本文主要是介绍【3D 图像分割】基于 Pytorch 的 VNet 3D 图像分割8(CT肺实质分割),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
针对医疗领域中的病灶检测中,采用分割算法最为常见。但是,针对特定脏器内的病灶检测,一直存在一个特别易出现假阳性的地方,就是脏器外的误检测。
这种错误是非常明显,且非常容易被判别为假阳性的。与此同时,这种脏器外的假阳性,也是最容易去除的。
本文就主要针对 CT 肺部,对肺实质部分进行切割,去除掉除肺部之外的组织干扰。需要注意的是:
针对肺结节类型的分割前处理中,一般会引入肺实质分割。但是,该方法不能适用于所有的肺部分割中的前处理。因为针对较大的病灶范围,尤其是钙化严重且面积较大,会使得病灶部分与肺区外部分较为相似,一同被切除掉,这是我们所不想看到的。所以对这块的弥补,本文也有处理。
分割步骤见后面的分割结果图,相信你能看懂。最终我们就是要把肺实质给留下来,其他的肺区外的组织,都不要了,如果能区分左、右肺实质,那就更棒了。
一、基于 KMean 的肺区分割
胸部CT之所以能够直接采用传统的方法对肺实质进行分割,主要的原因是肺实质部分与肋骨、脂肪等等组织,在切片层上面表现出来的特征差异化较大。反观DR胸片,就很难直接采用这种方式进行肺区提取。
那既然组织之间的差异性大,那能不能直接采用聚类的方式,对单层slice的区域进行分开呢?处理的大致步骤如下:
- 首先,这里的输入数据,是dicom转到0-255的数组,这部分处理可以参考这篇文章:【医学影像数据处理】 Dicom 文件格式处理汇总
- 其次,调整原图,凸显肺区
- kmean聚类,将单slice分割各个类别
- 对聚类结果根据先验规则进行过滤筛选
- 最后,得到肺区的mask,显示出来
下面是具体的代码实现:
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom skimage import morphology
from skimage import measure
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from skimage.color import label2rgbdef get_candidateLabel(regions, row_size, col_size):good_labels_n = []bbox_list_n = []area_list_n = []for prop in regions:B = prop.bboxarea = prop.area# 筛选满足条件,根据先验知识可能是肺区的部分labelx1, y1, x2, y2 = Bif x2 - x1 < row_size / 10 * 9 and y2 - y1 < col_size / 10 * 9 \and x1 > row_size / 5 and x2 < col_size / 5 * 4:good_labels_n.append(prop.label)bbox_list_n.append(prop.coords)area_list_n.append(area)return good_labels_n, bbox_list_n, area_list_ndef filter_Large(good_labels_n, bbox_list_n, area_list_n):# 找到该类别中的所有元素的索引indices = [i for i, x in enumerate(area_list_n)]# 找到该类别中前两个最大值的索引max_indices = sorted(indices, key=lambda i: area_list_n[i], reverse=True)[:2]good_labels = []bbox_list = []area_list = []for i in max_indices:good_labels.append(good_labels_n[i])bbox_list.append(bbox_list_n[i])area_list.append(area_list_n[i])print('area_list:', area_list)return good_labels, bbox_list, area_listdef generate_lungMask(img_origin, good_labels, labels):mask = np.zeros_like(img_origin, dtype=np.int8)print('good_label:', good_labels)for N in good_labels:mask = mask + np.where(labels == N, 1, 0)mask_e = morphology.erosion(mask, np.ones([5, 5]))mask = morphology.dilation(mask_e, np.ones([10, 10])) # one last dilationreturn maskdef make_lungMask(img_origin, display=False):row_size, col_size = img_origin.shape[:2]# 全图归一化mean = np.mean(img_origin)std = np.std(img_origin)img_norm = img_origin - meanimg_norm = img_norm / std# Find the average pixel value near the lungs to renormalize washed out imagesmiddle = img_norm[int(col_size / 5):int(col_size / 5 * 4), int(row_size / 5):int(row_size / 5 * 4)]mean = np.mean(middle)max = np.max(img_norm)min = np.min(img_norm)# To improve threshold finding, I'm moving the underflow and overflow on the pixel spectrumimg_norm[img_norm == max] = meanimg_norm[img_norm == min] = mean# Using Kmeans to separate foreground (soft tissue / bone) and background (lung/air)kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2).fit(np.reshape(middle, [np.prod(middle.shape), 1]))centers = sorted(kmeans.cluster_centers_.flatten())threshold = np.mean(centers)# remove small noisemask = img_norm < thresholdmask = morphology.remove_small_objects(mask, 100)mask_t = morphology.remove_small_holes(mask, 100)# Two pixels are connected when they are neighbors and have the same value,# Different labels are displayed in different colorslabels = measure.label(mask_t)regions = measure.regionprops(labels) # 测量标记图像区域的属性image_label_overlay = label2rgb(labels, image=img_origin, bg_label=0)good_labels_n, bbox_list_n, area_list_n = get_candidateLabel(regions, row_size, col_size)good_labels, bbox_list, area_list = filter_Large(good_labels_n, bbox_list_n, area_list_n)lung_mask = generate_lungMask(img_origin, good_labels, labels)if display:fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, 3, figsize=[12, 12])ax[0, 0].set_title("original image")ax[0, 0].imshow(img_origin, cmap='gray')ax[0, 0].axis('off')ax[0, 1].set_title("middle image")ax[0, 1].imshow(middle, cmap='gray')ax[0, 1].axis('off')ax[0, 2].set_title("threshold mask")ax[0, 2].imshow(mask_t, cmap='gray')ax[0, 2].axis('off')ax[1, 0].set_title("color labels")ax[1, 0].imshow(labels)ax[1, 0].axis('off')ax[1, 1].set_title("final