本文主要是介绍优化算法(寻优问题)\启发式算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言
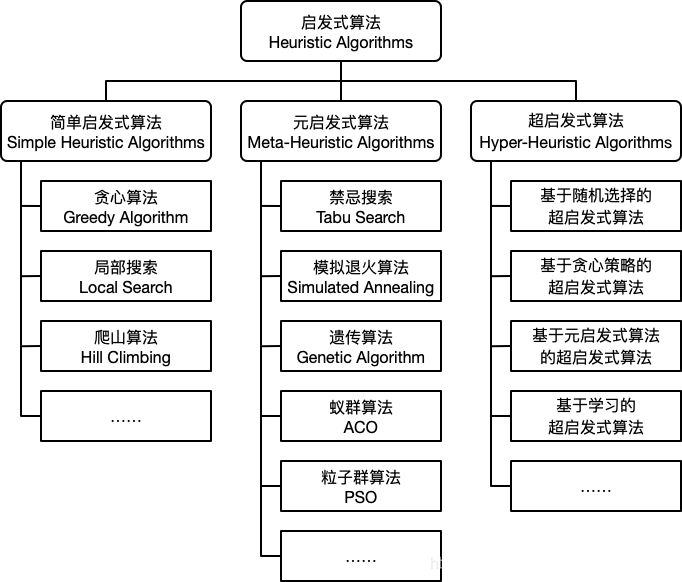
- 群智能算法(全局最优):模拟退火算法(Simulated annealing,SA),遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm, GA),粒子群算法(Particle Swarm Optimization,PSO)
- 局部搜索算法(local search algorithm):爬山算法 (Hill Climbing),禁忌算法(Tabu Search,TS)
- 路径搜索算法:A Search, A* Search,深度优先算法DFS/回溯法(backtracking),广度优先BFS
无信息搜索(uniformed search strategies)
- Breadth-First Search:FIFO queue
- Uniform-cost search:expands the node n with the lowest path cost,(total cost of a path)
- Depth-First Search:LIFO(aka. stack)
- Depth-limited search
- Iterative deepening DFS:每次加深1层的DFS,IDS does the Goal-test before the child is pushed onto the queue. The goal is found when parent node is expanded.
- Bidirectional search
启发式搜索 Informed (Heuristic) Search
- Greedy best-first search:贪心算法,采用启发函数 f(n) = h(n), which is estimated cost of the cheapest path from node n to a goal node
- A* search (A-star search):采用f(n) = g(n)+h(n),g(n)表示起点到n节点的花费,h(n)表示n节点到目标节点的花费。f(n)=estimated cost of the cheapest solution through n。
- Recursive best-first search (RBFS):memory-bounded heuristic search
- Local search:Hill climbing; simulated annealing
- genetic algorithm: is a stochastic hill-climbing search
- Online search
搜索策略的评估
- Completeness: does it always find a solution if one exists?
- Optimality: does it always find a least‐cost solution?
