result());Graph g2 = new Graph("g8.txt");FindBridges fb2 = new FindBridges(g2);System.out.println("Bridges in g8 : " + fb2.result());Graph g3 = new Graph("g3.txt");FindBridges fb3 = new FindBridges(g3);System.out.println("Bridges in g3 : " + fb3.result());Graph tree = new Graph("tree.txt");FindBridges fb_tree = new FindBridges(tree);System.out.println("Bridges in tree : " + fb_tree.result());}
}
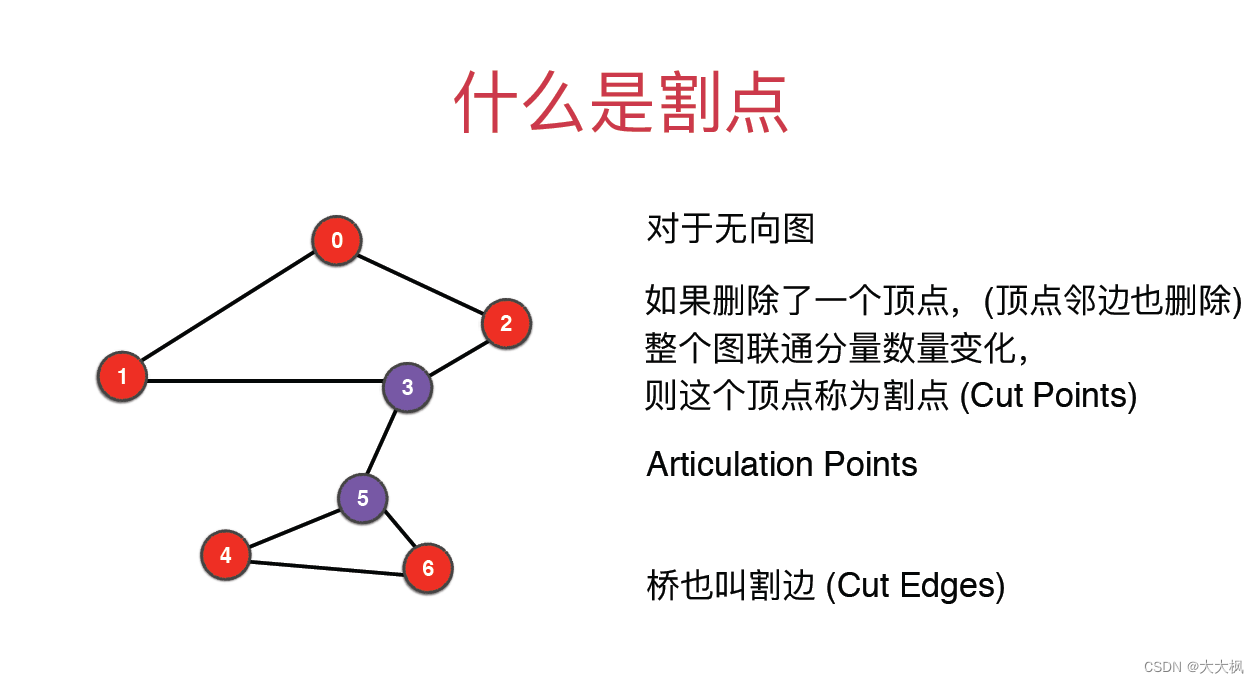
3 寻找割点的算法
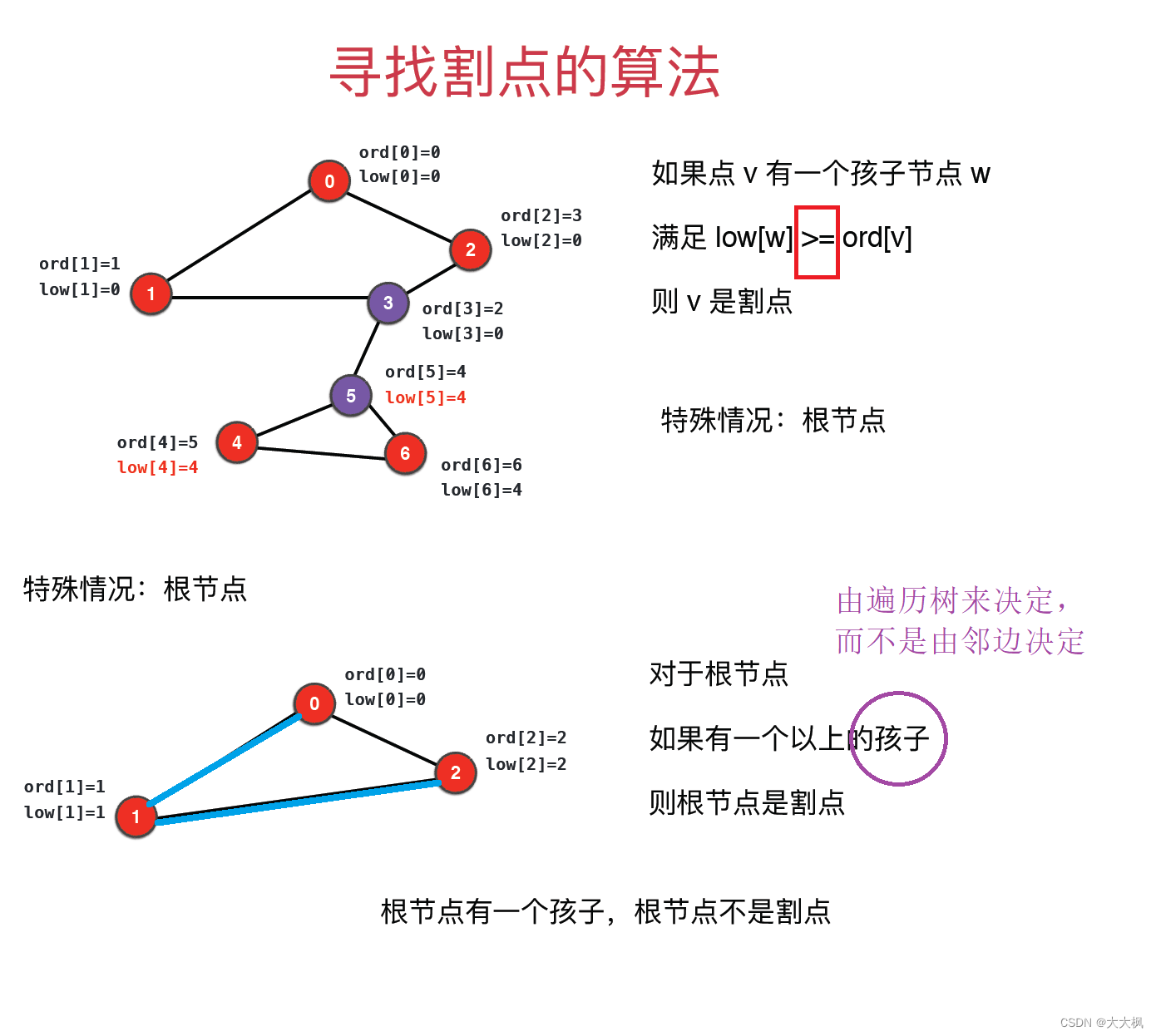
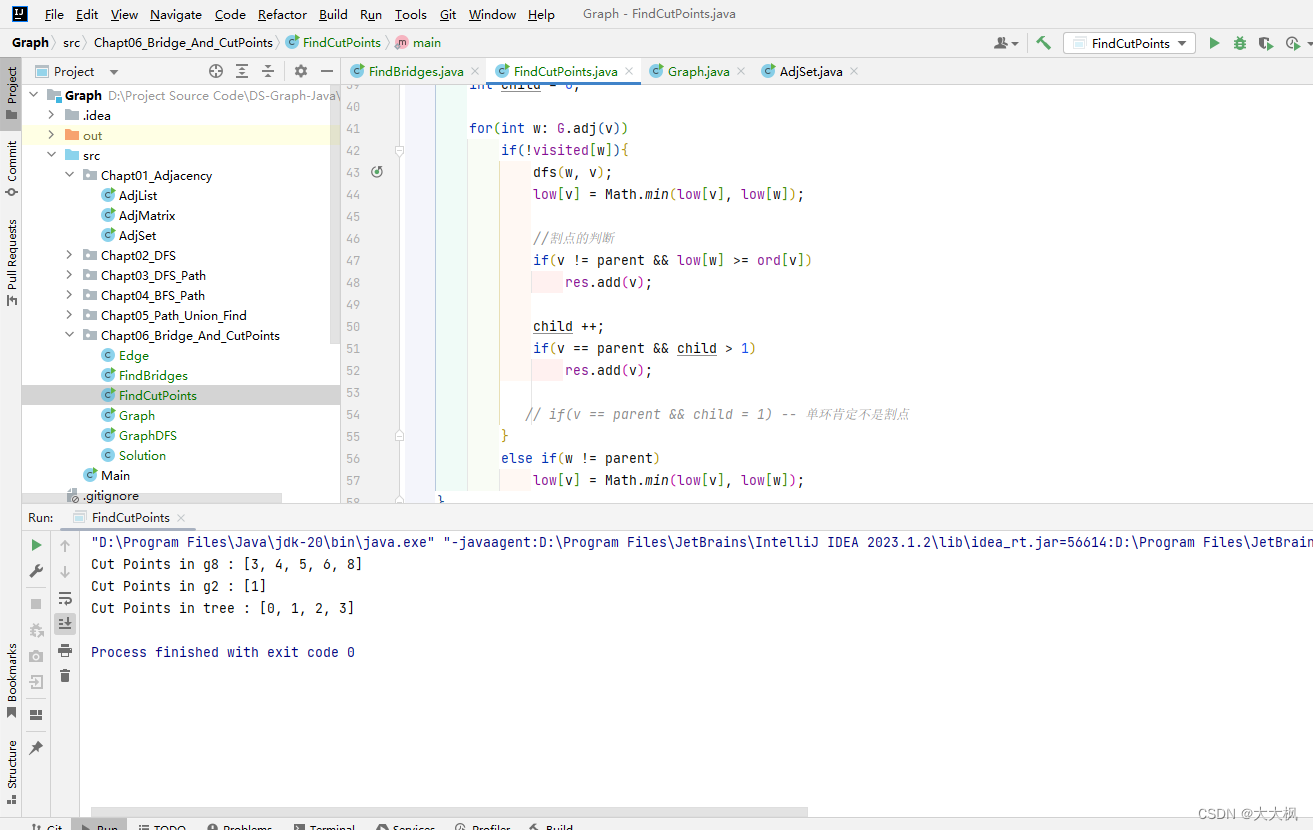
4 割点的代码实现
package Chapt06_Bridge_And_CutPoints;import java.util.HashSet;public class FindCutPoints {private