本文主要是介绍cs61C | lecture4,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
cs61C | lecture4
C 语言内存布局
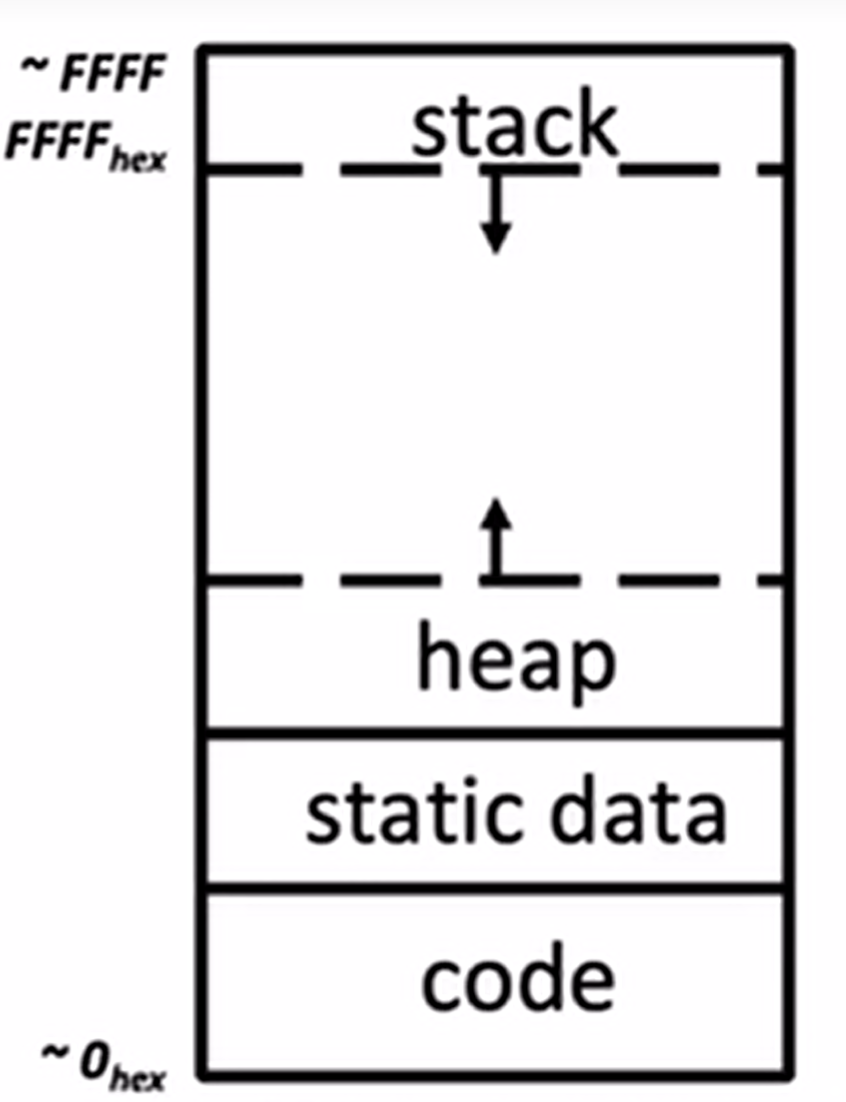 ### Stack 在最顶部,向下增长。包含局部变量和 function frame information。 > Each stack frame is a contiguous block of memory holding the local variables of a single procedure. > A stack frame includes: > - Location of caller function > - Function arguments > - Space for local variables
### Stack 在最顶部,向下增长。包含局部变量和 function frame information。 > Each stack frame is a contiguous block of memory holding the local variables of a single procedure. > A stack frame includes: > - Location of caller function > - Function arguments > - Space for local variables
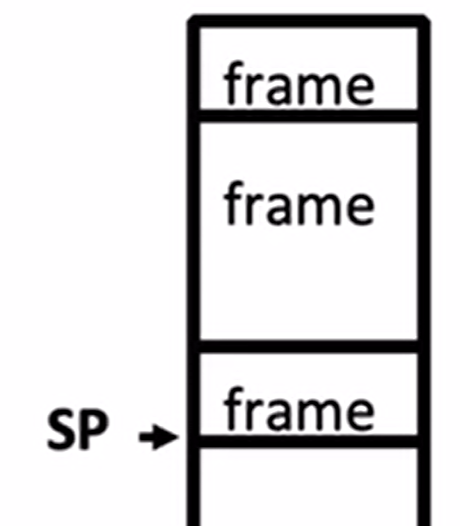 栈指针(SP, Stack Pointer) 告诉我们最低(当前)stack frame 在哪里。当进程结束时,SP 会移动回之前的位置,但是数据会保留(现在变成 garbage)。 ```c int main() { a(0); return 1; } void a(int m){ b(1); } void b(int n){ c(2); d(4); } void c(int o){ printf("c"); } void d(int p){ printf("d"); } ```  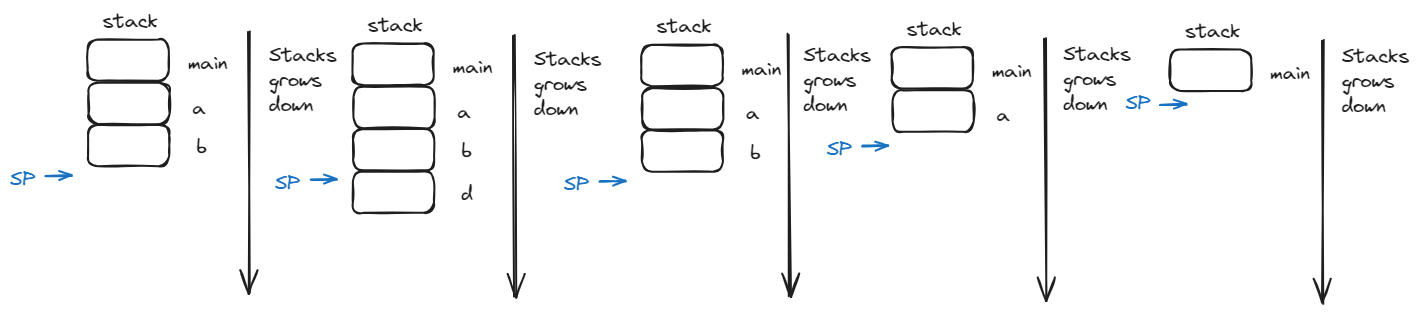 以下错误代码: ```c int *getPtr(){ int y; y = 3; return &y; } int main(){ int *stackAddr, content; stackAddr = getPtr(); content = *stackAddr; printf("%d", content); /* 