本文主要是介绍吴恩达老师机器学习ex2.Logistic Regression,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
吴恩达 coursera 机器学习 第3周作业 编程作业2 Logistic Regression
Octave代码
sigmoid.m
function g = sigmoid(z)
%SIGMOID Compute sigmoid function
% g = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z.% You need to return the following variables correctly
g = zeros(size(z));% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix,
% vector or scalar).g = 1 ./ (1 + exp(z .* (-1)))% =============================================================endcostFunction.m
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y)
%COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression
% J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost
% w.r.t. to the parameters.% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta
%% matrix_X = [ones(m, 1) X]
for i = 1 : m;
h = sigmoid(X(i, :) * theta);
J = J + 1 / m * (-y(i, :) * log(h) - ((1 - y(i, :)) * log(1 - h)));
grad = grad + 1 / m * ((h - y(i, :)) * X(i, :)');
end;% =============================================================end
predict.m
function p = predict(theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic
%regression parameters theta
% p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a
% threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1)m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(m, 1);% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters.
% You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's
%p = round(sigmoid(X * theta));% =========================================================================end
ex2运行结果
Octave command prompt
octave:23> ex2...Cost at initial theta (zeros): 0.693147
Expected cost (approx): 0.693
Gradient at initial theta (zeros): -0.100000 -12.009217 -11.262842
Expected gradients (approx):-0.1000-12.0092-11.2628
g = 0.1869
g = 1.0477e-04...Cost at test theta: 0.218330
Expected cost (approx): 0.218
Gradient at test theta: 0.042903 2.566234 2.646797
Expected gradients (approx):0.0432.5662.647...Cost at theta found by fminunc: 0.203498
Expected cost (approx): 0.203
theta: -25.161272 0.206233 0.201470
Expected theta (approx):-25.1610.2060.201Program paused. Press enter to continue.g = 0.7763
For a student with scores 45 and 85, we predict an admission probability of 0.776289
Expected value: 0.775 +/- 0.002...Train Accuracy: 89.000000
Expected accuracy (approx): 89.0

costFunctionReg.m
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
%COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization
% J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in thetafor i = 1 : m;
h = sigmoid(X(i, :) * theta);
J = J + 1 / m * (-y(i, :) * log(h) - ((1 - y(i, :)) * log(1 - h))) ;
grad = grad + 1 / m * ((h - y(i, :)) * X(i, :)');
end;theta_2 = theta(2 : length(theta), 1);
J = J + lambda / (2 * m) * ones(1, length(theta) - 1) * (theta_2 .^ 2);grad_tmp = grad;
grad = grad + lambda / m * theta;
grad(1) = grad_tmp(1);% =============================================================end
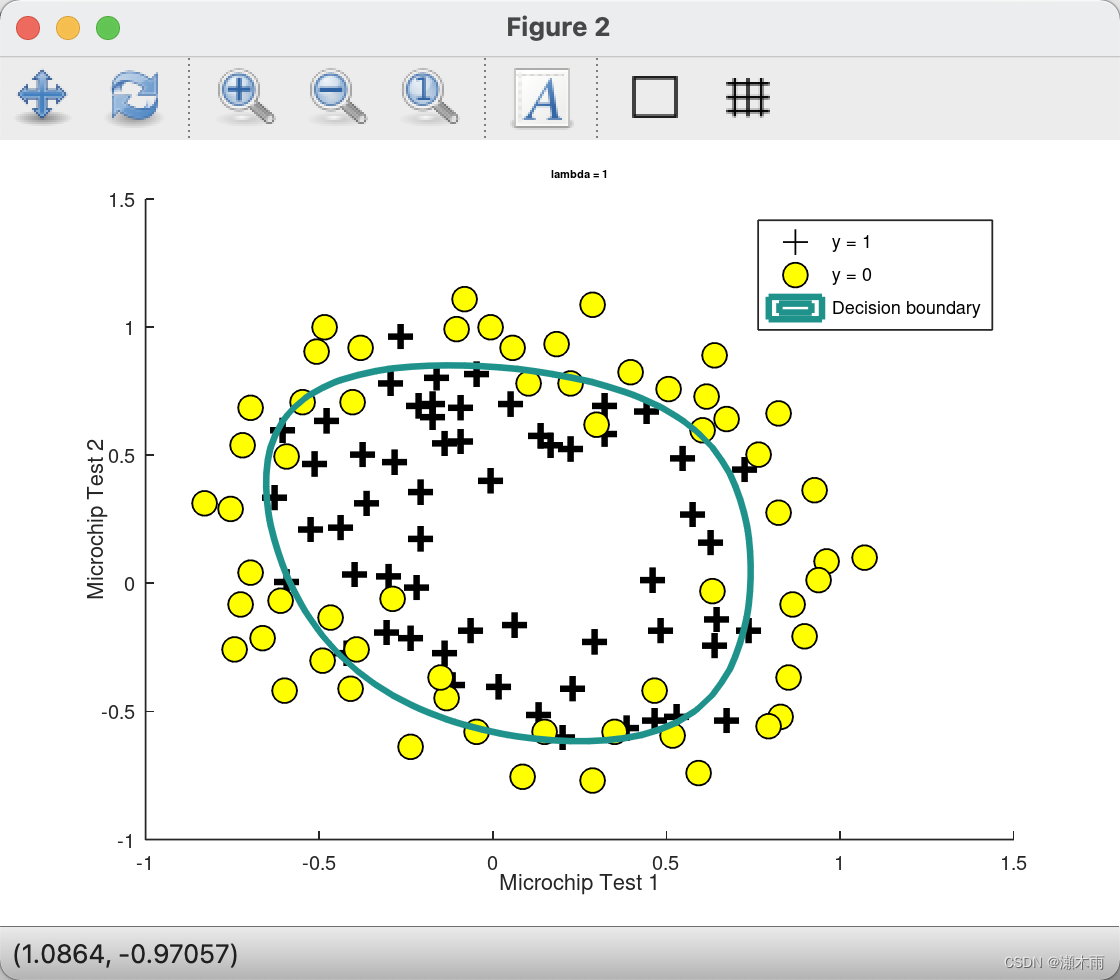
ex2_reg运行结果
Octave command prompt
octave:28> ex2_reg...g = 0.5000
Cost at initial theta (zeros): 0.693147
Expected cost (approx): 0.693
Gradient at initial theta (zeros) - first five values only:0.008475 0.018788 0.000078 0.050345 0.011501
Expected gradients (approx) - first five values only:0.00850.01880.00010.05030.0115...Cost at test theta (with lambda = 10): 3.164509
Expected cost (approx): 3.16
Gradient at test theta - first five values only:0.346045 0.161352 0.194796 0.226863 0.092186
Expected gradients (approx) - first five values only:0.34600.16140.19480.22690.0922...Train Accuracy: 83.050847
Expected accuracy (with lambda = 1): 83.1 (approx)
这篇关于吴恩达老师机器学习ex2.Logistic Regression的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!