本文主要是介绍雷达标定与解析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
融合雷达与解析雷达数据的相关代码。感谢开源社区的贡献。以下代码继承了很多人的工作。
如果是单雷达:
直接进行标定,所以就是接收相关的话题然后发布。
lidar_calibration_params.yaml:
calibration:在这个接口里面x_offset: 0.0y_offset: 0.0z_offset: 0.4roll_offset: -0.074pitch_offset: 0yaw_offset: -1.57input_topic: "/lslidar_point_cloud"
output_topic: "/fusion_points"
lidar_calibration_node.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/PointCloud2.h>
#include <tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h>
#include <tf2/LinearMath/Matrix3x3.h>
#include <pcl_conversions/pcl_conversions.h>
#include <pcl_ros/transforms.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <iostream>// 标定参数结构体
struct CalibrationParams
{double x_offset;double y_offset;double z_offset;double roll_offset;double pitch_offset;double yaw_offset;
};ros::Publisher calibrated_pub;
CalibrationParams calibration_params;void loadCalibrationParams(const ros::NodeHandle& nh)
{nh.getParam("calibration/x_offset", calibration_params.x_offset);nh.getParam("calibration/y_offset", calibration_params.y_offset);nh.getParam("calibration/z_offset", calibration_params.z_offset);nh.getParam("calibration/roll_offset", calibration_params.roll_offset);nh.getParam("calibration/pitch_offset", calibration_params.pitch_offset);nh.getParam("calibration/yaw_offset", calibration_params.yaw_offset);// 打印加载的参数以确认ROS_INFO("Loaded calibration parameters:");ROS_INFO("x_offset: %f", calibration_params.x_offset);ROS_INFO("y_offset: %f", calibration_params.y_offset);ROS_INFO("z_offset: %f", calibration_params.z_offset);ROS_INFO("roll_offset: %f", calibration_params.roll_offset);ROS_INFO("pitch_offset: %f", calibration_params.pitch_offset);ROS_INFO("yaw_offset: %f", calibration_params.yaw_offset);
}void laserCallback(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& cloud_msg)
{// Create transformation matrixEigen::Affine3f transform = Eigen::Affine3f::Identity();transform.translation() << calibration_params.x_offset, calibration_params.y_offset, calibration_params.z_offset;Eigen::AngleAxisf rollAngle(calibration_params.roll_offset, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitX());Eigen::AngleAxisf pitchAngle(calibration_params.pitch_offset, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitY());Eigen::AngleAxisf