3 */ content = *stackAddr; printf("%d", content); /* ? */ } ``` 第一次调用完 getPtr(),getPtr 的栈帧被收回,y 也相应地消失,stackAddr 指向 y 的地址,调用 printf,printf 函数覆盖了原先的栈帧位置,所以再次解引用 stackAddr,不能知道值为多少。 $\textcolor{red}{不要返回指向局部变量的指针!}$ ### Heap 向上增长,可以通过 malloc,realloc 和 calloc 请求空间。可以动态调整大小。 ### Static Data 存储全局和静态变量,这部分不会变化,在整个程序生命周期都一样。 字符串 char* str = "hi" 保存在该区域,**但是字符串数组 char str\[] = "hi" 是保存在栈区!** ### Code 这是程序加载到的位置,也是程序启动的地方。
栈指针(SP, Stack Pointer) 告诉我们最低(当前)stack frame 在哪里。当进程结束时,SP 会移动回之前的位置,但是数据会保留(现在变成 garbage)。 ```c int main() { a(0); return 1; } void a(int m){ b(1); } void b(int n){ c(2); d(4); } void c(int o){ printf("c"); } void d(int p){ printf("d"); } ```   以下错误代码: ```c int *getPtr(){ int y; y = 3; return &y; } int main(){ int *stackAddr, content; stackAddr = getPtr(); content = *stackAddr; printf("%d", content); /* 3 */ content = *stackAddr; printf("%d", content); /* ? */ } ``` 第一次调用完 getPtr(),getPtr 的栈帧被收回,y 也相应地消失,stackAddr 指向 y 的地址,调用 printf,printf 函数覆盖了原先的栈帧位置,所以再次解引用 stackAddr,不能知道值为多少。 $\textcolor{red}{不要返回指向局部变量的指针!}$ ### Heap 向上增长,可以通过 malloc,realloc 和 calloc 请求空间。可以动态调整大小。 ### Static Data 存储全局和静态变量,这部分不会变化,在整个程序生命周期都一样。 字符串 char* str = "hi" 保存在该区域,**但是字符串数组 char str\[] = "hi" 是保存在栈区!** ### Code 这是程序加载到的位置,也是程序启动的地方。