- Time complexity: number of nodes generated
- Space complexity: maximum number of nodes in memory
Time and space complexity are measured in terms of
- b: maximum branching factor of the search tree
- d: depth of the optimal solution
- m: maximum length of any path in the state space (may be infinite)
模拟退火算法
模拟退火算法(Simulate Anneal,SA)是一种通用概率演算法,用来在一个大的搜寻空间内找寻命题的最优解。它是基于Monte-Carlo迭代求解策略的一种随机寻优算法。模拟退火算法是解决TSP问题的有效方法之一。
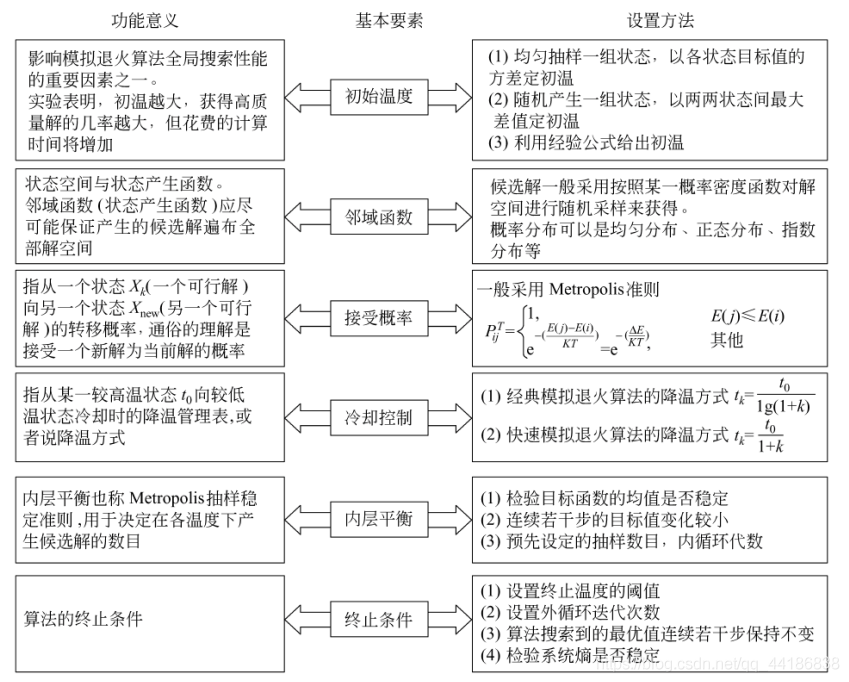
- 初始温度 T0、降温系数 Δ(0到1之间)、终止温度 Tk
- (外层循环)降温过程:每次T乘上Δ,直到 T≤Tk
- (内层循环)概率选择新解:在温度T时,选择领域解进行判断,优解直接接受,对于劣解,概率接受(T 越大时概率越大,新解和旧解差绝对值越小时概率越小)
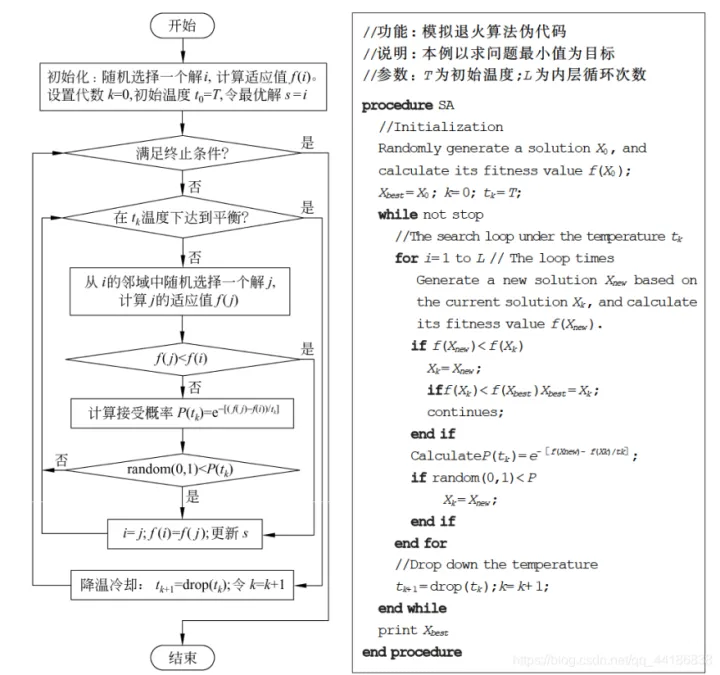
过程详解
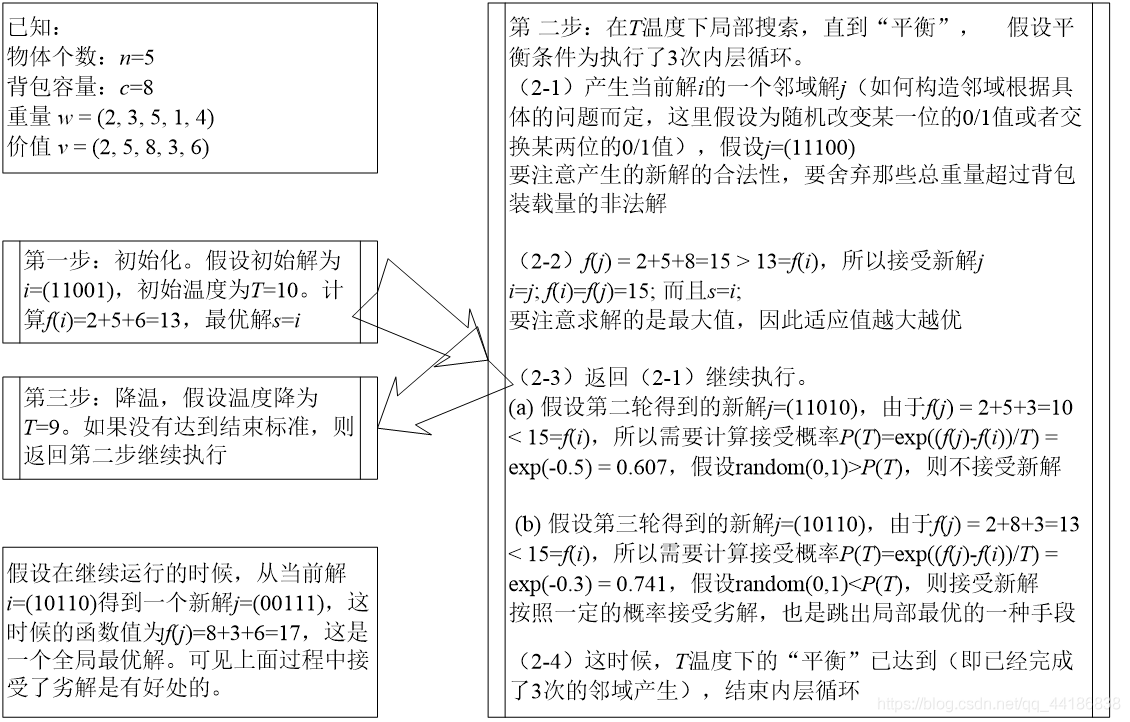
实际案例 - 背包问题
代码
class SimulatedAnnealing(object):def __init__(self, weight_list, volume_list, value_list, Weight_threshold_value, Volume_threshold_value, satisfying_value, break_T):"""背包物体属性"""self.object_total_number = len(weight_list)self.weight_list = weight_listself.volume_list = volume_listself.value_list = value_listself.Weight_threshold_value = Weight_threshold_valueself.Volume_threshold_value = Volume_threshold_valueself.best_value = -1 # 更新最优值self.cur_total_weight = 0self.cur_total_volume = 0self.cur_total_value = 0self.best_indexs_way = [0] * self.object_total_numberself.current_indexs_way = [0] * self.object_total_number # best_way 记录全局最优解方案 now_way 记录当前解方案self.weight = self.weight_listself.value = self.value_listself.volume = self.volume_list"""跳出条件"""self.satisfying_value = satisfying_valueself.break_T = break_T"""模拟退火属性"""self.T = 200.0 # 温度self.af = 0.95 # af退火率self.balance = 500 # 平衡次数self.iter_times = 100 # 迭代次数def initialize(self):"""初始化,产生随机解"""while True:for k in range(self.object_total_number):if random.random() < 