本文主要是介绍压缩感知重构算法之子空间追踪(SP),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目:压缩感知重构算法之子空间追踪(SP)
转载自彬彬有礼的专栏
如果掌握了压缩采样匹配追踪(CoSaMP)后,再去学习子空间追踪(Subspace Pursuit)是一件非常简单的事情,因为它们几乎是完全一样的。
SP的提出时间比CoSaMP提出时间略晚,首个论文版本是参考文献[1],后来更新了两次,最后在IEEE Transactions on Information Theory发表[2]。从算法角度来讲,SP与CoSaMP差别非常小,这一点作者也意识到了,在文献[1]首页的左下角就有注释:

在文献[2]第2页提到了SP与CoSaMP的具体不同:

从上面可以知道,SP与CoSaMP主要区别在于“Ineach iteration, in the SP algorithm, only K new candidates are added, while theCoSAMP algorithm adds 2K vectors.”,即SP每次选择K个原子,而CoSaMP则选择2K个原子;这样带来的好处是“This makes the SP algorithm computationally moreefficient,”。
以下是文献[2]中的给出的SP算法流程:
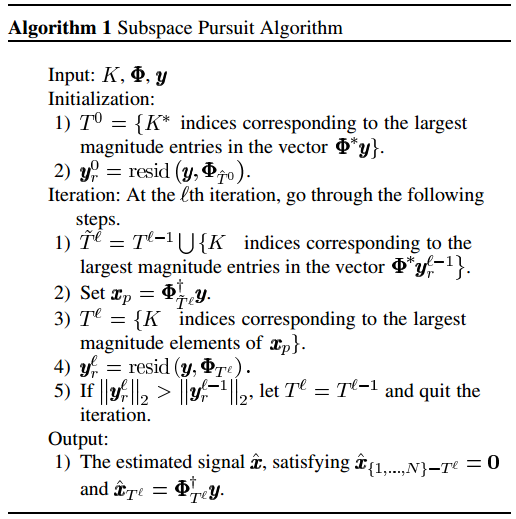
这个算法流程的初始化(Initialization)其实就是类似于CoSaMP的第1次迭代,注意第(1)步中选择了K个原子:“K indices corresponding to the largest magnitude entries”,在CoSaMP里这里要选择2K个最大的原子,后面的其它流程都一样。这里第(5)步增加了一个停止迭代的条件:当残差经过迭代后却变大了的时候就停止迭代。
不只是SP作者认识到了自己的算法与CoSaMP的高度相似性,CoSaMP的作者也同样关注到了SP算法,在文献[3]中就提到:

文献[3]是CoSaMP原始提出文献的第2个版本,文献[3]的早期版本[4]是没有提及SP算法的。
鉴于SP与CoSaMP如此相似,这里不就再单独给出SP的步骤了,参考《压缩感知重构算法之压缩采样匹配追踪(CoSaMP)》,只需将第(2)步中的2K改为K即可。
引用文献[5]的3.5节中的几句话:“贪婪类算法虽然复杂度低运行速度快,但其重构精度却不如BP类算法,为了寻求复杂度和精度更好地折中,SP算法应运而生”,“SP算法与CoSaMP算法一样其基本思想也是借用回溯的思想,在每步迭代过程中重新估计所有候选者的可信赖性”,“SP算法与CoSaMP算法有着类似的性质与优缺点”。
子空间追踪代码可实现如下(CS_SP.m),通过对比可以知道该程序与CoSaMP的代码基本完全一致。本代码未考虑文献[2]中的给出的SP算法流程的第(5)步。代码可参见参考文献[6]中的Demo_CS_SP.m。- function [ theta ] = CS_SP( y,A,K )
- %CS_SP Summary of this function goes here
- %Version: 1.0 written by jbb0523 @2015-05-01
- % Detailed explanation goes here
- % y = Phi * x
- % x = Psi * theta
- % y = Phi*Psi * theta
- % 令 A = Phi*Psi, 则y=A*theta
- % K is the sparsity level
- % 现在已知y和A,求theta
- % Reference:Dai W,Milenkovic O.Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing
- % signal reconstruction[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,
- % 2009,55(5):2230-2249.
