本文主要是介绍Curiously recurring template pattern ( 奇怪的重复模板模式,CRTP),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
CRTP是 C++中的一种技术,其中Derived类从类模板Base派生。关键是Base有一个Derived作为模板参数。
template<class T>
class Base{
...
};class Derived : public Base<Derived>{
...
};
CRTP是仅在需要时才实例化类模板的方法,使用静态多态方式。
静态多态与动态多态非常相似。但是与使用虚拟方法的动态多态性相反,方法调用的调度将在编译时进行。
// crtp.cpp#include <iostream>template <typename Derived>
struct Base{// void interface(){ implementation(); }// virtual void implementation(){}void interface(){static_cast<Derived*>(this)->implementation();}void implementation(){std::cout << "Implementation Base" << std::endl;}};struct Derived1: Base<Derived1>{void implementation(){std::cout << "Implementation Derived1" << std::endl;}
};struct Derived2: Base<Derived2>{void implementation(){std::cout << "Implementation Derived2" << std::endl;}
};struct Derived3: Base<Derived3>{};template <typename T>
void execute(T& base){base.interface();
}int main(){std::cout << std::endl;Derived1 d1;execute(d1);Derived2 d2;execute(d2);Derived3 d3;execute(d3);std::cout << std::endl;}
我在函数模板中使用execute(第34-37行)静态多态性。我在每个参数基础上调用方法base.interface。
第10-12行中的方法Base :: interface是CRTP习惯用法的关键点。这些方法分派给派生类的实现:static_cast <Derived *>(this)-> implementation()。这是可能的,因为该方法将在调用时实例化。
此时,派生类Derived1,Derived2和Derived3已完全定义。因此,方法Base::interface可以使用其派生类的详细信息。特别有趣的是Base :: implementation方法(第14-16行)。该方法充当Derived3类的静态多态性的默认实现(第32行)。
该技术实现了与virtual function的使用相似的效果。如果基类成员函数对所有成员函数调用均使用CRTP,则将在编译时选择派生类中的重写函数。这有效地在编译时模拟了虚拟函数调用系统,而没有大小或函数调用开销(VTBL结构和方法查找,多继承VTBL机制)的开销,但缺点是无法在运行时做出选择。
因此有些人将CRTP的这种特殊用法称为“模拟动态绑定”。 Windows ATL和WTL库中广泛使用此模式。
Mixins with CRTP
Mixins是在类中设计以混合新代码的流行概念。因此,它是Python中通过使用多个继承来更改类的行为的常用技术。与C ++相反,在Python中,在类层次结构中具有一个方法的多个定义是合法的。 Python仅使用方法解析顺序( Method Resolution Order,即MRO)中首先使用的方法。
您可以使用CRTP在C ++中实现mixin。一个著名的例子是类std :: enable_shared_from_this。通过使用此类,您可以创建向自己返回std :: shared_ptr的对象。
您可以从std :: enable_shared_from_this派生您的公共类MySharedClass。现在,您的类MySharedClass具有shared_from_this方法,用于为其对象创建std :: shared_ptr。
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>class ShareMe : public std::enable_shared_from_this<ShareMe> {
public:std::shared_ptr<ShareMe> getShared() {return shared_from_this();}
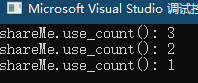
};int main() {std::shared_ptr<ShareMe> shareMe(new ShareMe);std::shared_ptr<ShareMe> shareMe1 = shareMe->getShared();//std :: shared_ptr <T> :: use_count返回不同shared_ptr实例的数量{auto shareMe2(shareMe1);std::cout << "shareMe.use_count(): " << shareMe.use_count() << std::endl; }std::cout << "shareMe.use_count(): " << shareMe.use_count() << std::endl;//当智能指针中有值的时候,调用reset()会使引用计数减1.shareMe1.reset();std::cout << "shareMe.use_count(): " << shareMe.use_count() << std::endl;return 0;
}
智能指针shareMe(第12行)并复制shareMe1(第13行)和shareMe2(第17行)引用相同的资源,并递增和递减引用计数器。
mixin的另一个典型用例是您要扩展的类,其类具有其实例支持相等性和不平等性比较的功能。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>template<class Derived>
class Equality
{};class Apple :public Equality<Apple> {
public:Apple(int s) : size{ s } {};int size;
};class Man :public Equality<Man> {
public:Man(std::string n) : name{ n } {}std::string name;
};template <class Derived>
bool operator == ( Equality<Derived> const & op1 , Equality<Derived> const & op2 )
{Derived const& d1 = static_cast<Derived const&>(op1);Derived const& d2 = static_cast<Derived const&>(op2);return !(d1 < d2) && !(d2 < d1);
}template <class Derived>
bool operator != ( Equality<Derived> const & op1 , Equality<Derived> const & op2 )
{Derived const& d1 = static_cast<Derived const&>(op1);Derived const& d2 = static_cast<Derived const&>(op2);return !(op1 == op2);
}bool operator < (Apple const& a1, Apple const& a2)
{return a1.size < a2.size;
}bool operator < (Man const& m1, Man const& m2)
{return m1.name < m2.name;
}int main()
{std::cout << std::boolalpha ;Apple apple1{ 5 };Apple apple2{ 10 };std::cout << "apple1 == apple2: " << (apple1 == apple2) << std::endl;Man man1{ "grimm" };Man man2{ "jaud" };std::cout << "man1 != man2: " << (man1 != man2) << std::endl;return 0;
}
参考文章:
- https://www.modernescpp.com/index.php/specialities-of-std-shared-ptr
- https://www.modernescpp.com/index.php/c-is-still-lazy
这篇关于Curiously recurring template pattern ( 奇怪的重复模板模式,CRTP)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