0.5:self.current_indexs_way[k] = 1else:self.current_indexs_way[k] = 0self.calculate_value(self.current_indexs_way)if self.cur_total_weight < self.Weight_threshold_value and self.cur_total_volume < self.Volume_threshold_value:breakself.best_value = self.calculate_value(self.current_indexs_way)self.copy_list(self.best_indexs_way, self.current_indexs_way)def copy_list(self, a, b): # 复制函数 把b列表的值赋值a列表for i in range(len(a)):a[i] = b[i]def calculate_value(self, x):"""计算背包的总重量、总体积、总价值"""self.cur_total_weight = 0self.cur_total_volume = 0self.cur_total_value = 0for i in range(self.object_total_number):self.cur_total_weight += x[i] * self.weight[i] # 当前总重量self.cur_total_volume += x[i] * self.volume[i] # 当前总体积self.cur_total_value += x[i] * self.value[i] # 当前总价值return self.cur_total_valuedef get_object(self, x): # 随机将背包中已经存在的物品取出while True:ob = random.randint(0, self.object_total_number - 1)if x[ob] == 1:x[ob] = 0breakdef put_object(self, x): # 随机放入背包中不存在的物品while True:ob = random.randint(0, self.object_total_number - 1)if x[ob] == 0:x[ob] = 1breakdef run(self):self.initialize() # 初始化,产生初始解for i in range(self.iter_times):test_indexs_way = [0] * self.object_total_numbernow_total_value = 0 # 当前背包价值for i in range(self.balance):now_total_value = self.calculate_value(self.current_indexs_way)self.copy_list(test_indexs_way, self.current_indexs_way)ob = random.randint(0, self.object_total_number - 1) # 随机选取某个物品if test_indexs_way[ob] == 1: # 如果物品在背包中self.put_object(test_indexs_way) # 随机放入背包中不存在的物品test_indexs_way[ob] = 0 # 在背包中则将其拿出,并加入其它物品else: # 不在背包中则直接加入或替换掉已在背包中的物品if random.random() < 0.5:test_indexs_way[ob] = 1else:self.get_object(test_indexs_way)test_indexs_way[ob] = 1temp_total_value = self.calculate_value(test_indexs_way)if