本文主要是介绍自然语言处理hanlp------9基于双数组字典树的AC自动机,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、原理
- 二、实现
- 测试
- 总结
前言
双数组字典树能在O( l l l)的时间内高速完成单串匹配,并且消耗的内存可控,软肋在于多模式匹配。如果要匹配多个模式串,必须先前缀查询,然后频繁截取文本的后缀才行。但是上一节测评的AC多模式匹配又还不如双数组字典树快,所以,本节就采用二者结合。称为AhoCorasickDoubleArrayTire(简称ACDAT)
一、原理
ACDAT的基本原理:
替换AC自动机的goto表
也可以看作为一棵双数组字典树的每个状态附上额外的信息,AC自动机的goto表就是字典树,只不过AC自动机多了fail表和output表。那么ACDAT的构建原理就是为每个状态构建output和fail表
具体三步如下:
- 构建一棵普通的字典树,让终止节点记住对应模式串的字典序。
- 构建双数组字典树,在将每个状态映射到双数组时,让它记住自己在双数组中的下标。
- 构建AC自动机,此时fail表中存储的就是状态的下标。
二、实现
代码可以说是贼多了,建议还是下载后阅读吧,我这里实在是难以展示
在晗佬的代码中:com\hankcs\hanlp\collection\AhoCorasick\AhoCorasickDoubleArrayTrie.java
我仅放出核心代码块吧
private class Builder{/*** 根节点,仅仅用于构建过程*/private State rootState = new State();/*** 是否占用,仅仅用于构建*/private boolean used[];/*** 已分配在内存中的大小*/private int allocSize;/*** 一个控制增长速度的变量*/private int progress;/*** 下一个插入的位置将从此开始搜索*/private int nextCheckPos;/*** 键值对的大小*/private int keySize;/*** 由一个排序好的map创建*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void build(TreeMap<String, V> map){// 把值保存下来v = (V[]) map.values().toArray();l = new int[v.length];Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();// 构建二分trie树addAllKeyword(keySet);// 在二分trie树的基础上构建双数组trie树buildDoubleArrayTrie(keySet);used = null;// 构建failure表并且合并output表constructFailureStates();rootState = null;loseWeight();}/*** 添加一个键** @param keyword 键* @param index 值的下标*/private void addKeyword(String keyword, int index){State currentState = this.rootState;for (Character character : keyword.toCharArray()){currentState = currentState.addState(character);}currentState.addEmit(index);l[index] = keyword.length();}/*** 一系列键** @param keywordSet*/private void addAllKeyword(Collection<String> keywordSet){int i = 0;for (String keyword : keywordSet){addKeyword(keyword, i++);}}/*** 建立failure表*/private void constructFailureStates(){fail = new int[size + 1];fail[1] = base[0];output = new int[size + 1][];Queue<State> queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<State>();// 第一步,将深度为1的节点的failure设为根节点for (State depthOneState : this.rootState.getStates()){depthOneState.setFailure(this.rootState, fail);queue.add(depthOneState);constructOutput(depthOneState);}// 第二步,为深度 > 1 的节点建立failure表,这是一个bfswhile (!queue.isEmpty()){State currentState = queue.remove();for (Character transition : currentState.getTransitions()){State targetState = currentState.nextState(transition);queue.add(targetState);State traceFailureState = currentState.failure();while (traceFailureState.nextState(transition) == null){traceFailureState = traceFailureState.failure();}State newFailureState = traceFailureState.nextState(transition);targetState.setFailure(newFailureState, fail);targetState.addEmit(newFailureState.emit());constructOutput(targetState);}}}/*** 建立output表*/private void constructOutput(State targetState){Collection<Integer> emit = targetState.emit();if (emit == null || emit.size() == 0) return;int output[] = new int[emit.size()];Iterator<Integer> it = emit.iterator();for (int i = 0; i < output.length; ++i){output[i] = it.next();}AhoCorasickDoubleArrayTrie.this.output[targetState.getIndex()] = output;}private void buildDoubleArrayTrie(Set<String> keySet){progress = 0;keySize = keySet.size();resize(65536 * 32); // 32个双字节base[0] = 1;nextCheckPos = 0;State root_node = this.rootState;List<Map.Entry<Integer, State>> siblings = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<Integer, State>>(root_node.getSuccess().entrySet().size());fetch(root_node, siblings);insert(siblings);}/*** 拓展数组** @param newSize* @return*/private int resize(int newSize){int[] base2 = new int[newSize];int[] check2 = new int[newSize];boolean used2[] = new boolean[newSize];if (allocSize > 0){System.arraycopy(base, 0, base2, 0, allocSize);System.arraycopy(check, 0, check2, 0, allocSize);System.arraycopy(used, 0, used2, 0, allocSize);}base = base2;check = check2;used = used2;return allocSize = newSize;}/*** 插入节点** @param siblings 等待插入的兄弟节点* @return 插入位置*/private int insert(List<Map.Entry<Integer, State>> siblings){int begin = 0;int pos = Math.max(siblings.get(0).getKey() + 1, nextCheckPos) - 1;int nonzero_num = 0;int first = 0;if (allocSize <= pos)resize(pos + 1);outer:// 此循环体的目标是找出满足base[begin + a1...an] == 0的n个空闲空间,a1...an是siblings中的n个节点while (true){pos++;if (allocSize <= pos)resize(pos + 1);if (check[pos] != 0){nonzero_num++;continue;}else if (first == 0){nextCheckPos = pos;first = 1;}begin = pos - siblings.get(0).getKey(); // 当前位置离第一个兄弟节点的距离if (allocSize <= (begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).getKey())){// progress can be zero // 防止progress产生除零错误double l = (1.05 > 1.0 * keySize / (progress + 1)) ? 