yawAngle(calibration_params.yaw_offset, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ());transform.rotate(yawAngle * pitchAngle * rollAngle);// 打印转换矩阵以确认std::cout << "Transformation Matrix:" << std::endl;std::cout << transform.matrix() << std::endl;// Transform the point cloudsensor_msgs::PointCloud2 calibrated_cloud_msg;pcl_ros::transformPointCloud(transform.matrix(), *cloud_msg, calibrated_cloud_msg);// Publish the calibrated point cloudcalibrated_cloud_msg.header = cloud_msg->header;calibrated_pub.publish(calibrated_cloud_msg);
}int main(int argc, char** argv)
{ros::init(argc, argv, "lidar_calibration_node");ros::NodeHandle nh;// 获取参数服务器中的参数std::string input_topic;std::string output_topic;int queue_size;nh.param<std::string>("input_topic", input_topic, "/lslidar_point_cloud");nh.param<std::string>("output_topic", output_topic, "/calibrated_point_cloud");nh.param<int>("queue_size", queue_size, 10);// 加载标定参数loadCalibrationParams(nh);// std::cout<<input_topic<<std::endl;// std::cout<<output_topic<<std::endl;// 订阅输入点云话题ros::Subscriber laser_sub = nh.subscribe(input_topic, queue_size, laserCallback);// 发布标定后的点云话题calibrated_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(output_topic, queue_size);ros::spin();return 0;
}
启动launch:
<launch><rosparam file="$(find lidar_calibration)/config/lidar_calibration_params.yaml" command="load"/><node pkg="lidar_calibration" type="lidar_calibration_node" name="lidar_calibration_node" output="screen"></node></launch>
以上是单个雷达的标定的,接下来是融合点云的数据标定:
来源于一个开源项目:git clone https://github.com/Hliu0313/fusion_pointclouds
也是直接修改接口就行了:
#参数加载对应 loadparams.h/loadparams.cpp,若修改params.yaml对应修改加载函数即可
fusion_lidar_num: 3 #融合 lidar 点云数量 2/3/4
topics: #订阅 lidar 点云话题
# parent_pc_topic: "/livox/lidar"
# child_pc_topic1: "/right/rslidar_points"
# child_pc_topic2: "/left/rslidar_points"
# child_pc_topic3: "/livox/lidar"parent_pc_topic: "/livox/lidar"child_pc_topic1: "/right/rslidar_points"child_pc_topic2: "/left/rslidar_points"child_pc_topic3: "/livox/lidar"fusion_pc_topic: "/fusion_points" #融合后发布点云话题名称fusion_pc_frame_id: "rslidar" #融合后发布点云话题名称#注意
#1.点云话题少于4个时,为了时间同步回调函数适应不同数量雷达,空位child_pc_topic可以填入parent_pc_topic
#例如 需要融合"/front/rslidar_points" 与"/left/rslidar_points"点云数据
#
#fusion_lidar_num: 2