self.cur_total_weight > self.Weight_threshold_value or self.cur_total_volume > self.Volume_threshold_value:continue # 非法解则跳过if temp_total_value > self.best_value: # 如果新的解更好,更新全局最优self.best_value = temp_total_valueself.copy_list(self.best_indexs_way, test_indexs_way)if temp_total_value > now_total_value: # 如果新的解比当前解更好,直接接受新解self.copy_list(self.current_indexs_way, test_indexs_way)else:g = 1.0 * (temp_total_value - now_total_value) / self.Tif random.random() < math.exp(g): # 概率接受劣解self.copy_list(self.current_indexs_way, test_indexs_way)self.T = self.T * self.af # 温度下降"""跳出条件, 达到满意的解或者温度直接跳出"""if self.best_value > self.satisfying_value or self.T < self.break_T:break# 方案转为索引的形式best_object_number = []for i in range(object_total_number):if self.best_indexs_way[i]:best_object_number.append(i)print(f"最好的选择方案是取第best_object_number:{best_object_number}个物品,total_value:{self.best_value}")import random, math
object_total_number=9
weight_list = random.sample(range(1, 100), object_total_number)
volume_list = random.sample(range(1, 100), object_total_number)
value_list = random.sample(range(1, 1000), object_total_number)
Weight_threshold_value = sum(weight_list) / 2 # 取总和值的一半算了?直接不用改动了
Volume_threshold_value = sum(volume_list) / 2print(f"Weight_threshold_value:{Weight_threshold_value}")
print(f"Volume_threshold_value:{Volume_threshold_value}")
print(f"weight_list:{weight_list}")
print(f"volume_list:{volume_list}")
print(f"value_list:{value_list}")satisfying_value = 999999 # 设置满意解,达到就直接退出了
break_T = 1 # 设置跳出温度
SimulatedAnnealing_obj = SimulatedAnnealing(weight_list=weight_list, volume_list=volume_list, value_list=value_list,Weight_threshold_value=Weight_threshold_value,Volume_threshold_value=Volume_threshold_value,satisfying_value=satisfying_value, break_T=break_T)
