本文主要是介绍Java设计模式——Adapter(适配器)模式,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
适配器模式保留现有类所提供的服务,向客户提供接口,以满足客户的期望。适配器模式可分为类适配器模式、对象适配器模式和标识适配器模式三种。
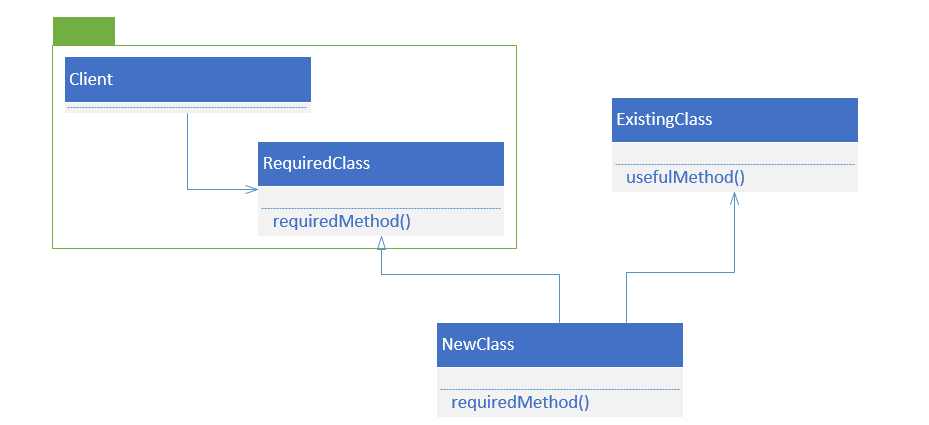
类适配器模式
拓展一个现有的类,并实现一个目标接口,将把客户的调用转变为调用现有类的方法。
对象适配器模式
拓展一个目标类,并把它委派给一个现有的类,将客户调用转发给现有类的实例。
- 如果希望适配的方法没有在接口中指定时,就应该使用委托方式,而不是创建子类方式。即对象适配器模式。
- 只要我们所适配的接口可以得到抽象类的支持,也必须使用对象适配器模式。
- 如果适配器类需要从多个对象中提取信息,也应当使用对象适配器。
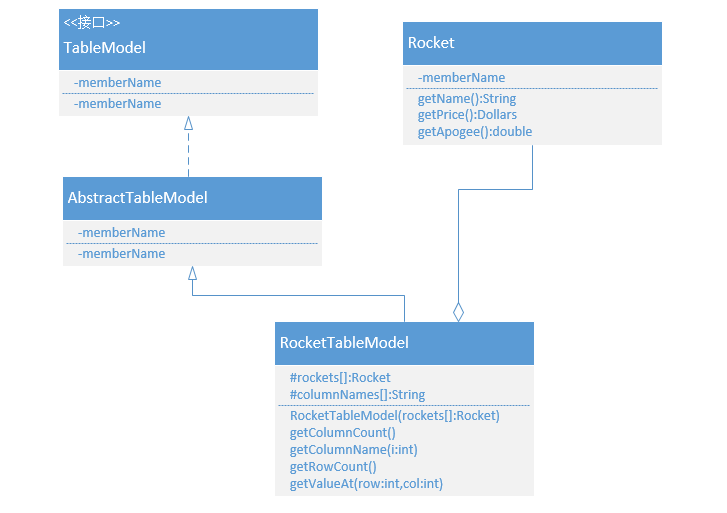
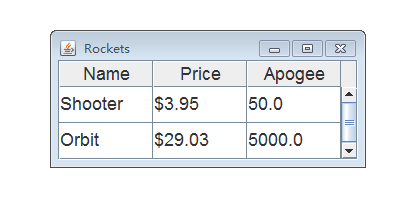
Swing中的JTable组件是应用对象适配器模式的很好例子。JTable组件通过调用TableModel接口中定义的方法获取表格
的相关信息,这样就可以很容易地写出一个适配器类,从域对象中获取用于填充表格的数据。
import javax.swing.table.*;
/*** Adapt a collection of rockets for display in a JTable.* * @author Steven J. Metsker*/
public class RocketTableModel extends AbstractTableModel {protected Rocket[] rockets;protected String[] columnNames = new String[] { "Name", "Price", "Apogee" };/*** Construct a rocket table from an array of rockets.* * @param rockets* an array of rockets*/public RocketTableModel(Rocket[] rockets) {this.rockets = rockets;}/*** @return the number of columns in this table.*/public int getColumnCount() {return columnNames.length;}/*** @param index* which column is interesting* @return the name of the indicated column*/public String getColumnName(int i) {return columnNames[i];}/*** @return the number of rows in this table.*/public int getRowCount() {return rockets.length;}/*** @param row* which row is interesting* @param col* which column is interesting* @return the value at the indicated row and column.*/public Object getValueAt(int row, int col) {switch (col) {case 0:return rockets[row].getName();case 1:return rockets[row].getPrice();case 2:return new Double(rockets[row].getApogee());default:return null;}}
}import java.awt.Component;
import java.awt.Font;import javax.swing.*;
public class ShowRocketTable { public static void main(String[] args) {setFonts();JTable table = new JTable(getRocketTable());table.setRowHeight(36);JScrollPane pane = new JScrollPane(table);pane.setPreferredSize(new java.awt.Dimension(300, 100));display(pane, " Rockets");}public static void display(Component c, String title) {JFrame frame = new JFrame(title);frame.getContentPane().add(c);frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.pack();frame.setVisible(true);}private static RocketTableModel getRocketTable() {Rocket r1 = new Rocket("Shooter", 1.0, new Dollars(3.95), 50.0, 4.5);Rocket r2 = new Rocket("Orbit", 2.0, new Dollars(29.03), 5000, 3.2);return new RocketTableModel(new Rocket[] { r1, r2 });}private static void setFonts() {Font font = new Font("Dialog", Font.PLAIN, 18);UIManager.put("Table.font", font);UIManager.put("TableHeader.font", font);}
}public class Dollars {public static final Dollars cent = new Dollars(0.01);static final int CENTS_PER_DOLLAR = 100;long cents;public Dollars(double value) {this.cents = Math.round(value * CENTS_PER_DOLLAR);}public boolean isZero() {return cents == 0;}public Dollars plus(Dollars that) {return new Dollars(1.0 * (this.cents + that.cents) / CENTS_PER_DOLLAR);}public Dollars times(int multiplier) {return new Dollars((this.cents * multiplier) / CENTS_PER_DOLLAR);}public Dollars dividedBy(int divisor) {double newCents = (1.0 * cents / divisor) / CENTS_PER_DOLLAR;return new Dollars(newCents);}public double dividedBy(Dollars that) {return (1.0 * this.cents) / that.cents;}public boolean isLessThan(Dollars that) {return this.cents < that.cents;}public String toString() {StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer("$");long dollars = cents / CENTS_PER_DOLLAR;result.append(dollars);result.append('.');long pennies = cents % CENTS_PER_DOLLAR;if (pennies < 10) result.append('0');result.append(pennies);return result.toString();}public boolean equals(Object obj) {if (!obj.getClass().equals(this.getClass()))return false;Dollars that = (Dollars) obj;return this.cents == that.cents;}public int hashCode() {return (int) cents;}public long asCents() {return cents;}
