本文主要是介绍程序设计实习MOOC / 程序设计与算法(二)测验汇总(2022秋季)024-026,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目来源:openjudge
024:Gone Fishing
总时间限制: 2000ms 内存限制: 65536kB
描述
John is going on a fishing trip. He has h hours available (1 <= h <= 16), and there are n lakes in the area (2 <= n <= 25) all reachable along a single, one-way road. John starts at lake 1, but he can finish at any lake he wants. He can only travel from one lake to the next one, but he does not have to stop at any lake unless he wishes to. For each i = 1,…,n - 1, the number of 5-minute intervals it takes to travel from lake i to lake i + 1 is denoted ti (0 < ti <=192). For example, t3 = 4 means that it takes 20 minutes to travel from lake 3 to lake 4. To help plan his fishing trip, John has gathered some information about the lakes. For each lake i, the number of fish expected to be caught in the initial 5 minutes, denoted fi( fi >= 0 ), is known. Each 5 minutes of fishing decreases the number of fish expected to be caught in the next 5-minute interval by a constant rate of di (di >= 0). If the number of fish expected to be caught in an interval is less than or equal to di , there will be no more fish left in the lake in the next interval. To simplify the planning, John assumes that no one else will be fishing at the lakes to affect the number of fish he expects to catch.
Write a program to help John plan his fishing trip to maximize the number of fish expected to be caught. The number of minutes spent at each lake must be a multiple of 5.
输入
You will be given a number of cases in the input. Each case starts with a line containing n. This is followed by a line containing h. Next, there is a line of n integers specifying fi (1 <= i <=n), then a line of n integers di (1 <=i <=n), and finally, a line of n - 1 integers ti (1 <=i <=n - 1). Input is terminated by a case in which n = 0.
输出
For each test case, print the number of minutes spent at each lake, separated by commas, for the plan achieving the maximum number of fish expected to be caught (you should print the entire plan on one line even if it exceeds 80 characters). This is followed by a line containing the number of fish expected.
If multiple plans exist, choose the one that spends as long as possible at lake 1, even if no fish are expected to be caught in some intervals. If there is still a tie, choose the one that spends as long as possible at lake 2, and so on. Insert a blank line between cases.
样例输入
2
1
10 1
2 5
2
4
4
10 15 20 17
0 3 4 3
1 2 3
4
4
10 15 50 30
0 3 4 3
1 2 3
0
样例输出
45, 5
Number of fish expected: 31 240, 0, 0, 0
Number of fish expected: 480 115, 10, 50, 35
Number of fish expected: 724
来源
East Central North America 1999
一个参考解答
其中clear函数 来自清水汪汪
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>using namespace std;
// 此处Node 的j 可以删去
struct Node{int fs;int i,j;Node(int _fs, int _i, int _j):fs(_fs),i(_i),j(_j){};Node(){};bool operator<(const Node & node) const{if(fs<node.fs) return true;else if(fs>node.fs) return false;else{return i>node.i;}}
};void clear(priority_queue<Node>& q) {priority_queue<Node> empty;swap(empty, q);
}int main(){int n,h;cin >> n;int fi[30];int di[30];int ti[30];int fish[30][200];int st[30];int stp[30];int maxFish;int tmaxFish;priority_queue<Node> pq;while(n!=0){memset(fish,0,sizeof(fish));memset(st,0,sizeof(st));maxFish=-1;clear(pq);cin >> h;h = h*12;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {cin >> fi[i];fish[i][1]=fi[i];}for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) {int tp1,tp2=fi[i];cin >> tp1;di[i] = tp1;for(int j=1;tp2>0&&j<200;++j){fish[i][j] = tp2;tp2 -= tp1;}}for(int i=1;i<n;++i) cin >> ti[i];int tleft = h;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){if(tleft<=0) break;memset(stp,0,sizeof(stp));tmaxFish=0;clear(pq);for(int j=1;j<=i;++j){for(int k=1;k<=tleft;++k){pq.push(Node(fish[j][k],j,k));}}for(int j=0;j<tleft;++j){Node node=pq.top();//if(node.j>stp[node.i]) // stp[node.i] = node.j;stp[node.i]++;tmaxFish += node.fs;pq.pop();}if(tmaxFish>maxFish){maxFish=tmaxFish;for(int j=1;j<=n;++j) st[j]=stp[j];}tleft -= ti[i];}for(int i=1;i<n;++i) cout << st[i]*5 << ", ";cout << st[n]*5 << endl << "Number of fish expected: ";cout << maxFish << endl << endl;cin >> n;}return 0;
}
025:Radar Installation
总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB
描述
Assume the coasting is an infinite straight line. Land is in one side of coasting, sea in the other. Each small island is a point locating in the sea side. And any radar installation, locating on the coasting, can only cover d distance, so an island in the sea can be covered by a radius installation, if the distance between them is at most d.
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.
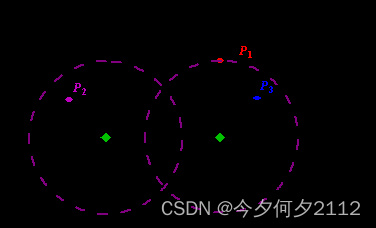
图片来自 这里
Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
输入
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of each case contains two integers n (1<=n<=1000) and d, where n is the number of islands in the sea and d is the distance of coverage of the radar installation. This is followed by n lines each containing two integers representing the coordinate of the position of each island. Then a blank line follows to separate the cases.