SimulatedAnnealing_obj.run()输出结果:
Weight_threshold_value:258.0 Volume_threshold_value:228.0 weight_list:[53, 71, 16, 66, 74, 75, 55, 18, 88] volume_list:[46, 41, 31, 15, 21, 47, 78, 89, 88] value_list:[732, 886, 98, 889, 128, 966, 355, 140, 491] 最好的选择方案是取第best_object_number:[1, 2, 3, 5, 7]个物品,total_value:2979
A(A*) 寻路算法
狄克斯特拉算法求最短路径时只根据起点到候补顶点的距离来决定下一个顶点。
A算法是启发式算法重要的一种,主要是用于在两点之间选择一个最优路径,而A的实现也是通过一个估值函数: F=G+H
- G表示该点到起始点位所需要的代价
- H表示该点到终点的曼哈顿距离。
- F就是G和H的总和,而最优路径也就是选择最小的F值,进行下一步移动
- Open list 里的格子是路径可能会是沿途经过的,也有可能不经过。基本上 open list 是一个待检查的方格列表。
- 从 open list 中移除,加入到 close list 中, close list 中的每个方格都是现在不需要再关注的
- 父节点(parent): 在路径规划中用于回溯的节点。
- 计算G值时,在场景中横向或纵向移动消耗10,对角移动消耗14。
- 估算 H 值使用 Manhattan 方法,计算从当前方格横向或纵向移动到达目标所经过的方格数,忽略对角移动。
- 路径是这么产生的:反复遍历 open list ,选择 F 值最小的方格。
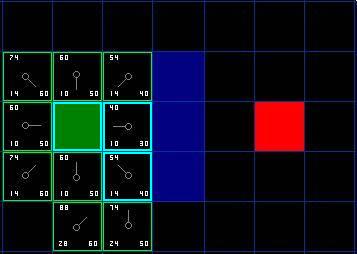
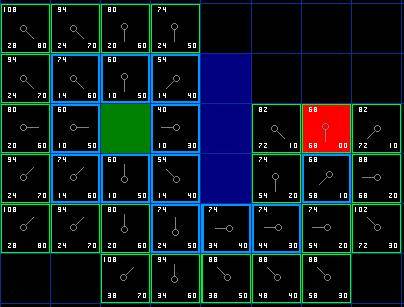
- 如果不设置启发函数,则 A* 就是 Dijkstra 算法,这时可以找到最短路径。
- 如果启发函数 H(n) 的值一定小于等于 n 到终点的实际距离,则 A* 可以保证找到最短路径。
- 如果 H(n) 的值等于 n 到终点的实际距离,则 A* 会直接找到最短路径,而不用扩展搜索额外的节点,此时运行是最快的。
- 如果 H(n) 的值有可能大于 n 到终点的实际距离,则 A* 算法不一定可以找到最短路径,但是运行速度会比较快。
- A* is optimal if h(n) is an admissible heuristic —— that is, provided that h(n) never overestimates the cost to reach the goal.
- A* is optimal if heuristic is admissible (and non‐negative) for tree-search
- A* optimal if heuristic is consistent for graph-search
对于A*算法来说,评判函数也是f(n)=g∗(n)+h∗(n) 这个,只不过加了约束条件,g∗(n)>0,h*(n)<=任意h(n); 以上只不过是定义,对于一个实例来说,h(n)由很多种,h(n)只是估值函数的一个集合,有各种方法h1(n)h2(n) h3(n)…,取其中任意一个方法带入上述公式,组成评判函数,都是A算法的实现,现在取从集合中一个函数h*(n),使得它比集合中任意的函数都优秀,这样的算法叫A*算法。 也就是A*算法是最优的A算法。(因为估值函数最优)。
References
A*算法详解(个人认为最透彻的一个)_inCorning的博客-CSDN博客
这篇关于优化算法(寻优问题)\启发式算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