}public class Rocket extends Firework {private double apogee;private double thrust;/*** Allow creation of empty objects to support reconstruction from persistent* store.*/public Rocket() {}/*** Create a rocket with all its expected properties. See the superclass for* descriptions of other parameters* * @param apogee* The height (in meters) that the rocket is expected to reach* @param thrust* The rated thrust (or force, in newtons) of this rocket*/public Rocket(String name, double mass, Dollars price, double apogee,double thrust) {super(name, mass, price);setApogee(apogee);setThrust(thrust);}/*** The height (in meters) that the rocket is expected to reach.*/public double getApogee() {return apogee;}public void setApogee(double value) {apogee = value;}/*** The rated thrust (or force, in newtons) of this rocket.*/public double getThrust() {return thrust;}public void setThrust(double value) {thrust = value;}
}public class Firework {/*** @return a firework of the given name. This method supports a "Strategy"* example, but it isn't really implemented.* @param name* a name to lookup*/public static Firework lookup(String name) {return new Firework(name, 9.0, new Dollars(3));}/*** @return a random firework from our shelves. This method is not actually* implemented -- it's here as part of a "Strategy" example.*/public static Firework getRandom() {return new Firework("Random firework", 10.0, new Dollars(15));}private String name;private double mass;private Dollars price;/*** Allow creation of empty objects to support reconstruction from persistent* store.*/public Firework() {}public Firework(String name, double mass, Dollars price) {setName(name);setMass(mass);setPrice(price);}/*** The unique name of this type of firework*/public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String value) {name = value;}/*** The mass, in kilograms, of one instance of this type*/public double getMass() {return mass;}public void setMass(double value) {mass = value;}/*** The price (in dollars) of one instance of this type*/public Dollars getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(Dollars value) {price = value;}/*** @return a textual representation of this firework.*/public String toString() {return getName();}
}
JTable类有两个原因不能使用类适配器:
- 表适配器必须拓展现AbstractTableModel类,应此它不能再拓展现有的类;
- JTable类需要收集多个对象的数据,只有对象适配器才可以对多个对象进行适配。
今天培训的时候讲的一个例子感觉更易于理解适配器模式:
package test.lindl.t2;public interface China {void onChina();
}
package test.lindl.t2;public class ChinaPC implements China{@Overridepublic void onChina() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("This is a adapter for America!!");}}
package test.lindl.t2;public interface Usa {void onAmerica();
}
package test.lindl.t2;public class UsaPC implements Usa {@Overridepublic void onAmerica() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("This is a adapter for China!!");}}
package test.lindl.t2;public class Adapter implements Usa, China {private Usa usa;private China china;public Adapter(Usa usa) {this.usa = usa;}public Adapter(China china) {this.china = china;}@Overridepublic void onChina() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubusa.onAmerica();}@Overridepublic void onAmerica() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubchina.onChina();}}
package test.lindl.t2;public class Runner {public static void main(String[] args) {Usa usaPC = new UsaPC();China china = new ChinaPC();Usa adapter1 = new Adapter(china);adapter1.onAmerica();China adapter2 = new Adapter(usaPC);adapter2.onChina();}
}
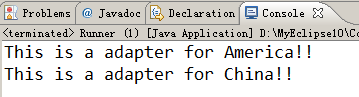
话说学设计模式看head first系列还真不错
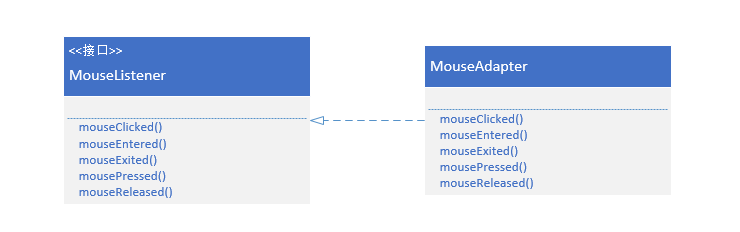
标识适配器模式
创建存根类MouseAdapter以后,在实现鼠标监听器类的时候,就不用实现MouseAdapter接口的所有方法
这篇关于Java设计模式——Adapter(适配器)模式的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!