- [y_rows,y_columns] = size(y);
- if y_rows<y_columns
- y = y';%y should be a column vector
- end
- [M,N] = size(A);%传感矩阵A为M*N矩阵
- theta = zeros(N,1);%用来存储恢复的theta(列向量)
- Pos_theta = [];%用来迭代过程中存储A被选择的列序号
- r_n = y;%初始化残差(residual)为y
- for kk=1:K%最多迭代K次
- %(1) Identification
- product = A'*r_n;%传感矩阵A各列与残差的内积
- [val,pos]=sort(abs(product),'descend');
- Js = pos(1:K);%选出内积值最大的K列
- %(2) Support Merger
- Is = union(Pos_theta,Js);%Pos_theta与Js并集
- %(3) Estimation
- %At的行数要大于列数,此为最小二乘的基础(列线性无关)
- if length(Is)<=M
- At = A(:,Is);%将A的这几列组成矩阵At
- else%At的列数大于行数,列必为线性相关的,At'*At将不可逆
- break;%跳出for循环
- end
- %y=At*theta,以下求theta的最小二乘解(Least Square)
- theta_ls = (At'*At)^(-1)*At'*y;%最小二乘解
- %(4) Pruning
- [val,pos]=sort(abs(theta_ls),'descend');
- %(5) Sample Update
- Pos_theta = Is(pos(1:K));
- theta_ls = theta_ls(pos(1:K));
- %At(:,pos(1:K))*theta_ls是y在At(:,pos(1:K))列空间上的正交投影
- r_n = y - At(:,pos(1:K))*theta_ls;%更新残差
- if norm(r_n)<1e-6%Repeat the steps until r=0
- break;%跳出for循环
- end
- end
- theta(Pos_theta)=theta_ls;%恢复出的theta
- end
function [ theta ] = CS_SP( y,A,K )
%CS_SP Summary of this function goes here
%Version: 1.0 written by jbb0523 @2015-05-01
% Detailed explanation goes here
% y = Phi * x
% x = Psi * theta
% y = Phi*Psi * theta
% 令 A = Phi*Psi, 则y=A*theta
% K is the sparsity level
% 现在已知y和A,求theta
% Reference:Dai W,Milenkovic O.Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing
% signal reconstruction[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,
% 2009,55(5):2230-2249.[y_rows,y_columns] = size(y);if y_rows<y_columnsy = y';%y should be a column vectorend[M,N] = size(A);%传感矩阵A为M*N矩阵theta = zeros(N,1);%用来存储恢复的theta(列向量)Pos_theta = [];%用来迭代过程中存储A被选择的列序号r_n = y;%初始化残差(residual)为yfor kk=1:K%最多迭代K次%(1) Identificationproduct = A'*r_n;%传感矩阵A各列与残差的内积[val,pos]=sort(abs(product),'descend');Js = pos(1:K);%选出内积值最大的K列%(2) Support MergerIs = union(Pos_theta,Js);%Pos_theta与Js并集%(3) Estimation%At的行数要大于列数,此为最小二乘的基础(列线性无关)if length(Is)<=MAt = A(:,Is);%将A的这几列组成矩阵Atelse%At的列数大于行数,列必为线性相关的,At'*At将不可逆break;%跳出for循环end%y=At*theta,以下求theta的最小二乘解(Least Square)theta_ls = (At'*At)^(-1)*At'*y;%最小二乘解%(4) Pruning[val,pos]=sort(abs(theta_ls),'descend');%(5) Sample UpdatePos_theta = Is(pos(1:K));theta_ls = theta_ls(pos(1:K));%At(:,pos(1:K))*theta_ls是y在At(:,pos(1:K))列空间上的正交投影r_n = y - At(:,pos(1:K))*theta_ls;%更新残差 if norm(r_n)<1e-6%Repeat the steps until r=0break;%跳出for循环endendtheta(Pos_theta)=theta_ls;%恢复出的theta
end- clear all;close all;clc;
- load CoSaMPMtoPercentage1000;
- PercentageCoSaMP = Percentage;
- load SPMtoPercentage1000;
- PercentageSP = Percentage;
- S1 = ['-ks';'-ko';'-kd';'-kv';'-k*'];
- S2 = ['-rs';'-ro';'-rd';'-rv';'-r*'];
- figure;
- for kk = 1:length(K_set)
- K = K_set(kk);
- M_set = 2*K:5:N;
- L_Mset = length(M_set);
- plot(M_set,PercentageCoSaMP(kk,1:L_Mset),S1(kk,:));%绘出x的恢复信号
- hold on;
- plot(M_set,PercentageSP(kk,1:L_Mset),S2(kk,:));%绘出x的恢复信号
- end
- hold off;
- xlim([0 256]);
- legend('CoSaK=4','SPK=4','CoSaK=12','SPK=12','CoSaK=20',...