lung mask")ax[1, 1].imshow(lung_mask, cmap='gray')ax[1, 1].axis('off')ax[1, 2].set_title("image_label_overlay")ax[1, 2].imshow(image_label_overlay, cmap='gray')ax[1, 2].axis('off')ax[2, 0].set_title("apply lung mask on original image")ax[2, 0].imshow(lung_mask * img_origin, cmap='gray')ax[2, 0].axis('off')plt.show()return mask, bbox_listif __name__ == '__main__':save_dir = r'./save'os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)png_path = './1.png'img = cv2.imread(png_path)gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)mask, bbox_list = make_lungMask(gray, display=True)cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(save_dir, filename), mask * gray)print('\n')单张图的分割算法的流程及展示的结果如下,注意:display需要设定为True

可以看到各个处理阶段得到的图像形式,最终将肺区mask与原始图像相乘,得到了分割后的样子。下面对上述代码,做个简单的介绍:
# Standardize the pixel values
def make_lungmask(img, display=False):row_size = img.shape[0]col_size = img.shape[1]这部分代码定义了一个名为make_lungmask的函数,用于标准化像素值。row_size和col_size分别获取图像的行数和列数。
mean = np.mean(img)std = np.std(img)img = img - meanimg = img / std这部分代码对图像进行像素值标准化,通过计算图像的均值和标准差,将图像的像素值转换为具有零均值和单位方差的形式。
middle = img[int(col_size / 5):int(col_size / 5 * 4), int(row_size / 5):int(row_size / 5 * 4)]mean = np.mean(middle)max = np.max(img)min = np.min(img)img[img == max] = meanimg[img == min] = mean这部分代码找到了图像中肺部附近的像素值,并计算了该区域的平均值。然后,将图像中最大和最小的像素值替换为该平均值,以便对洗涤出的图像进行重新归一化。
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2).fit(np.reshape(middle, [np.prod(middle.shape), 1]))centers = sorted(kmeans.cluster_centers_.flatten())threshold = np.mean(centers)thresh_img = np.where(img < threshold, 1.0, 0.0)这部分代码使用K均值聚类算法将图像中的前景(软组织/骨骼)和背景(肺部/空气)分离开来。首先,将肺部附近的像素值进行重塑,并使用K均值聚类算法将其分为两个簇。然后,通过计算聚类中心的平均值来确定阈值,并使用阈值将图像进行二值化处理。
eroded = morphology.erosion(thresh_img, np.ones([3, 3]))dilation = morphology.dilation(eroded, np.ones([8, 8]))这部分代码先对二值化后的图像进行腐蚀操作,去除细小的元素。然后再进行膨胀操作,以包括一些周围的像素,但不会意外截断肺部。
对单个series检查,应用肺区分割,裁剪后的结果展示如下:

二、基于Dicom的Hu值的肺区分割
代码实现如下,对于其中具体的细节,待补充:
from skimage.segmentation import clear_border
from skimage.measure import label, regionprops
from skimage.morphology import disk, dilation, binary_erosion, binary_closing
from skimage.filters import roberts, sobel
from scipy import ndimage as ndidef get_CT_info(src_dir):Slices = []for file in os.listdir(src_dir):if file.endswith('.dcm'):slice = pydicom.read_file(src_dir + '/' + file)# print ("AAA:", Slices)Slices.append(slice)Slices.sort(key=lambda x: int(x.InstanceNumber)) # 层序列号return Slicesdef get_pixels_hu(Slices):images = np.stack([s.pixel_array for s in Slices])images_temp = imagesimages_temp = images_temp.astype("int32")print("Start Dicom pixel_array:", images_temp.dtype)for slice_number in range(len(Slices)):intercept = Slices[slice_number].RescaleInterceptslope = Slices[slice_number].RescaleSlopeimages_temp[slice_number] = slope * images_temp[slice_number] + interceptreturn images_tempdef get_segmented_lungs(im):'''Args:- im:Return:- im:- binary:'''# Step 1: Convert into a binary image.binary = im < -400# Step 2: Remove the blobs connected to the border of the image.cleared = clear_border(binary)# Step 3: Label the image.label_image = label(cleared)# Step 4: Keep the labels with 2 largest areas.areas = [r.area for r in regionprops(label_image)]areas.sort()if len(areas) > 2:for region in regionprops(label_image):if region.area < areas[-2]:for coordinates in region.coords:label_image[coordinates[0], coordinates[1]] = 0binary = label_image > 0# Step 5: Erosion operation with a disk of radius 2. This operation is# seperate the lung nodules attached to the blood vessels.selem = disk(2)binary = binary_erosion(binary, selem)# Step 6: Closure operation with a disk of radius 10. This operation is to# keep nodules attached to the lung wall.selem = disk(10) # CHANGE BACK TO 10binary = binary_closing(binary, selem)# Step 7: Fill in the small holes inside the binary mask of lungs.edges = roberts(binary)binary = ndi.binary_fill_holes(edges)# Step 8: Superimpose the binary mask on the input image.get_high_vals = binary == 0im[get_high_vals] = -2000return im, binarydef set_img_WindowCenterWidth(images, window_width, window_center):try:if len(window_width) > 1:window_width = window_width[0]window_center = window_center[0]except:window_width = window_widthwindow_center = window_centerif window_center > 0:window_center = -600window_width = 1600images.astype(np.float64)# upper = 600# lower = -1000# images[images > upper] = upper# images[images < lower] = lowermin_value = window_center - window_width / 2max_value = window_center + window_width / 2images = (images - min_value) * 255.0 / (max_value - min_value)images[images > 255.0] = 255.0images[images < 0] = 0.0return images.astype(np.uint8)def seg_method():int_path = r'./data/dcm'save_dir = r'./results'for patient in os.listdir(int_path):SeriesInstanceUID_path = os.path.join(int_path, patient, 'dcm')print(SeriesInstanceUID_path)##########################肺区分割部分################################Slices_info = get_CT_info(SeriesInstanceUID_path) # 一个序列CT的所有slice—dcm信息images = get_pixels_hu(Slices_info) # 一个序列的dcm转为png做准备for i in range(images.shape[0]):plt.figure(figsize=[15, 5])org_img_one = images[i]_, mask = get_segmented_lungs(org_img_one.copy())index_num = "0"*(4-len(str(i+1)))+str(i+1)#try:WindowWidth = Slices_info[i].WindowWidthexcept:WindowWidth = 1600try:WindowCenter = Slices_info[i].WindowCenterexcept:WindowCenter = -600img = set_img_WindowCenterWidth(org_img_one, WindowWidth, WindowCenter)rlo = mask * imgplt.subplot(131)plt.title('origin')plt.imshow(img)plt.subplot(132)plt.title('mask')plt.imshow(mask*255)plt.subplot(133)plt.title('lung')plt.imshow(rlo)plt.show()save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, patient)if not os.path.exists(save_path):os.makedirs(save_path)cv2.imwrite(save_path + '/{}_{}.png'.format(patient, index_num), mask*255)if __name__ == '__main__':seg_method()这里是没有区分左右肺区的,采用了粗暴的中心划分的方式进行区分,如下所示:(左右可能有误)
_, mask = get_segmented_lungs(org_img_one.copy())mask = mask.astype(np.uint8)
maskL = np.where(mask[:, 0:256]==1., 3, 0)
maskR = np.where(mask[:, 256:]==1., 4, 0)
mask = np.hstack((maskL, maskR))三、基于Dicom的Hu值肺区分割(区分左右)
3部分是不能够区分左右的,区分的方式也是简单暴力。在这一节里面,记录了可以区分左右分区的分割方式,代码实现如下:
import numpy as np
import scipy.ndimage
from skimage import measure, morphology
import SimpleITK as sitk
from multiprocessing import Pool
import os
import nrrd
from scipy.ndimage import label, generate_binary_structure, binary_dilation
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def extract_main(binary_mask, cover=0.95):"""Extract lung without bronchi/trachea. Remove small componentsbinary_mask: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only region of interest is True. One side of the lung in thisspecifical case.cover: float, percetange of the total area to keep of each slice, bykeeping the total connected componentsreturn: binary mask with the same shape of the image, that only region ofinterest is True. One side of the lung in this specifical case."""for i in range(binary_mask.shape[0]):slice_binary = binary_mask[i]label = measure.label(slice_binary)properties = measure.regionprops(label)properties.sort(key=lambda x: x.area, reverse=True)areas = [prop.area for prop in properties]count = 0area_sum = 0area_cover = np.sum(areas) * cover# count how many components covers, e.g 95%, of total area (lung)while area_sum < area_cover:area_sum += areas[count]count += 1# SLICE-WISE: exclude trachea/bronchi.# only keep pixels in convex hull of big components, since# convex hull contains small components of lungs we still wantslice_filter = np.zeros(slice_binary.shape, dtype=bool)for j in range(count):min_row, min_col, max_row, max_col = properties[j].bboxslice_filter[min_row:max_row, min_col:max_col] |= \properties[j].convex_imagebinary_mask[i] = binary_mask[i] & slice_filterlabel = measure.label(binary_mask)properties = measure.regionprops(label)properties.sort(key=lambda x: x.area, reverse=True)# VOLUME: Return lung, ie the largest component.binary_mask = (label == properties[0].label)return binary_maskdef fill_2d_hole(binary_mask):"""Fill in holes of binary single lung slicewise.binary_mask: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only region of interest is True. One side of the lung in thisspecifical case.return: binary mask with the same shape of the image, that only region ofinterest is True. One side of the lung in this specifical case."""for i in