本文主要是介绍什么是LMS算法(Least mean square),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
LMS算法可认为是机器学习里面最基本也比较有用的算法,神经网络中对参数的学习使用的就是LMS的思想,在通信信号处理领域LMS也非常常见,比如自适应滤波器。
其它就是利用梯度下降的算法来实现的,具体推导如下:
最后这条公式,就是LMS算法的实现基础,可以使用python代码实现如下:
import numpy as np
import random
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt# m是点的数量
def gradientDescent(x, y, theta, alpha, m, numIterations):#矩阵转置xTrans = x.transpose()cost = Nonefor i in range(0, numIterations):#点积hypothesis = np.dot(x, theta)#计算最小平方数loss = hypothesis - y cost = np.sum(loss ** 2) / (2 * m)#print("Iteration %d | Cost: %f" % (i, cost))# 计算梯度gradient = np.dot(xTrans, loss) / m# 更新值theta = theta - alpha * gradientprint("Iteration %d | Cost: %f" % (numIterations, cost)) return thetadef genData(numPoints, bias, variance):x = np.zeros(shape=(numPoints, 2))y = np.zeros(shape=numPoints)# 构造一条直线左右的点for i in range(0, numPoints):# 偏移x[i][0] = 1x[i][1] = i# 目标值y[i] = bias + i * variance + random.uniform(0, 1) * 15return x, ydef plotModel(x, y, w): plt.plot(x[:,1], y, "x") plt.plot(x[:,1], [i+j for i, j in x * w], "r-") plt.show()# 生成 100个点,截距为6, 斜率为0.8
x, y = genData(50, 6, 0.8)
#获取x矩阵的行列
m, n = np.shape(x)#迭代次数
numIterations = 100000#学习步伐
alpha = 0.00005#计算回归参数
theta = np.ones(n)
print(theta)
theta = gradientDescent(x, y, theta, alpha, m, numIterations)
print(theta)
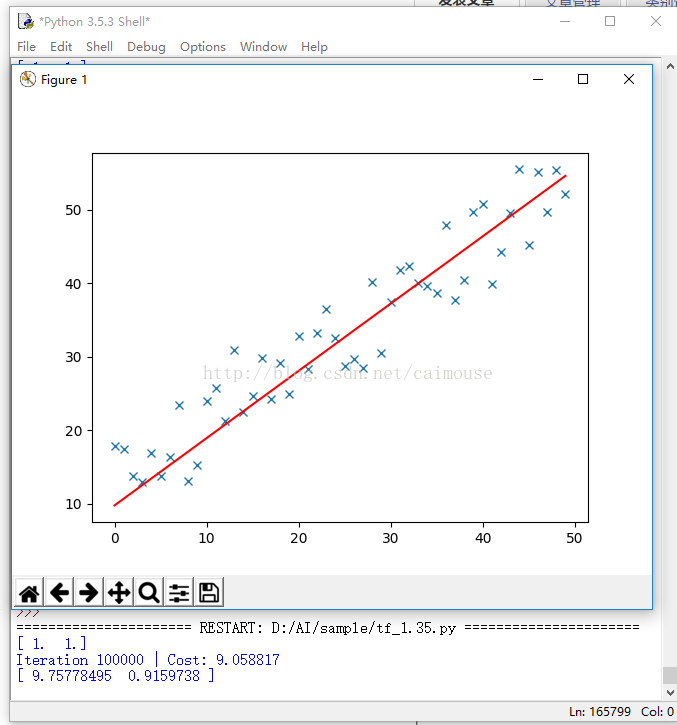
plotModel(x, y, theta)
输出结果如下:
从这个代码里,可以理解前面学习梯度的作用,以及梯度求解,就是最优化的方法。通过这个例子,也明白了什么叫做LMS算法,以及它的实现方法,同时也可以理解TensorFlow梯度优化器的原理,为什么需要不断对它进行迭代运行,以及更新梯度和应用梯度的过程。
1. C++标准模板库从入门到精通
http://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/3324
2.跟老菜鸟学C++
3. 跟老菜鸟学python
4. 在VC2015里学会使用tinyxml库
5. 在Windows下SVN的版本管理与实战
http://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/2579
这篇关于什么是LMS算法(Least mean square)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!