- 'SPK=20','CoSaK=28','SPK=28','CoSaK=36','SPK=36');
- xlabel('Number of measurements(M)');
- ylabel('Percentage recovered');
- title('Percentage of input signals recovered correctly(N=256)(Gaussian)');
clear all;close all;clc;
load CoSaMPMtoPercentage1000;
PercentageCoSaMP = Percentage;
load SPMtoPercentage1000;
PercentageSP = Percentage;
S1 = ['-ks';'-ko';'-kd';'-kv';'-k*'];
S2 = ['-rs';'-ro';'-rd';'-rv';'-r*'];
figure;
for kk = 1:length(K_set)K = K_set(kk);M_set = 2*K:5:N;L_Mset = length(M_set);plot(M_set,PercentageCoSaMP(kk,1:L_Mset),S1(kk,:));%绘出x的恢复信号hold on; plot(M_set,PercentageSP(kk,1:L_Mset),S2(kk,:));%绘出x的恢复信号
end
hold off;
xlim([0 256]);
legend('CoSaK=4','SPK=4','CoSaK=12','SPK=12','CoSaK=20',...'SPK=20','CoSaK=28','SPK=28','CoSaK=36','SPK=36');
xlabel('Number of measurements(M)');
ylabel('Percentage recovered');
title('Percentage of input signals recovered correctly(N=256)(Gaussian)');运行结果如下:
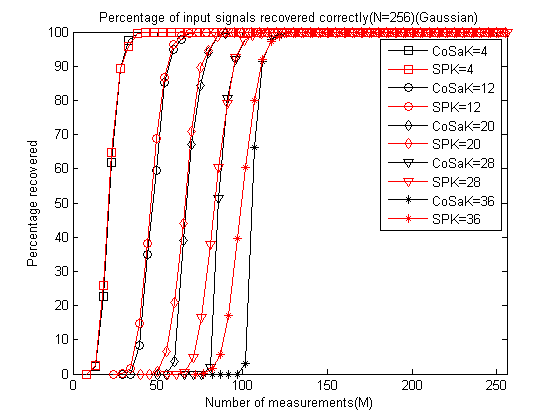
可以发现在M较小时SP略好于CoSaMP,当M变大时二者重构性能几乎一样。
参考文献:
[1]Dai W,Milenkovic O. Subspace pursuitfor compressive sensing: Closing the gap between performance and complexity.http://arxiv.org/pdf/0803.0811v1.pdf
[2]Dai W,Milenkovic O.Subspacepursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction[J].IEEETransactions on Information Theory,2009,55(5):2230-2249.
[3]D. Needell, J.A. Tropp.CoSaMP: Iterative signal recoveryfrom incomplete and inaccurate samples. http://arxiv.org/pdf/0803.2392v2.pdf
[4]D. Needell, J.A. Tropp.CoSaMP: Iterative signal recoveryfrom incomplete and inaccurate samples. http://arxiv.org/pdf/0803.2392v1.pdf
[5]杨真真,杨震,孙林慧.信号压缩重构的正交匹配追踪类算法综述[J]. 信号处理,2013,29(4):486-496.
[6]Li Zeng. CS_Reconstruction. http://www.pudn.com/downloads518/sourcecode/math/detail2151378.html
这篇关于压缩感知重构算法之子空间追踪(SP)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