range(binary_mask.shape[0]):slice_binary = binary_mask[i]label = measure.label(slice_binary)properties = measure.regionprops(label)for prop in properties:min_row, min_col, max_row, max_col = prop.bboxslice_binary[min_row:max_row, min_col:max_col] |= \prop.filled_image # 2D component without holesbinary_mask[i] = slice_binaryreturn binary_maskdef seperate_two_lung(binary_mask, spacing, max_iter=22, max_ratio=4.8):"""Gradually erode binary mask until lungs are in two separate components(trachea initially connects them into 1 component) erosions are just usedfor distance transform to separate full lungs.binary_mask: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only region of interest is True.spacing: float * 3, raw CT spacing in [z, y, x] order.max_iter: max number of iterations for erosion.max_ratio: max ratio allowed between the volume differences of two lungsreturn: two 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only region of interest is True. Each binary mask is ROI of oneside of the lung."""found = Falseiter_count = 0binary_mask_full = np.copy(binary_mask)while not found and iter_count < max_iter:label = measure.label(binary_mask, connectivity=2)properties = measure.regionprops(label)# sort componets based on their areaproperties.sort(key=lambda x: x.area, reverse=True)if len(properties) > 1 and \properties[0].area / properties[1].area < max_ratio:found = True# binnary mask for the larger eroded lungeroded1 = (label == properties[0].label)# binnary mask for the smaller eroded lungeroded2 = (label == properties[1].label)else:# erode the convex hull of each 3D component by 1 voxelbinary_mask = scipy.ndimage.binary_erosion(binary_mask)iter_count += 1# because eroded lung will has smaller volums than the original lung,# we need to label those eroded voxel based on their distances to the# two eroded lungs.if found:# distance1 has the same shape as the 3D CT image, each voxel contains# the euclidient distance from the voxel to the closest voxel within# eroded1, so voxel within eroded1 will has distance 0.distance1 = scipy.ndimage.distance_transform_edt(~eroded1, sampling=spacing)distance2 = scipy.ndimage.distance_transform_edt(~eroded2, sampling=spacing)# Original mask & lung1 maskbinary_mask1 = binary_mask_full & (distance1 < distance2)# Original mask & lung2 maskbinary_mask2 = binary_mask_full & (distance1 > distance2)# remove bronchi/trachea and other small componentsbinary_mask1 = extract_main(binary_mask1)binary_mask2 = extract_main(binary_mask2)else:# did not seperate the two lungs, use the original lung as one of thembinary_mask1 = binary_mask_fullbinary_mask2 = np.zeros(binary_mask.shape).astype('bool')binary_mask1 = fill_2d_hole(binary_mask1)binary_mask2 = fill_2d_hole(binary_mask2)return binary_mask1, binary_mask2def binarize(image, spacing, intensity_thred=-600, sigma=1.0, area_thred=30.0,eccen_thred=0.99, corner_side=10):"""Binarize the raw 3D CT image slice by sliceimage: 3D numpy array of raw HU values from CT series in [z, y, x] order.spacing: float * 3, raw CT spacing in [z, y, x] order.intensity_thred: float, thredhold for lung and airsigma: float, standard deviation used for Gaussian filter smoothing.area_thred: float, min threshold area measure in mm.eccen_thred: float, eccentricity thredhold measure how round is an ellipsecorner_side: int, side length of top-left corner in each slice,in terms of pixels.return: binary mask with the same shape of the image, that only region ofinterest is True."""binary_mask = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=bool)side_len = image.shape[1] # side length of each slice, e.g. 512# [-side_len/2, side_len/2], e.g. [-255.5, -254.5, ..., 254.5, 255.5]grid_axis = np.linspace(-side_len / 2 + 0.5, side_len / 2 - 0.5, side_len)x, y = np.meshgrid(grid_axis, grid_axis)# pixel distance from each pixel to the origin of the slice of shape# [side_len, side_len]distance = np.sqrt(np.square(x) + np.square(y))# four corners are 0, elsewhere are 1nan_mask = (distance < side_len / 2).astype(float)nan_mask[nan_mask == 0] = np.nan # assing 0 to be np.nan# binarize each slicefor i in range(image.shape[0]):slice_raw = np.array(image[i]).astype('float32')# number of differnet values in