本文主要是介绍matlab中stc,Scattered translates collocation matrix,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
stcol
Scattered translates collocation matrix
Syntax
colmat = stcol(centers,x,type)
colmat = stcol(...,'tr')
Description
colmat = stcol(centers,x,type) is the
matrix whose (i,j)th entry is
ψj(x(:,i)),i=1:size(x,2),j=1:n
with the bivariate functions ψj and the
number n depending on the centers and the
character vector type, as detailed in the description of
stmak.
centers and x must be matrices with the same
number of rows.
The default for type is the character vector
'tp', and for this default, n equals
size(centers,2), and the functions
ψj are given by
ψj(x)=ψ(x−centers(:,j)),j=1:n
with ψ the thin-plate spline basis function
ψ(x)=|x|2log|x|2
and with |x| denoting the Euclidean norm of the vector
x.
Note
See stmak for a description of
other possible values for type.
The matrix colmat is the coefficient matrix in the linear
system
∑jajψj(x(:,i))=yi,i=1:size(x,2)
that the coefficients aj of the function
f =
Σjajψj
must satisfy in order that f interpolate the value
yi at the site
x(:,i), all i.
colmat = stcol(...,'tr') returns the
transpose of the matrix returned by stcol(...).
Examples
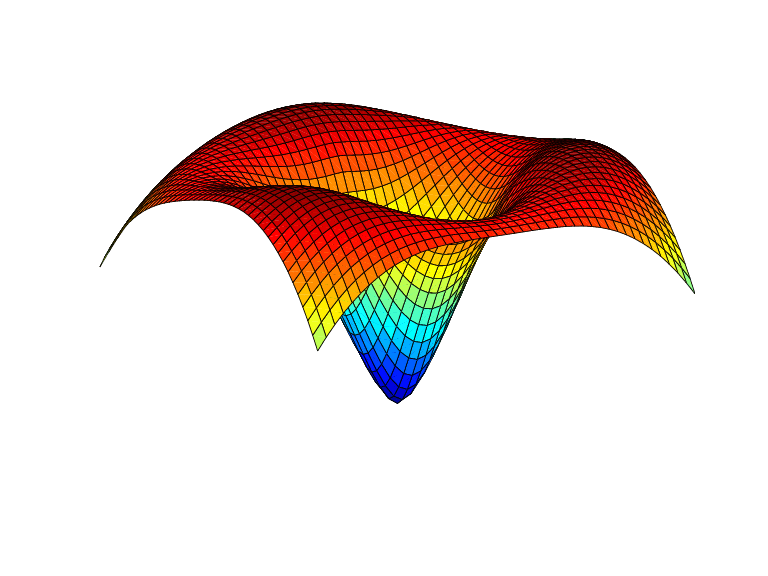
Example 1. The following evaluates and plots the
function
f(x)=ψ(x−c1)+ψ(x−c2)+ψ(x−c3)−3.5ψ(x)
on a regular mesh, with ψ the above thin-plate basis function,
and with c1,
c2,
c3 three points on the unit circle;
see the figure below.
a = [0,2/3*pi,4/3*pi]; centers = [cos(a), 0; sin(a), 0];
[xx,yy] = ndgrid(linspace(-2,2,45));
xy = [xx(:) yy(:)].';
coefs = [1 1 1 -3.5];
zz = reshape( coefs*stcol(centers,xy,'tr') , size(xx));
surf(xx,yy,zz), view([240,15]), axis off
Example 2. The following also evaluates, on the
same mesh, and plots the length of the gradient of the function in Example 1.
zz = reshape( sqrt(...
([coefs,0]*stcol(centers,xy,'tp10','tr')).^2 + ...
([coefs,0]*stcol(centers,xy,'tr','tp01')).^2),
size(xx));
figure, surf(xx,yy,zz), view([220,-15]), axis off
这篇关于matlab中stc,Scattered translates collocation matrix的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


![C# double[] 和Matlab数组MWArray[]转换](/front/images/it_default2.jpg)
![[论文笔记]LLM.int8(): 8-bit Matrix Multiplication for Transformers at Scale](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/172ed0ed26123345e1773ba0e0505cb3.png)


