本文主要是介绍深度学习基础知识 nn.Sequential | nn.ModuleList | nn.ModuleDict,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
深度学习基础知识 nn.Sequential | nn.ModuleList | nn.ModuleDict
- 1、nn.Sequential 、 nn.ModuleList 、 nn.ModuleDict 类都继承自 Module 类。
- 2、nn.Sequential、nn.ModuleList 和 nn.ModuleDict语法
- 3、Sequential 、ModuleDict、 ModuleList 的区别
- 4、ModuleDict、 ModuleList 的区别
- 5、nn.ModuleList 、 nn.ModuleDict 与 Python list、Dict 的区别
1、nn.Sequential 、 nn.ModuleList 、 nn.ModuleDict 类都继承自 Module 类。
2、nn.Sequential、nn.ModuleList 和 nn.ModuleDict语法
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.ReLU()) →→只需要将定义的层按照顺序写入括号内就可以了
net = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(32, 6)4, nn.ReLU()]) →→在定义式需要加上中括号[],将定义的层写入到中括号内
net = nn.ModuleDict({‘linear’: nn.Linear(32, 64), ‘act’: nn.ReLU()}) →→需要大括号,将定义的层以键值对的形式写入
代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nnnet1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.ReLU())
net2 = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.ReLU()])
net3 = nn.ModuleDict({'linear': nn.Linear(32, 64), 'act': nn.ReLU()})print(net1)
print(net2)
print(net3)
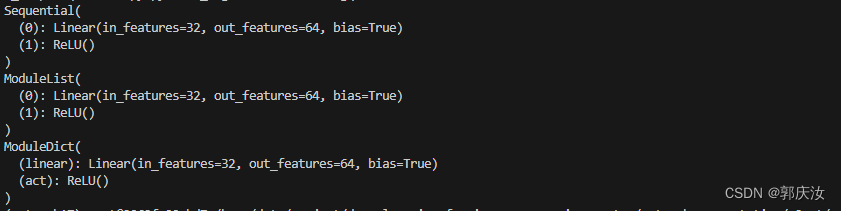
3、Sequential 、ModuleDict、 ModuleList 的区别
1、 ModuleList 仅仅是一个储存各种模块的列表,这些模块之间没有联系也没有顺序(所以不用保证相邻层的输入输出维度匹配),而且没有实现 forward 功能需要自己实现
2、和 ModuleList 一样, ModuleDict 实例仅仅是存放了一些模块的字典,并没有定义 forward 函数需要自己定义
3、而 Sequential 内的模块需要按照顺序排列,要保证相邻层的输入输出大小相匹配,内部 forward 功能已经实现,所以,直接如下写模型,是可以直接调用的,不再需要写forward,sequential 内部已经有 forward
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nnnet1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.ReLU())
net2 = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.ReLU()])
net3 = nn.ModuleDict({'linear': nn.Linear(32, 64), 'act': nn.ReLU()})x = torch.randn(8, 3, 32)
print(net1(x).shape) # 输出内容: torch.Size([8, 3, 64])
# print(net2(x).shape) # 会报错,提示缺少forward
# print(net3(x).shape) # 会报错,提示缺少forward为 nn.ModuleList 写 forward 函数
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nnclass My_Model(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(My_Model, self).__init__()self.layers = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(32, 64),nn.ReLU()])def forward(self, x):for layer in self.layers:x = layer(x)return xnet = My_Model()x = torch.randn(8, 3, 32)
out = net(x)
print(out.shape)
输出结果:

为 nn.ModuleDict 写 forward 函数
import torch
import torch.nn as nnclass My_Model(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(My_Model, self).__init__()self.layers = nn.ModuleDict({'linear': nn.Linear(32, 64), 'act': nn.ReLU()})def forward(self, x):for layer in self.layers.values():x = layer(x)return xnet = My_Model()
x = torch.randn(8, 3, 32)
out = net(x)
print(out.shape)
将 nn.ModuleList 转换成 nn.Sequential
import torch
import torch.nn as nnmodule_list = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.ReLU()])
net = nn.Sequential(*module_list)
x = torch.randn(8, 3, 32)
print(net(x).shape)
输出如下:

将 nn.ModuleDict 转换成 nn.Sequential
import torch
import torch.nn as nnmodule_dict = nn.ModuleDict({'linear': nn.Linear(32, 64), 'act': nn.ReLU()})
net = nn.Sequential(*module_dict.values())
x = torch.randn(8, 3, 32)
print(net(x).shape)
输出如下:

4、ModuleDict、 ModuleList 的区别
1、ModuleDict 可以给每个层定义名字,ModuleList 不会
2、ModuleList 可以通过索引读取,并且使用 append 添加元素
import torch.nn as nnnet = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.ReLU()])
net.append(nn.Linear(64, 10))
print(net)
3、ModuleDict 可以通过 key 读取,并且可以像 字典一样添加元素
import torch.nn as nnnet = nn.ModuleDict({'linear1': nn.Linear(32, 64), 'act': nn.ReLU()})
net['linear2'] = nn.Linear(64, 128)
print(net)
5、nn.ModuleList 、 nn.ModuleDict 与 Python list、Dict 的区别
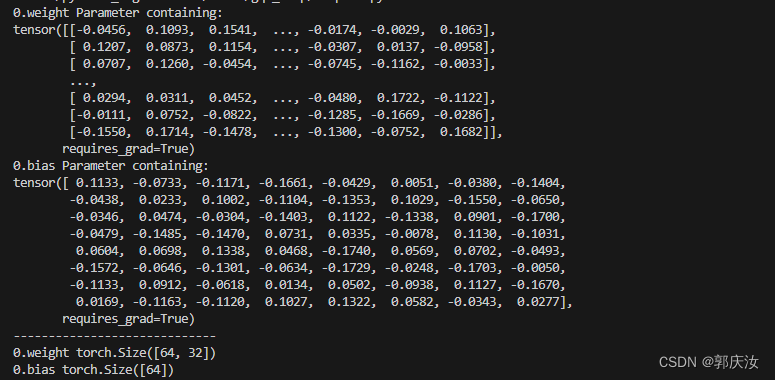
import torch.nn as nnnet = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(32, 64), nn.ReLU()])for name, param in net.named_parameters():print(name, param)print("-----------------------------")
for name, param in net.named_parameters():print(name, param.size())
显示结果如下:
import torch.nn as nnnet = nn.ModuleDict({'linear': nn.Linear(32, 64), 'act': nn.ReLU()})for name, param in net.named_parameters():print(name, param.size())
print("--------------------------")for name, param in net.named_parameters():print(name, param.size())显示结果:

这篇关于深度学习基础知识 nn.Sequential | nn.ModuleList | nn.ModuleDict的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



