本文主要是介绍UVA | Optimal Binary Search Tree,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
原题
题目链接:https://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&category=514&page=show_problem&problem=1245
Given a set S = (e1, e2, …, en) of n distinct elements such that e1 < e2 < … < en and considering a binary search tree (see the previous problem) of the elements of S, it is desired that higher the query frequency of an element, closer will it be to the root.
The cost of accessing an element ei of S in a tree (cost(ei)) is equal to the number of edges in the path that connects the root with the node that contains the element. Given the query frequencies of the elements of S, (f(e1), f(e2), … , f(en)), we say that the total cost of a tree is the following summation:
f(e1) ∗ cost(e1) + f(e2) ∗ cost(e2) + … + f(en) ∗ cost(en)
In this manner, the tree with the lowest total cost is the one with the best representation for searching elements of S. Because of this, it is called the Optimal Binary Search Tree.
Input
The input will contain several instances, one per line.
Each line will start with a number 1 ≤ n ≤ 250, indicating the size of S. Following n, in the
same line, there will be n non-negative integers representing the query frequencies of the elements of
S: f(e1), f(e2), … , f(en), 0 ≤ f(ei) ≤ 100. Input is terminated by end of file.
Output
For each instance of the input, you must print a line in the output with the total cost of the Optimal Binary Search Tree.
Sample Input
1 5
3 10 10 10
3 5 10 20
Sample Output
0
20
20
思路
一开始以为要弄平衡二叉搜索树…懵逼了好久
而注意二叉搜索树的定义是:
左侧子树的所有节点<根节点,右侧子树的所有节点权值>根节点。
而既然给出了一个按照节点权值排好序的数组,构建一个BST其实非常简单。
具体构建树的方法是利用二分,找到中间节点,并将中间节点的左侧化为左子树,右侧化为右子树,可以参考:http://blog.csdn.net/u013033845/article/details/52148718
而这题需要求相应的路径长度最小值,也即权值*depth的最小值
关键点在于选取哪一个节点作为根节点可以使得整个深度取得最小。
利用一个二维DP矩阵:
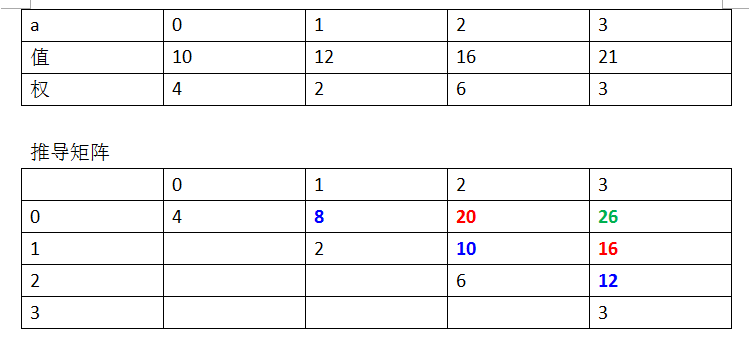
推导的过程如下:
推导
Len=1时,dp[0][0]=a[0]=4,dp[1][1]=a[1]=2…
Len=2时,dp[0][1]值分别为:
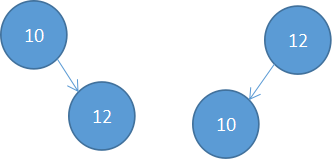
4*1【根节点深度为1】+2*2=8 , 2*1+4*2=10,故dp[0][1]=8
与之类似,dp[1][2]=min{2*2+6,6*2+2}=2*2+6=2+6 + 2=10,dp[2][3]=12
Len=3时,dp[0][2]一共有3种情况
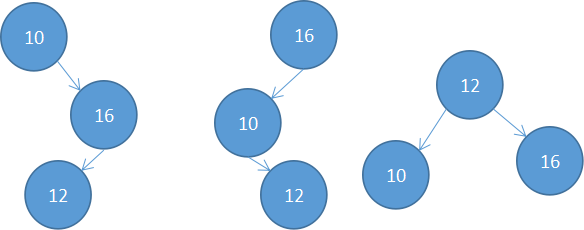
这三种情况的值分别为
0为根:4+6*2+2*3=4+6+2 + 6+2*2 = sum+dp[1][2] = 22
1为根:2+4*2+6*2 = sum+dp[0][0]+dp[2][2]=22
2为根:6+4*2+2*3=sum+dp[0][1]=12+8=20
故可以得出DP方程:
dp[i][i]=sum[i~j]+min{dp[i][k-1]+dp[k+1][j]},if k>=i && k<=j
有个需要注意的地方是需要判断左右子树是否存在,防止越界的情况发生【不过其实越界的dp部分也都是0,不过算一下总是好的】
class Solution{
public:int bstcode(vector<int> &val,vector<int> &weight){memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)) ;int n=val.size();for(int i=0;i<n;i++) dp[i][i]=weight[i];for(int len=1;len<=n;len++){for(int i=0;i<n && i+len<n;i++){int j=i+len;int sum=0;for(int k=i;k<=j;k++) sum+=weight[k];int min=INT_MAX;//从i到j每一个尝试作根节点 for(int k=i;k<=j;k++){//需要判断左右子树是否存在 int left= dp[i][k-1];int right= k==j?0:dp[k+1][j];if(left+right<min)min=left+right;}dp[i][j]=sum+min;}}for(int i=0;i<n;i++){for(int j=0;j<n;j++){printf("%d ",dp[i][j]);}printf("\n");}printf("\n");return dp[0][n-1];}
};小结
与矩阵链乘、Cutting Sticks一样,这道题用的是区间DP。
区间DP其实也挺好理解,不过自己必须要手推一下规律才能得出来。
最重要的是,这些题目本身所蕴含的规律和表面题意不一定就是贴合的那么近。
比如Cutting Sticks所给的是切点但是需要关注的是切后的片段。
而本题给的二叉搜索树,我们知道二叉搜索树形态众多,但是在DP中我们经过推导就会发现,其实最优解并不需要考虑这棵树的形态究竟如何,而是要考虑所能求得的最小权值。
所以这类题目隐藏的比线性规划可能要深一点,需要仔细分析才能得出结果。
这篇关于UVA | Optimal Binary Search Tree的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