the top-left cornernum_uniq = len(np.unique(slice_raw[0:corner_side, 0:corner_side]))# black corners out-of-scan, make corners nan before Gaussian filtering# (to make corners False in mask)if num_uniq == 1:slice_raw *= nan_maskslice_smoothed = scipy.ndimage.gaussian_filter(slice_raw, sigma,truncate=2.0)# mask of low-intensity pixels (True = lungs, air)slice_binary = slice_smoothed < intensity_thred# get connected componets annoated by labellabel = measure.label(slice_binary)properties = measure.regionprops(label)label_valid = set()for prop in properties:# area of each componets measured in mmarea_mm = prop.area * spacing[1] * spacing[2]# only include comppents with curtain min area and round enoughif area_mm > area_thred and prop.eccentricity < eccen_thred:label_valid.add(prop.label)# test each pixel in label is in label_valid or not and add those True# into slice_binaryslice_binary = np.in1d(label, list(label_valid)).reshape(label.shape)binary_mask[i] = slice_binaryreturn binary_maskdef exclude_corner_middle(label):"""Exclude componets that are connected to the 8 corners and the middle ofthe 3D imagelabel: 3D numpy array of connected component labels with same shape of theraw CT imagereturn: label after setting those components to 0"""# middle of the left and right lungsmid = int(label.shape[2] / 2)corner_label = set([label[0, 0, 0],label[0, 0, -1],label[0, -1, 0],label[0, -1, -1],label[-1, 0, 0],label[-1, 0, -1],label[-1, -1, 0],label[-1, -1, -1]])middle_label = set([label[0, 0, mid],label[0, -1, mid],label[-1, 0, mid],label[-1, -1, mid]])for l in corner_label:label[label == l] = 0for l in middle_label:label[label == l] = 0return labeldef volume_filter(label, spacing, vol_min=0.2, vol_max=8.2):"""Remove volumes too large/small to be lungs takes out most of air aroundbody.adult M total lung capacity is 6 L (3L each)adult F residual volume is 1.1 L (0.55 L each)label: 3D numpy array of connected component labels with same shape of theraw CT image.spacing: float * 3, raw CT spacing in [z, y, x] order.vol_min: float, min volume of the lungvol_max: float, max volume of the lung"""properties = measure.regionprops(label)for prop in properties:if prop.area * spacing.prod() < vol_min * 1e6 or \prop.area * spacing.prod() > vol_max * 1e6:label[label == prop.label] = 0return labeldef exclude_air(label, spacing, area_thred=3e3, dist_thred=62):"""Select 3D components that contain slices with sufficient area that,on average, are close to the center of the slice. Select component(s) thatpasses this condition:1. each slice of the component has significant area (> area_thred),2. average min-distance-from-center-pixel < dist_thredshould select lungs, which are closer to center than out-of-body spaceslabel: 3D numpy array of connected component labels with same shape of theraw CT image.spacing: float * 3, raw CT spacing in [z, y, x] order.area_thred: float, sufficient areadist_thred: float, sufficient closereturn: binary mask with the same shape of the image, that only region ofinterest is True. has_lung means if the remaining 3D component is lungor not"""# prepare a slice map of distance to centery_axis = np.linspace(-label.shape[1]/2+0.5, label.shape[1]/2-0.5,label.shape[1]) * spacing[1]x_axis = np.linspace(-label.shape[2]/2+0.5, label.shape[2]/2-0.5,label.shape[2]) * spacing[2]y, x = np.meshgrid(y_axis, x_axis)# real distance from each pixel to the origin of a slicedistance = np.sqrt(np.square(y) + np.square(x))distance_max = np.max(distance)# properties of each 3D componet.vols = measure.regionprops(label)label_valid = set()for vol in vols:# 3D binary matrix, only voxels within label matches vol.label is Truesingle_vol = (label == vol.label)# measure area and min_dist for each slice# min_distance: distance of closest voxel to center# (else max(distance))slice_area = np.zeros(label.shape[0])min_distance = np.zeros(label.shape[0])for i in range(label.shape[0]):slice_area[i] = np.sum(single_vol[i]) * np.prod(spacing[1:3])min_distance[i] = np.min(single_vol[i] * distance +(1 - single_vol[i]) * distance_max)# 1. each slice of the component has enough area (> area_thred)# 2. average min-distance-from-center-pixel < dist_thredif np.average([min_distance[i] for i in range(label.shape[0])if slice_area[i] > area_thred]) < dist_thred:label_valid.add(vol.label)binary_mask = np.in1d(label, list(label_valid)).reshape(label.shape)has_lung = len(label_valid) > 0return binary_mask, has_lungdef fill_hole(binary_mask):"""Fill in 3D holes. Select every component that isn't touching corners.binary_mask: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only region of interest is True."""