本文主要是介绍HDU 3649 New Game,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
New Game
Yehr Game is a board game involving two players. It is played on a board with 40 squares arranged in an ten-by-four grid. At the beginning of the game each player controls four pieces: one acm, one bahamas, one cab and one daze. If one player has no pieces to move, he lost the game.
Setup:
Yehr Game is played on a rectangle board of ten rows and four columns. The pieces are divided, by convention, into red and black sets. The players are referred to as "Red" and "Black", and each begins the game with four pieces of the specified color. These consist of one acm, one bahamas, one cab and one daze.
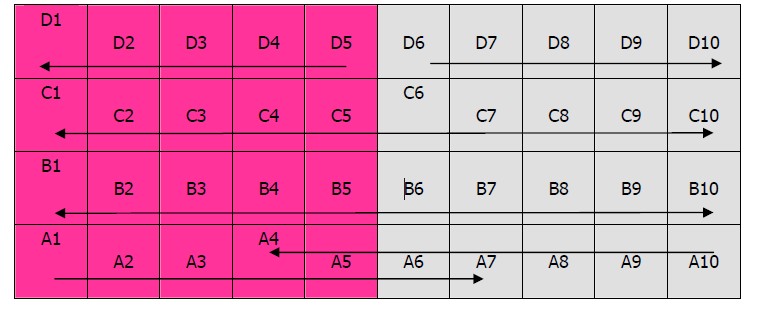
Movement:
First, they setup their pieces on the board.
(1) the piece red acm can be placed on A1~,A2,A3,A4,A5;the piece black acm A6~A10;
(2) the piece red bahamas can place on B1~B5; the piece black Bahamas B6~B10;
(3) the piece red cab can place on C1~C5; the piece black cab C6~C10;
(4) the piece red daze cab can place on D1~D5; the piece black daze D6~D10;
Second, they determine who moves first by dice. After the initial move, the players alternately move one piece at a time.
Each chess piece has its own style of moving.
(1) Acm can only move one direction: red from left to right; black from right to left. Acm can only move to the next square. If one player’s acm moves to a square with the opponent acm, he win the game.
(2) Bahamas and cab can move two direction: from left to right or from right to left. And they can move any number of squares but may not leap over other pieces.
(3) Daze can only move one direction: red from right to left; black from left to right.Daze can only move to the next square. In order to win the game, every clever player places the red daze on d5 and the black on d6.
Of Course, we assume that all players are clever.
Each test case contains three lines:
First line contains one integer number 0 or 1: 0 indicated red move first and 1 black first.
Second line contains four integer numbers r1, r2, r3, r4 indicating the four red pieces’ square. For example, r3=3 indicating the red cab on C3.
Third line contains four integer numbers k1, k2, k3, k4 indicating the four black pieces’ square. For example, k1=9 indicating the black acm on A9.
We assume that r4 is always 5, and K4 is 6.
0 4 5 5 5 7 6 6 6
Red
题目大意:
首先告诉你0或1,0表示红色先手,1表示黑色先手,接下来四个数字表示 红方 A,B,C,D四个子的位置,在接下来四个数字表示黑方 A,B,C,D四个子的位置。
游戏规则如下:
(1) the piece red acm can be placed on A1~,A2,A3,A4,A5;the piece black acm A6~A10;
(2) the piece red bahamas can place on B1~B5; the piece black Bahamas B6~B10;
(3) the piece red cab can place on C1~C5; the piece black cab C6~C10;
(4) the piece red daze cab can place on D1~D5; the piece black daze D6~D10;
解题思路:点击打开链接
SG函数
记a=k1-r1 b=k2-r2-1 c=k3-r3-1则
D:r4和k4不属于SG游戏,因为在D这个游戏里,两个玩家是互相独立的。所以r4和k4代表各自的机会,通俗的说就是我们玩魂斗罗时候的“命”
B,C:这两个游戏的SG函数都是b,c 即一个nim子游戏。
A:此游戏的SG函数值为a%2
证明D:当A,B,C游戏已经决定败局时,先手可以在D中进行一次操作(称“缓冲”),
即ABC的败局扭转给后手。显然后手也只能在D中操作挽回败局。故谁在D
中的缓冲区大谁就必胜。通俗的说就是局势以定的时候玩家拼命,谁命多,
谁就胜了。
证明A:当A中两个棋子重合时后手败(被吃子)a=0 sg(A)=0
否则,a的状态只能到达a-1所以sg(A)=a%2
证明B:显然b=0时必败,sg(B)=0。当然此时先手可以增加b的值来苟延残喘,但后
手下一步操作只要再把b减到0,一直下去,先手不能再增加时,还是败了。
然而b>0时的状态不好说,如果我们只考虑b只能减小,那不就成了nim子游
戏了吗。事实上b的增大操作我们称为无效操作,因为处于优势的玩家可以
不靠增加b来取状态,处于劣势的玩家即使增加了b,下一玩家再取回来就可
以了。所以B与NIM子游戏等价。
证明C:同B
解题代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;int red[10],black[10],first;int solve(){if(black[1]-red[1]==1) return first;if(red[4]-1>10-black[4]) return 0;if(red[4]-1<10-black[4]) return 1;int sg=0;sg^=(black[2]-red[2]-1);sg^=(black[3]-red[3]-1);sg^=(black[1]-red[1])%2;if(sg) return first;else return first^1;
}int main(){while(scanf("%d",&first)!=EOF){for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) scanf("%d",&red[i]);for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) scanf("%d",&black[i]);if ( !solve() ) printf("Red\n");else printf("Black\n");}return 0;
}
这篇关于HDU 3649 New Game的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




