本文主要是介绍Java实现之马踏棋盘算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一.问题引入
1.问题引入
1)马踏棋盘算法也被称为骑士周游问题
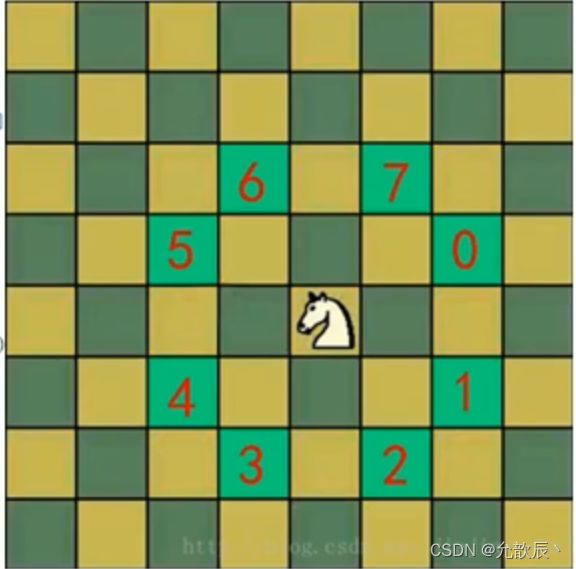
2)将马随机放在国际象棋的8×8棋盘,Board[0~~7][0~7]的某个方格中,马按走棋规则(马走日字)进行移动。要求每个方格只进入一次,走遍棋盘上全部64个方格
二.马踏棋盘算法
1.基本介绍
1)马踏棋盘问题(骑士周游问题)实际上是图的深度优先搜索(DFS)的应用。
2)如果使用回溯(就是深度优先搜索)来解决,假如马儿踏了53个点,如图:走到了第53个,坐标(1,0),发现已经走到尽头,没办法,那就只能回退了,查看其他的路径,就在棋盘上不停的回溯.......,
3)分析第一种方式的问题,并使用贪心算法(greedyalgorithm)进行优化。解决马踏棋盘问题.
2.解决思路
1.创建棋盘chessBoard ,是一个二维数组
2.将当前位置设置为已经访问,然后根据当前位置,计算马儿还能走哪些位置并放入到一个集合中(ArrayList),最多有8个位置,每走一步,就使用step+1
3.遍历ArrayList中存放的所有位置,看看哪个可以走通,如果走通,就继续,走不通,就回溯.
4.判断马儿是否完成了任务,使用step和应该走的步数比较,如果没有达到数量,则表示没有完成任务,将整个棋盘置0
注意:马儿不同的走法〈策略),会得到不同的结果,效率也会有影响(优化)
3.代码实现
public class HorseChessBoard {public static int X; //棋盘的列数public static int Y; //棋盘的行数public static boolean[] isVisted;//标记棋盘的各个位置是否被访问过了public static boolean isFinshed; //表示所有位置都被访问过了public static void main(String[] args) {X = 8;Y = 8;isVisted = new boolean[X * Y];int x = 1, y = 1;int[][] chessBoard = new int[X][Y];travelChessBoard(chessBoard, x - 1, y - 1, 1);for (int[] ints : chessBoard) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));}}/*** 完成其实周游问题的算法** @param chessBoard 棋盘* @param row 马儿当前在哪一行* @param column 马儿当前在哪一列* @param step 当前在第几步*/public static void travelChessBoard(int[][] chessBoard, int row, int column, int step) {chessBoard[row][column] = step;isVisted[row * X + column] = true; //标记位置已经被访问//获取当前位置可以走的位置ArrayList<Point> next = next(new Point(column, row));while (!next.isEmpty()) {Point point = next.remove(0); //取出下一个可以访问的结点//判断此点是否访问过if (!isVisted[point.y * X + point.x]) {//没有访问过travelChessBoard(chessBoard, point.y, point.x, step + 1);}}//.判断马儿是否完成了任务,使用step和应该走的步数比较,// 如果没有达到数量,则表示没有完成任务,将整个棋盘置0if (step < X * Y && !isFinshed) {chessBoard[row][column] = 0;isVisted[row * X + column] = false;} else {isFinshed = true;}}public static ArrayList<Point> next(Point curPoint) {ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<>();Point point = new Point();if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0) {//5points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0) {//6points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (point.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0) {//7points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (point.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0) {//0points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (point.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y) {//1points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (point.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y) {//2points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y) {//3points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y) {//4points.add(new Point(point));}return points;}}打印结果:
[1, 8, 11, 16, 3, 18, 13, 64]
[10, 27, 2, 7, 12, 15, 4, 19]
[53, 24, 9, 28, 17, 6, 63, 14]
[26, 39, 52, 23, 62, 29, 20, 5]
[43, 54, 25, 38, 51, 22, 33, 30]
[40, 57, 42, 61, 32, 35, 48, 21]
[55, 44, 59, 50, 37, 46, 31, 34]
[58, 41, 56, 45, 60, 49, 36, 47]
4.代码优化
马儿不同的走法〈策略),会得到不同的结果,效率也会有影响(优化)
使用贪心算法对原来的算法优化
1。我们获取当前位置,可以走的下一个位置的集合//获取当前位置可以走的下一个位置的集合
ArrayList<Point> ps= next(new point(column, row));
⒉我们斋要对ps 中所有的Point 的下一步的所有集合的数目,进行非递减排序,就ok ,
public class HorseChessBoard {public static int X; //棋盘的列数public static int Y; //棋盘的行数public static boolean[] isVisted;//标记棋盘的各个位置是否被访问过了public static boolean isFinshed; //表示所有位置都被访问过了public static void main(String[] args) {X = 8;Y = 8;isVisted = new boolean[X * Y];int x = 1, y = 1;int[][] chessBoard = new int[X][Y];travelChessBoard(chessBoard, x - 1, y - 1, 1);for (int[] ints : chessBoard) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));}}/*** 完成其实周游问题的算法** @param chessBoard 棋盘* @param row 马儿当前在哪一行* @param column 马儿当前在哪一列* @param step 当前在第几步*/public static void travelChessBoard(int[][] chessBoard, int row, int column, int step) {chessBoard[row][column] = step;isVisted[row * X + column] = true; //标记位置已经被访问//获取当前位置可以走的位置ArrayList<Point> next = next(new Point(column, row));//对next进行排序,排序的规则是next的下一个的数目sort(next);while (!next.isEmpty()) {Point point = next.remove(0); //取出下一个可以访问的结点//判断此点是否访问过if (!isVisted[point.y * X + point.x]) {//没有访问过travelChessBoard(chessBoard, point.y, point.x, step + 1);}}//.判断马儿是否完成了任务,使用step和应该走的步数比较,// 如果没有达到数量,则表示没有完成任务,将整个棋盘置0if (step < X * Y && !isFinshed) {chessBoard[row][column] = 0;isVisted[row * X + column] = false;} else {isFinshed = true;}}public static ArrayList<Point> next(Point curPoint) {ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<>();Point point = new Point();if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0) {//5points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0) {//6points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (point.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0) {//7points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (point.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0) {//0points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (point.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y) {//1points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (point.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y) {//2points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y) {//3points.add(new Point(point));}if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y) {//4points.add(new Point(point));}return points;}//根据当前这一步的下一步的选择位置,进行排序public static void sort(ArrayList<Point> next){next.sort(new Comparator<Point>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Point o1, Point o2) {ArrayList<Point> next1 = next(o1);ArrayList<Point> next2 = next(o2);return next1.size()-next2.size();}});}}
这篇关于Java实现之马踏棋盘算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