# 3D components that are not ROIlabel = measure.label(~binary_mask)# idendify corner componentscorner_label = set([label[0, 0, 0],label[0, 0, -1],label[0, -1, 0],label[0, -1, -1],label[-1, 0, 0],label[-1, 0, -1],label[-1, -1, 0],label[-1, -1, -1]])binary_mask = ~np.in1d(label, list(corner_label)).reshape(label.shape)return binary_maskdef extract_lung(image, spacing):"""Preprocess pipeline for extracting the lung from the raw 3D CT image.image: 3D numpy array of raw HU values from CT series in [z, y, x] order.spacing: float * 3, raw CT spacing in [z, y, x] order.return: two 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only region of interest is True. Each binary mask is ROI of oneside of the lung. Also return if lung is found or not."""# binary mask with the same shape of the image, that only region of# interest is True.binary_mask = binarize(image, spacing)# labelled 3D connected componets, with the same shape as image. each# commponet has a different int number > 0label = measure.label(binary_mask, connectivity=1)# exclude componets that are connected to the 8 corners and the middle# of the 3D imagelabel = exclude_corner_middle(label)# exclude componets that are too small or too large to be lunglabel = volume_filter(label, spacing)# exclude more air chunks and grab lung mask regionbinary_mask, has_lung = exclude_air(label, spacing)# fill in 3D holes. Select every component that isn't touching corners.binary_mask = fill_hole(binary_mask)# seperate two lungsbinary_mask1, binary_mask2 = seperate_two_lung(binary_mask, spacing)return binary_mask1, binary_mask2, has_lungdef load_itk_image(filename):"""Return img array and [z,y,x]-ordered origin and spacing"""itkimage = sitk.ReadImage(filename)numpyImage = sitk.GetArrayFromImage(itkimage)numpyOrigin = np.array(list(reversed(itkimage.GetOrigin())))numpySpacing = np.array(list(reversed(itkimage.GetSpacing())))return numpyImage, numpyOrigin, numpySpacingdef resample(image, spacing, new_spacing=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], order=1):"""Resample image from the original spacing to new_spacing, e.g. 1x1x1image: 3D numpy array of raw HU values from CT series in [z, y, x] order.spacing: float * 3, raw CT spacing in [z, y, x] order.new_spacing: float * 3, new spacing used for resample, typically 1x1x1,which means standardizing the raw CT with different spacing all into1x1x1 mm.order: int, order for resample function scipy.ndimage.interpolation.zoomreturn: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image after,resampling. The actual resampling spacing is also returned."""# shape can only be int, so has to be rounded.new_shape = np.round(image.shape * spacing / new_spacing)# the actual spacing to resample.resample_spacing = spacing * image.shape / new_shaperesize_factor = new_shape / image.shapeimage_new = scipy.ndimage.zoom(image, resize_factor, mode='nearest', order=order)return (image_new, resample_spacing)import pydicom
def get_CT_info(src_dir):Slices = []for file in os.listdir(src_dir):if file.endswith('.dcm'):slice = pydicom.read_file(src_dir + '/' + file)# print ("AAA:", Slices)Slices.append(slice)Slices.sort(key=lambda x: int(x.InstanceNumber)) # 层序列号return Slicesdef get_pixels_hu(Slices):images = np.stack([s.pixel_array for s in Slices])images_temp = imagesimages_temp = images_temp.astype("int32")print("Start Dicom pixel_array:", images_temp.dtype)for slice_number in range(len(Slices)):intercept = Slices[slice_number].RescaleInterceptslope = Slices[slice_number].RescaleSlopeimages_temp[slice_number] = slope * images_temp[slice_number] + interceptreturn images_tempif __name__ == '__main__':dcm_dir = r'./cao2-ming2-fang4-CT1872889-1/dcm'lstFilesDCM = os.listdir(dcm_dir)RefDs = pydicom.read_file(os.path.join(dcm_dir, lstFilesDCM[0])) # 