#parent_pc_topic: "/front/rslidar_points"
#child_pc_topic1: "/left/rslidar_points"
#child_pc_topic2: "/front/rslidar_points" "
#child_pc_topic3: "/front/rslidar_points" #----> 如果只是融合点云数据,下方参数填 false 即可 <-------
set_params_tf: true #是否对点云进行坐标变换
set_params_internal_bounds: true #是否对点云内边界 XYZ 滤除
set_params_external_bounds: true #是否对点外内边界 XYZ 滤除
set_dynamic_params: true #是否开启动态调整,配合 rqt_reconfigure 动态调整坐标变化参数 ---> 解决标定参数不准确,实时微调# cpc1_to_ppc: #child_pc1_to_parent_pc,坐标变化信息传入节点,按需填写即可
# x: -0.75
# y: -0.8
# z: 0.58
# roll: 0.05
# pitch: 0.01
# yaw: 0.06
# cpc2_to_ppc:
# x: -0.75
# y: 0.72
# z: 0.58
# roll: 0.0
# pitch: 0.0
# yaw: -0.1
# cpc3_to_ppc:
# x: 0.0
# y: 0.0
# z: 0.0
# roll: 0.0
# pitch: 0.0
# yaw: 0.0cpc1_to_ppc: #child_pc1_to_parent_pc,坐标变化信息传入节点,按需填写即可x: -0.8y: -0.5z: 1.06roll: 0.04pitch: 0.0yaw: 0.0cpc2_to_ppc:x: -0.75y: 0.75z: 1.06roll: -0.018pitch: 0.018yaw: -0.168# cpc2_to_ppc:
# x: -0.
# y: 0.
# z: 0.0
# roll: -0.0
# pitch: -0.0
# yaw: -0.0cpc3_to_ppc:x: 0.0y: 0.0z: 0.0roll: 0.0pitch: 0.0yaw: 0# Dynamic rqt_reconfigure default bounds
internal_bounds : #内边界x_min: 0.0x_max: 0.0y_min: 0.0y_max: 0.0z_min: 0.0z_max: 0.0external_bounds : #外边界x_min: -100x_max: 100y_min: -100y_max: 100z_min: -5z_max: 5
最后是聚类,也是来源于一个开源项目:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42905141/article/details/122977315?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522171888729016777224495812%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334…%2522%257D&request_id=171888729016777224495812&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2allsobaiduend~default-1-122977315-null-null.142v100control&utm_term=%E4%B8%9A%E4%BD%99%E5%86%99%E7%9A%84%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AA%E7%B2%97%E7%89%88demo%EF%BC%8C%E6%9C%89%E5%BE%88%E5%A4%9A%E5%9C%B0%E6%96%B9%E6%98%AF%E5%8F%AF%E4%BB%A5%E6%94%B9%E8%BF%9B%E7%9A%84%EF%BC%8C%E5%A4%A7%E5%AE%B6%E8%87%AA%E8%A1%8C%E4%BF%AE%E6%94%B9%E5%90%A7&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
非常感谢他的工作,接下来要做的就是把障碍物的信息用我们需要的方式重新就行发布就行了。我这里直接借鉴一下之前的比赛所遇到的障碍物的接口,我很喜欢他的这一系列的定义。
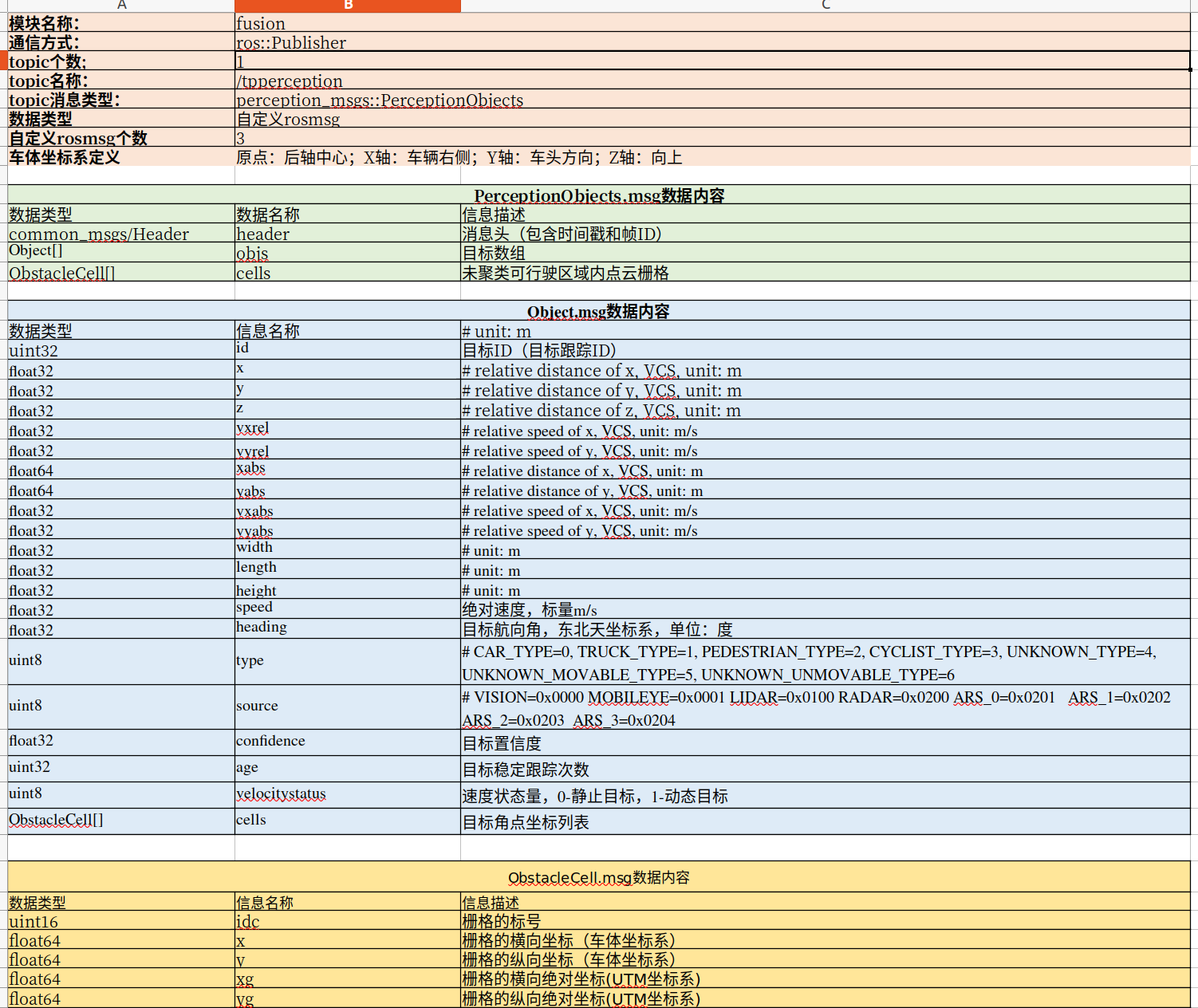
在这个接口里面主要是用上述msg来定义雷达给出的数据。
上述单雷达标定,多雷达融合,以及雷达的聚类都放到这里面了:
https://github.com/chan-yuu/lidar_ws
后续会继续做雷达处理的相关的工作
这篇关于雷达标定与解析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