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
输出
For each test case output one line consisting of the test case number followed by the minimal number of radar installations needed. “-1” installation means no solution for that case.
样例输入
3 2
1 2
-3 1
2 11 2
0 20 0
样例输出
Case 1: 2
Case 2: 1
来源
Beijing 2002
一个参考解答
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>using namespace std;struct Node{double start, end;Node(double s, double e):start(s),end(e){}Node(){}bool operator<(const Node & n) const{return start>n.start;}
};void clear(priority_queue<Node> & q){priority_queue<Node> tq;swap(tq,q);
}int main(){int n,d,cnt;double x,y,dx,minx;priority_queue<Node> pq;cin >> n >> d;int casenum=1;bool cansolve=true;while(!(n==0 && d==0)){cansolve=(d>=0);for(int i=0;i<n;++i){cin >> x >> y;if(y>d) cansolve=false;else{dx = sqrt(d*d*1.0-y*y);pq.push(Node(x-dx,x+dx));}}if(!cansolve) cnt=-1;else {Node node = pq.top();cnt=1;minx=node.end;pq.pop();while(!pq.empty()){Node node = pq.top();if(node.start>minx){++cnt;minx=node.end;} else {minx = min(minx, node.end);}pq.pop();}}cout << "Case " << casenum++ << ": " << cnt << endl;clear(pq);cin >> n >> d;}return 0;
}
026:Tian Ji – The Horse Racing
总时间限制: 5000ms 内存限制: 65536kB
描述
Here is a famous story in Chinese history.
That was about 2300 years ago. General Tian Ji was a high official in the country Qi. He likes to play horse racing with the king and others.
Both of Tian and the king have three horses in different classes, namely, regular, plus, and super. The rule is to have three rounds in a match; each of the horses must be used in one round. The winner of a single round takes two hundred silver dollars from the loser.
Being the most powerful man in the country, the king has so nice horses that in each class his horse is better than Tian’s. As a result, each time the king takes six hundred silver dollars from Tian.
Tian Ji was not happy about that, until he met Sun Bin, one of the most famous generals in Chinese history. Using a little trick due to Sun, Tian Ji brought home two hundred silver dollars and such a grace in the next match.
It was a rather simple trick. Using his regular class horse race against the super class from the king, they will certainly lose that round. But then his plus beat the king’s regular, and his super beat the king’s plus. What a simple trick. And how do you think of Tian Ji, the high ranked official in China?
Were Tian Ji lives in nowadays, he will certainly laugh at himself. Even more, were he sitting in the ACM contest right now, he may discover that the horse racing problem can be simply viewed as finding the maximum matching in a bipartite graph. Draw Tian’s horses on one side, and the king’s horses on the other. Whenever one of Tian’s horses can beat one from the king, we draw an edge between them, meaning we wish to establish this pair. Then, the problem of winning as many rounds as possible is just to find the maximum matching in this graph. If there are ties, the problem becomes more complicated, he needs to assign weights 0, 1, or -1 to all the possible edges, and find a maximum weighted perfect matching…
However, the horse racing problem is a very special case of bipartite matching. The graph is decided by the speed of the horses – a vertex of higher speed always beat a vertex of lower speed. In this case, the weighted bipartite matching algorithm is a too advanced tool to deal with the problem.
In this problem, you are asked to write a program to solve this special case of matching problem.
输入
The input consists of up to 50 test cases. Each case starts with a positive integer n ( n<=1000) on the first line, which is the number of horses on each side. The next n integers on the second line are the speeds of Tian’s horses. Then the next n integers on the third line are the speeds of the king’s horses. The input ends with a line that has a single `0’ after the last test case.
输出
For each input case, output a line containing a single number, which is the maximum money Tian Ji will get, in silver dollars.
样例输入
3
92 83 71
95 87 74
2
20 20
20 20
2
20 19
22 18
0
样例输出
200
0
0
来源
Shanghai 2004
一个参考解答
参考改编自KonoSuba
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>using namespace std;const int maxn = 1010;int main(){int tian[maxn];int king[maxn];int n;cin >> n;while(n){for(int i=0;i<n;++i) cin >> tian[i];for(int i=0;i<n;++i) cin >> king[i];sort(tian,tian+n);sort(king,king+n);int tl=0,tr=n-1,kl=0,kr=n-1;int score=0;while(tl<=tr){if(tian[tl]>king[kl]){++score;++tl;++kl;} else if(tian[tl]<king[kl]){--score;++tl;--kr;} else if(tian[tr]<king[kr]){--score;++tl;--kr;} else if(tian[tr]>king[kr]){++score;--tr;--kr;} else {if(tian[tl]<king[kr]) --score;++tl;--kr;}/*if(tian[tr]>king[kr]){++score;--tr;--kr;} else if(tian[tr]<king[kr]){--score;++tl;--kr;} else if(tian[tl]<king[kl]){--score;++tl;--kr;} else if(tian[tl]>king[kl]){++score;++tl;++kl;} else {if(tian[tl]<king[kr]) --score;++tl;--kr;}*/}cout << 200*score << endl;cin >> n;}return 0;
}
这篇关于程序设计实习MOOC / 程序设计与算法(二)测验汇总(2022秋季)024-026的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