读取第一张dicom图片# 第二步:得到dicom图片所组成3D图片的维度ConstPixelDims = (int(RefDs.Rows), int(RefDs.Columns), len(lstFilesDCM)) # ConstPixelDims是一个元组# 第三步:得到x方向和y方向的Spacing并得到z方向的层厚ConstPixelSpacing = (float(RefDs.PixelSpacing[0]), float(RefDs.PixelSpacing[1]), float(RefDs.SliceThickness))spacing = np.array(ConstPixelSpacing, dtype=float)[::-1]# 第四步:得到图像的原点Origin = RefDs.ImagePositionPatientprint(spacing, type(spacing))Slices_info = get_CT_info(dcm_dir) # 一个序列CT的所有slice—dcm信息img_org = get_pixels_hu(Slices_info) # # 一个序列的dcm转为ct hu值print(img_org.shape)# img_org, resampled_spacing = resample(img_org, spacing, order=3)binary_mask1, binary_mask2, has_lung = extract_lung(img_org, spacing)maskL = np.where(binary_mask1[:] == 1., 170, 0)maskR = np.where(binary_mask2[:] == 1., 255, 0)maskRL = maskL + maskRprint(binary_mask1.shape)print(binary_mask2.shape)print(has_lung)for i in range(maskRL.shape[0]):arr = maskRL[i, :, :] # 获得第i张的单一数组save_path =r'./mask'if not os.path.exists(save_path):os.makedirs(save_path)plt.imsave(os.path.join(save_path, "{}_mask.png".format(i)), arr, cmap='gray') # 定义命名规则,保存图片为彩色模式print('photo {} finished'.format(i))结果展示如下,代码可以看到:
- 左肺赋值170
- 右肺赋值255

ITK打开查看,如下所示:

四、肺实质缺失部分找补方法
从上面的不同方法对肺实质的分割结果来看,都会存在两个问题:
- 分的过于细致,导致存在边缘病灶的钙化区域,都当做了肺外组织,一起被切除掉。这样就导致,肺区不是一个完整的部分,这样对于后期的病灶检测,及其不利。
- 肺尖和肺底的肺区域,由于面积太少,导致无法分出来的情况。
能不能尽量给找补一些回来,尤其是对于结节病灶,找补一部分回来,就已经够了。相对于大病灶,这里暂时不做讨论。

这里借鉴:GitHub - uci-cbcl/NoduleNet: [MICCAI' 19] NoduleNet: Decoupled False Positive Reduction for Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Segmentation[MICCAI' 19] NoduleNet: Decoupled False Positive Reduction for Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Segmentation - GitHub - uci-cbcl/NoduleNet: [MICCAI' 19] NoduleNet: Decoupled False Positive Reduction for Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Segmentation![]() https://github.com/uci-cbcl/NoduleNet对结节数据部分的处理方法。从上面存在的两个问题,可以发现,一个是在CT的一个横截面上的问题,一个是在纵截面的问题。
https://github.com/uci-cbcl/NoduleNet对结节数据部分的处理方法。从上面存在的两个问题,可以发现,一个是在CT的一个横截面上的问题,一个是在纵截面的问题。
import syssys.path.append('./')
import numpy as np
import scipy.ndimage
from skimage import measure, morphology
import SimpleITK as sitk
from multiprocessing import Pool
import os
import nrrd
import cv2def load_itk_image(filename):"""Return img array and [z,y,x]-ordered origin and spacing"""itkimage = sitk.ReadImage(filename)numpyImage = sitk.GetArrayFromImage(itkimage)numpyOrigin = np.array(list(reversed(itkimage.GetOrigin())))numpySpacing = np.array(list(reversed(itkimage.GetSpacing())))return numpyImage, numpyOrigin, numpySpacingdef HU2uint8(image, HU_min=-1200.0, HU_max=600.0, HU_nan=-2000.0):"""Convert HU unit into uint8 values. First bound HU values by predfined minand max, and then normalizeimage: 3D numpy array of raw HU values from CT series in [z, y, x] order.HU_min: float, min HU value.HU_max: float, max HU value.HU_nan: float, value for nan in the raw CT image."""image_new = np.array(image)image_new[np.isnan(image_new)] = HU_nan# normalize to [0, 1]image_new = (image_new - HU_min) / (HU_max - HU_min)image_new = np.clip(image_new, 0, 1)image_new = (image_new * 255).astype('uint8')return image_newdef resample(image, spacing, new_spacing=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0], order=1):"""Resample image from the original spacing to new_spacing, e.g. 1x1x1image: 3D numpy array of raw HU values from CT series in [z, y, x] order.spacing: float * 3, raw CT spacing in [z, y, x] order.new_spacing: float * 3, new spacing used for resample, typically 1x1x1,which means standardizing the raw CT with different spacing all into1x1x1 mm.order: int, order for resample function scipy.ndimage.interpolation.zoomreturn: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image after,resampling. The actual resampling spacing is also returned."""