1.05 : 1.0 * keySize / (progress + 1);resize((int) (allocSize * l));}if (used[begin])continue;for (int i = 1; i < siblings.size(); i++)if (check[begin + siblings.get(i).getKey()] != 0)continue outer;break;}// -- Simple heuristics --// if the percentage of non-empty contents in check between the// index// 'next_check_pos' and 'check' is greater than some constant value// (e.g. 0.9),// new 'next_check_pos' index is written by 'check'.if (1.0 * nonzero_num / (pos - nextCheckPos + 1) >= 0.95)nextCheckPos = pos; // 从位置 next_check_pos 开始到 pos 间,如果已占用的空间在95%以上,下次插入节点时,直接从 pos 位置处开始查找used[begin] = true;size = (size > begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).getKey() + 1) ? size : begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).getKey() + 1;for (Map.Entry<Integer, State> sibling : siblings){check[begin + sibling.getKey()] = begin;}for (Map.Entry<Integer, State> sibling : siblings){List<Map.Entry<Integer, State>> new_siblings = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<Integer, State>>(sibling.getValue().getSuccess().entrySet().size() + 1);if (fetch(sibling.getValue(), new_siblings) == 0) // 一个词的终止且不为其他词的前缀,其实就是叶子节点{base[begin + sibling.getKey()] = (-sibling.getValue().getLargestValueId() - 1);progress++;}else{int h = insert(new_siblings); // dfsbase[begin + sibling.getKey()] = h;}sibling.getValue().setIndex(begin + sibling.getKey());}return begin;}/*** 释放空闲的内存*/private void loseWeight(){int nbase[] = new int[size + 65535];System.arraycopy(base, 0, nbase, 0, size);base = nbase;int ncheck[] = new int[size + 65535];System.arraycopy(check, 0, ncheck, 0, size);check = ncheck;}}
代码冗多,我个人理解来说,我们只要过一遍代码,理解思路是什么即可,毕竟我们之后去使用这些,仅仅需要会用即可。
测试
展示晗佬的全切分速度对比图:
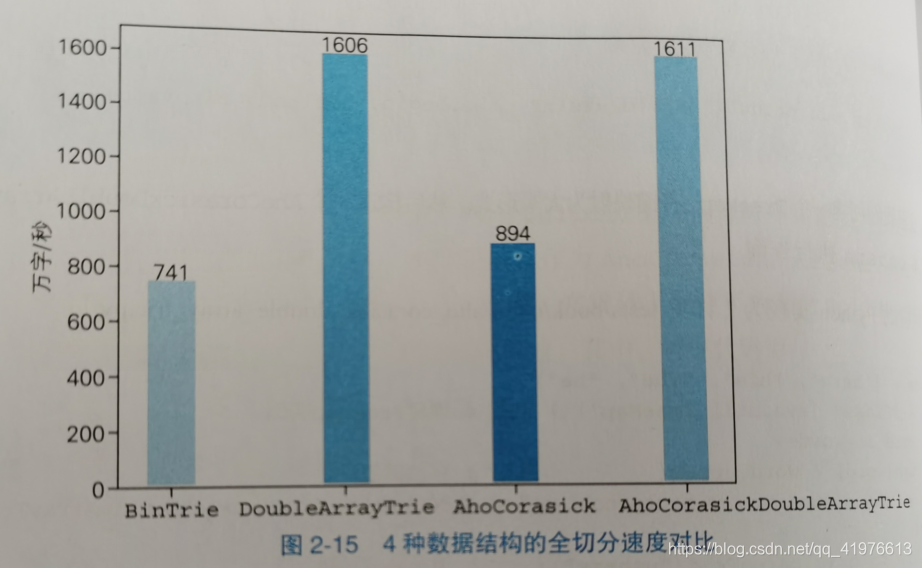
结果与双数组字典树不相上下。主要原因是汉语中的词汇都不长,有的其至是单字词汇,这使得前缀树的优势占了较大比重,AC自动机的fail机制没有了用武之地,其次要原因是全切分需要将结果添加到链表,也会占用时间。
下面增加词汇的长度来观察词汇长度对匹配速度的影响
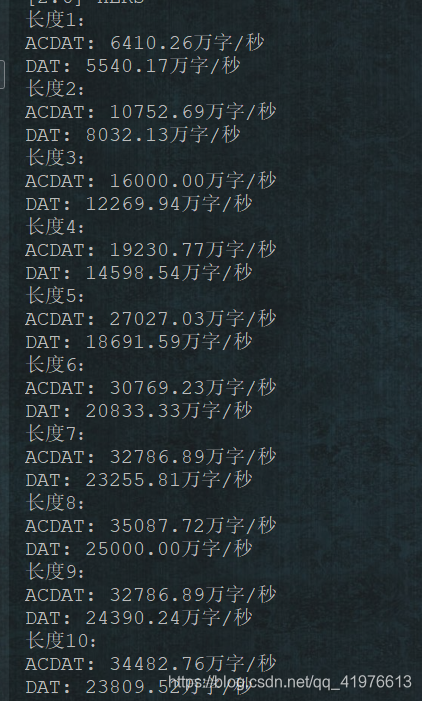
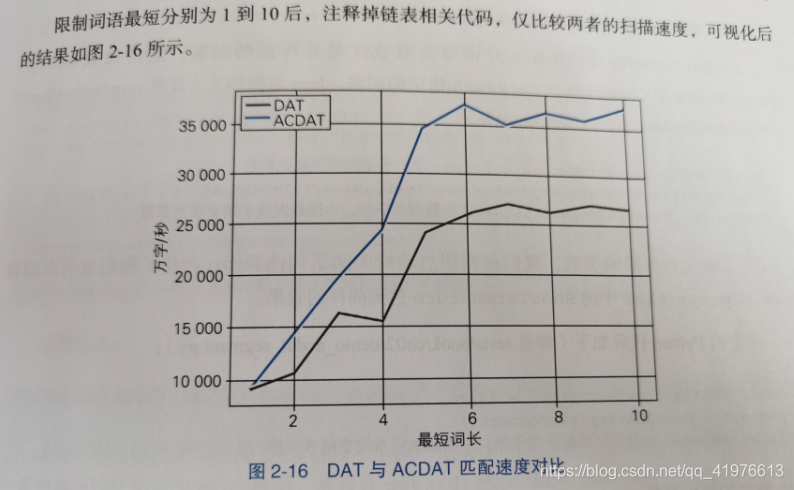
可见,随着模式串长度的增加,ACDAT的优势渐渐体现了出来。总之,当含有短模式串时,优先用DAT,否则优先用ACDAT。
总结
本节重在对晗佬代码和思路的多读多看。读者可以下载源码自行深度理解一下,找不到资源的加群呀。
此外:本人创建了QQ交流群,希望大家来交流学习(新群人少,不是假群o(╥﹏╥)o…)

这篇关于自然语言处理hanlp------9基于双数组字典树的AC自动机的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