Graph G;private boolean[] visited;private int[] ord;private int[] low;private int cnt;private HashSet<Integer> res;public FindCutPoints(Graph G){this.G = G;visited = new boolean[G.V()];res = new HashSet<>();ord = new int[G.V()];low = new int[G.V()];cnt = 0;for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)if(!visited[v])dfs(v, v);}private void dfs(int v, int parent){visited[v] = true;ord[v] = cnt;low[v] = ord[v];cnt ++;// 记录子节点的数量int child = 0;for(int w: G.adj(v))if(!visited[w]){dfs(w, v);low[v] = Math.min(low[v], low[w]);//割点的判断if(v != parent && low[w] >= ord[v])res.add(v);child ++;if(v == parent && child > 1)res.add(v);// if(v == parent && child = 1) -- 单环肯定不是割点}else if(w != parent)low[v] = Math.min(low[v], low[w]);}public HashSet<Integer> result(){return res;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g8.txt");FindCutPoints fc = new FindCutPoints(g);System.out.println("Cut Points in g8 : " + fc.result());Graph g2 = new Graph("g2.txt");FindCutPoints fc2 = new FindCutPoints(g2);System.out.println("Cut Points in g2 : " + fc2.result());Graph tree = new Graph("tree.txt");FindCutPoints fc3 = new FindCutPoints(tree);System.out.println("Cut Points in tree : " + fc3.result());}
}
这篇关于图论09-桥和割点的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!