# shape can only be int, so has to be rounded.new_shape = np.round(image.shape * spacing / new_spacing)# the actual spacing to resample.resample_spacing = spacing * image.shape / new_shaperesize_factor = new_shape / image.shapeimage_new = scipy.ndimage.zoom(image, resize_factor, mode='nearest', order=order)return (image_new, resample_spacing)def convex_hull_dilate(binary_mask, dilate_factor=1.5, iterations=10):"""Replace each slice with convex hull of it then dilate. Convex hulls usedonly if it does not increase area by dilate_factor. This applies mainly tothe inferior slices because inferior surface of lungs is concave.binary_mask: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only region of interest is True. One side of the lung in thisspecifical case.dilate_factor: float, factor of increased area after dilationiterations: int, number of iterations for dilationreturn: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only region of interest is True. Each binary mask is ROI of oneside of the lung."""binary_mask_dilated = np.array(binary_mask)for i in range(binary_mask.shape[0]):slice_binary = binary_mask[i] # one slice imgif np.sum(slice_binary) > 0:slice_convex = morphology.convex_hull_image(slice_binary) # 凸包处理#if np.sum(slice_convex) <= dilate_factor * np.sum(slice_binary):binary_mask_dilated[i] = slice_convexstruct = scipy.ndimage.generate_binary_structure(3, 1)binary_mask_dilated = scipy.ndimage.binary_dilation(binary_mask_dilated, structure=struct, iterations=iterations)return binary_mask_dilateddef apply_mask(image, binary_mask1, binary_mask2, pad_value=170,bone_thred=210, remove_bone=False):"""Apply the binary mask of each lung to the image. Regions out of interestare replaced with pad_value.image: 3D uint8 numpy array with the same shape of the image.binary_mask1: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only one side of lung is True.binary_mask2: 3D binary numpy array with the same shape of the image,that only the other side of lung is True.pad_value: int, uint8 value for padding image regions that is notinterested.bone_thred: int, uint8 threahold value for determine parts of image isbone.return: D uint8 numpy array with the same shape of the image afterapplying the lung mask."""binary_mask = binary_mask1 + binary_mask2binary_mask1_dilated = convex_hull_dilate(binary_mask1)binary_mask2_dilated = convex_hull_dilate(binary_mask2)binary_mask_dilated = binary_mask1_dilated + binary_mask2_dilatedbinary_mask_extra = binary_mask_dilated ^ binary_mask# replace image values outside binary_mask_dilated as pad valueimage_new = image * binary_mask_dilated + pad_value * (1 - binary_mask_dilated).astype('uint8')# set bones in extra mask to 170 (ie convert HU > 482 to HU 0;# water).if remove_bone:image_new[image_new * binary_mask_extra > bone_thred] = pad_valuereturn image_newimg_org, origin, spacing = load_itk_image(os.path.join(img_dir, '%s.mhd' % (pid))) # ct 图像
lung_mask, _, _ = load_itk_image(os.path.join(lung_mask_dir, '%s.mhd' % (pid))) # 肺区分割maskimg_org = HU2uint8(img_org)# 由于层厚比较厚,所以先resample,再进行后续的mask操作
print('Resampling origin image...')
img_org, resampled_spacing = resample(img_org, spacing, order=3) # resample img
print('Resampling lung mask...')
lung_mask, _ = resample(lung_mask, spacing, order=3) # resample img# 4-右肺 3-左肺 5-气管
binary_mask_r = lung_mask == 4
binary_mask_l = lung_mask == 3
binary_mask = binary_mask_r + binary_mask_limg_lungRL = apply_mask(img_org, binary_mask_r, binary_mask_l)关键1:凸包处理(二维)
凸包是指一个凸多边形,这个凸多边形将图片中所有的白色像素点都包含在内。
函数为:
skimage.morphology.convex_hull_image(image)输入为二值图像,输出一个逻辑二值图像。在凸包内的点为True, 否则为False。
经过这么一波操作,那些细微的在肺区边界的洞洞,就会被补上了,一个层面的问题就解决了。
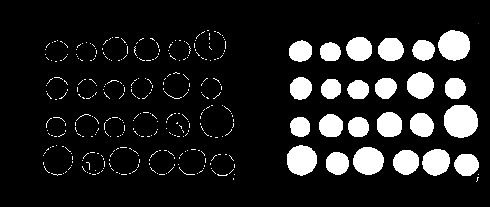
关键2:膨胀操作(三维)
原理:一般对二值图像进行操作。找到像素值为1的点,将它的邻近像素点都设置成这个值。 1值表示白,0值表示黑,因此膨胀操作可以扩大白色值范围,压缩黑色值范围。 一般用来扩充边缘或填充小的孔洞。
struct = scipy.ndimage.generate_binary_structure(3, 1)
binary_mask_dilated = scipy.ndimage.binary_dilation(binary_mask_dilated, structure=struct, iterations=iterations)这个函数是可以直接对三维数组进行操作的,也就可以利用存在肺区的图层,经过膨胀操作,添加到之前缺失的层。
但是,需要注意一点,就是对于层数较少的情况,会发生较大的改变。所以我再这里先对图像和肺区图进行resample到1mm的薄层,这里你也可以尝试修改算子和迭代次数进行尝试。
五、总结
本文是对前面对LIDC-IDRI数据集处理中,肺实质分割部分的一个补充。尽管在上面的数据集中,官方提供了肺实质已经分割好的mask,但是对于新收集的数据,肺实质的分割,还是需要我们自己处理。
本文提供的几种方法,基本上也是目前主流的方法,有比较复杂的,也有比较简单好理解的。但是,最终得到的效果好不好,还需要自己实践中选择。
上述的几种方法中,都大量的使用到了skimage这个python的第三方图像处理库,具体的思路和代码详解还需要慢慢补充。但是这这个补充章节里面,先给出一些关于skimage的学习资料,给需要补充的小伙伴一些帮助。
推荐skimage学习网站:Ⅵ 图像处理:使用scikit-image — Python基础与应用 文档
里面用到了很多关于skimage的形态学操作,相信在上面这个链接里面,你可以学习到很多。
这篇关于【3D 图像分割】基于 Pytorch 的 VNet 3D 图像分割8(CT肺实质分割)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









