本文主要是介绍HDU 1253 胜利大逃亡 (BFS,剪枝),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1253
胜利大逃亡
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 24270 Accepted Submission(s): 9300
Problem Description
Ignatius被魔王抓走了,有一天魔王出差去了,这可是Ignatius逃亡的好机会.
魔王住在一个城堡里,城堡是一个A*B*C的立方体,可以被表示成A个B*C的矩阵,刚开始Ignatius被关在(0,0,0)的位置,离开城堡的门在(A-1,B-1,C-1)的位置,现在知道魔王将在T分钟后回到城堡,Ignatius每分钟能从一个坐标走到相邻的六个坐标中的其中一个.现在给你城堡的地图,请你计算出Ignatius能否在魔王回来前离开城堡(只要走到出口就算离开城堡,如果走到出口的时候魔王刚好回来也算逃亡成功),如果可以请输出需要多少分钟才能离开,如果不能则输出-1.
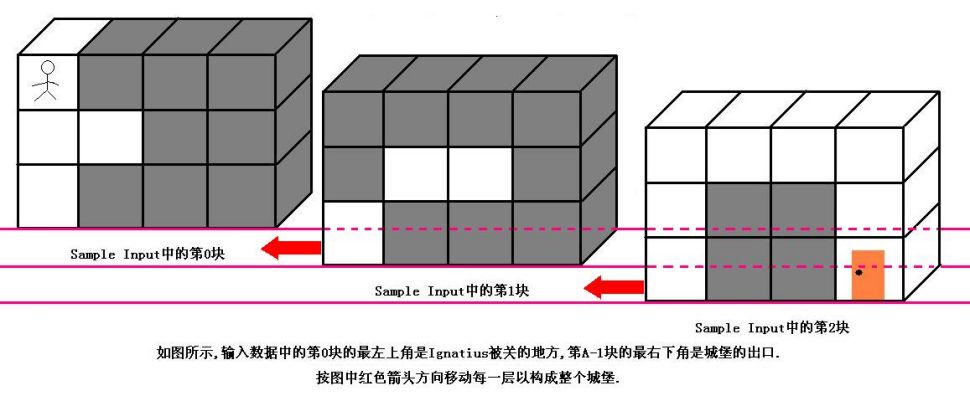
魔王住在一个城堡里,城堡是一个A*B*C的立方体,可以被表示成A个B*C的矩阵,刚开始Ignatius被关在(0,0,0)的位置,离开城堡的门在(A-1,B-1,C-1)的位置,现在知道魔王将在T分钟后回到城堡,Ignatius每分钟能从一个坐标走到相邻的六个坐标中的其中一个.现在给你城堡的地图,请你计算出Ignatius能否在魔王回来前离开城堡(只要走到出口就算离开城堡,如果走到出口的时候魔王刚好回来也算逃亡成功),如果可以请输出需要多少分钟才能离开,如果不能则输出-1.

Input
输入数据的第一行是一个正整数K,表明测试数据的数量.每组测试数据的第一行是四个正整数A,B,C和T(1<=A,B,C<=50,1<=T<=1000),它们分别代表城堡的大小和魔王回来的时间.然后是A块输入数据(先是第0块,然后是第1块,第2块......),每块输入数据有B行,每行有C个正整数,代表迷宫的布局,其中0代表路,1代表墙.(如果对输入描述不清楚,可以参考Sample Input中的迷宫描述,它表示的就是上图中的迷宫)
特别注意:本题的测试数据非常大,请使用scanf输入,我不能保证使用cin能不超时.在本OJ上请使用Visual C++提交.
特别注意:本题的测试数据非常大,请使用scanf输入,我不能保证使用cin能不超时.在本OJ上请使用Visual C++提交.
Output
对于每组测试数据,如果Ignatius能够在魔王回来前离开城堡,那么请输出他最少需要多少分钟,否则输出-1.
Sample Input
1 3 3 4 20 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
Sample Output
11
Author
Ignatius.L
Recommend
Ignatius.L | We have carefully selected several similar problems for you: 1372 1072 1240 1175 1241
显然的BFS,如果不加任何优化并且写得很搓的话估计会超时,注意常数优化(传引用,加inline)的话可能会1800ms左右,输入优化的话可能会1000ms以内,加上剪枝我优化到93ms,这里的剪枝用到了A*的思想,利用Manhattan距离可以剔除大量不比较搜索的点
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<ctime>
#include<cctype>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#define sqr(x) ((x)*(x))
#define LL long long
#define itn int
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PI 3.1415926535897932384626
#define eps 1e-10
#define mmusing namespace std;itn A,B,C,T,MAP[55][55][55];
int dx[]={1,-1,0,0,0,0};
itn dy[]={0,0,1,-1,0,0};
itn dz[]={0,0,0,0,1,-1};struct node
{int x,y,z,t;void Set(int X=0,int Y=0,int Z=0,int T=0){x=X;y=Y;z=Z;t=T;}int MANHATTAN_DIS(){return abs(x-A)+abs(y-B)+abs(z-C);}
}q[200000];
int f,r;inline int ReadInt()
{int flag=0;char ch = getchar();int data = 0;while (ch < '0' || ch > '9'){if(ch=='-') flag=1;ch = getchar();}do{data = data*10 + ch-'0';ch = getchar();}while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9');if(flag) data=-data;return data;
}inline bool check(int &x,int &y,itn &z)
{return x>=1 && x<=A && y>=1 && y<=B && z>=1 && z<=C;
}int bfs()
{int x,y,z;node now;q[f=r=0].x=q[f].y=q[f].z=1;q[f].t=0;MAP[1][1][1]=1;while (f<=r){now=q[f];f++;if (now.x==A && now.y==B && now.z==C) return now.t;if (now.MANHATTAN_DIS()+now.t>T) continue;//用Manhattan距离剪枝if (now.t>T) return -1;for (int i=0;i<6;i++){x=now.x+dx[i];y=now.y+dy[i];z=now.z+dz[i];if (check(x,y,z) && MAP[x][y][z]==0){q[++r].x=x;q[r].y=y;q[r].z=z;q[r].t=now.t+1;MAP[x][y][z]=1;}}}return -1;
}int main()
{#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGEfreopen("/home/fcbruce/文档/code/t","r",stdin);#endif // ONLINE_JUDGEint T_T;T_T=ReadInt();while (T_T--){A=ReadInt();B=ReadInt();C=ReadInt();T=ReadInt();for (itn i=1;i<=A;i++){for (itn j=1;j<=B;j++){for (int k=1;k<=C;k++){MAP[i][j][k]=ReadInt();}}}printf("%d\n",bfs());}return 0;
}
这篇关于HDU 1253 胜利大逃亡 (BFS,剪枝)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