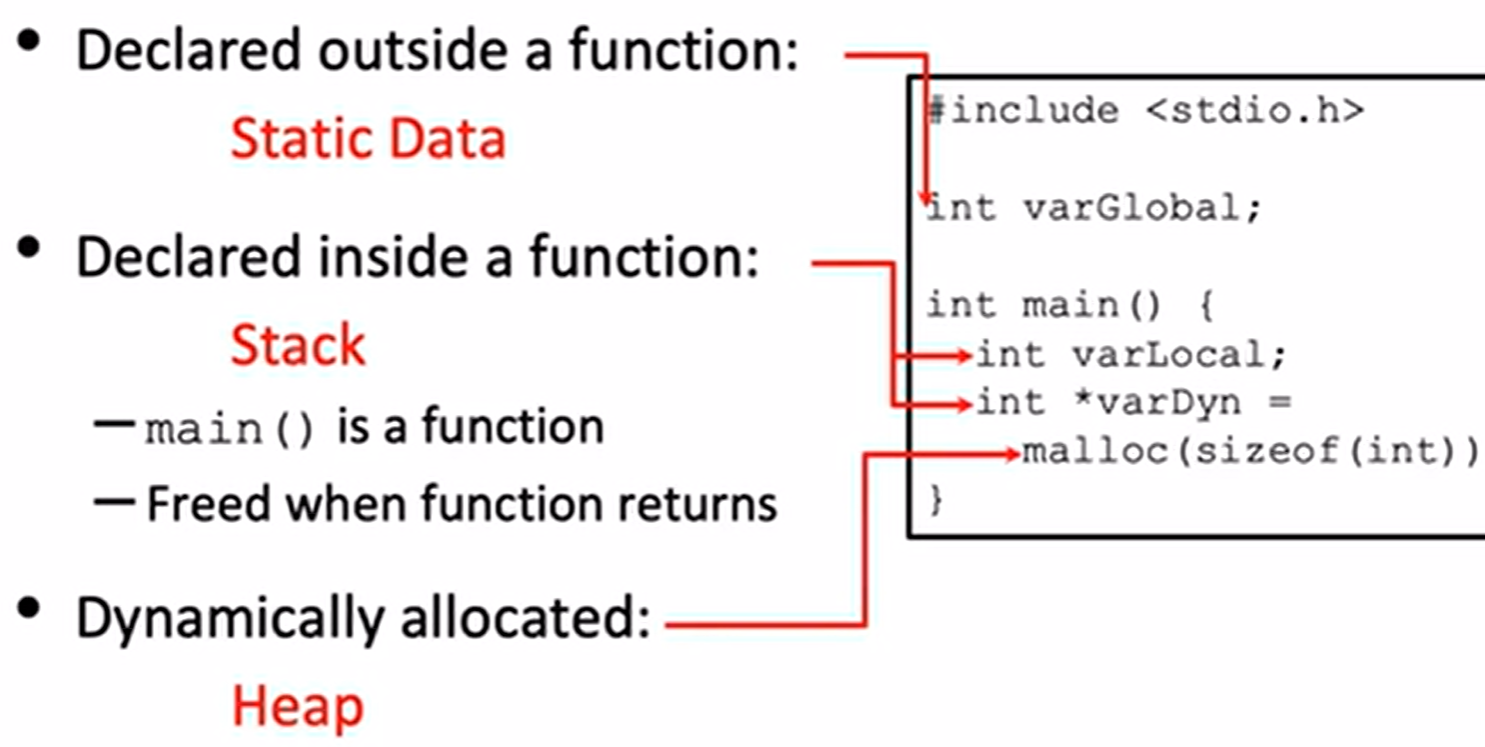
在函数外定义的变量存储在 Static Data
在函数内部声明的变量存储在 Stack,在函数返回时释放
动态分配的内存存储在 Heap
#include <stdio.h>int varGlobal; int main() {int varLocal;int *varDyn = malloc(sizeof(int));
}
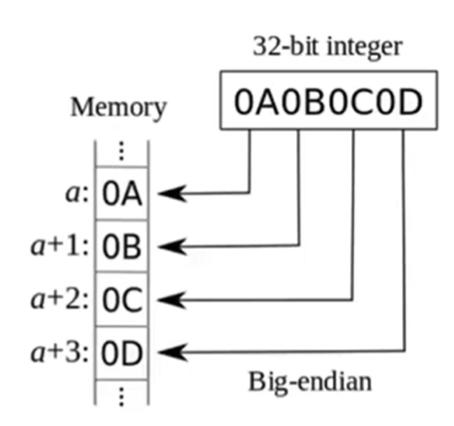
 ## Big Endian && Little Endian [字节序 Wiki](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%AD%97%E8%8A%82%E5%BA%8F) ### Big Endian 大端序:最高位字节存储在最低的内存地址处。
## Big Endian && Little Endian [字节序 Wiki](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%AD%97%E8%8A%82%E5%BA%8F) ### Big Endian 大端序:最高位字节存储在最低的内存地址处。
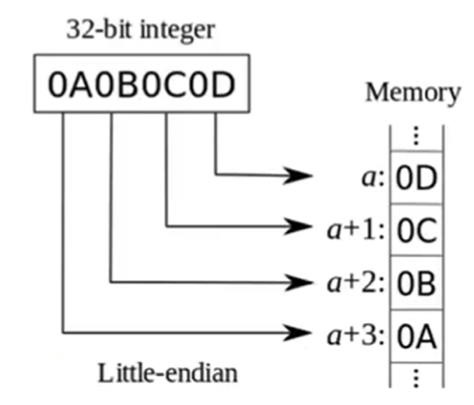
 ### Little Endian 最低位字节存储在最低的内存地址处。
### Little Endian 最低位字节存储在最低的内存地址处。
 ### 常见误区 1.字节序仅适用于那些占有多个字节的值,对于 char c = 97,c == 0b01100001 在大端序和小端序中存储是一样的。 2.寄存器没有任何字节顺序的概念 3.数组和指针的顺序依旧一样。 - int a\[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 假设地址为 0x40 - &(a\[0]) == 0x40 && a\[0] == 1 ## 动态内存分配 ### malloc 接受一个参数也就是连续内存块的字节大小,但是它是未初始化的,返回一个指向分配开始的指针。如果分配失败了返回 NULL。 malloc 一般返回 void \*,所以我们要进行类型转换。 ```c int *p = (int *) malloc(n * sizeof(int)); ``` ### free 释放内存,需要传入一个指向分配的块头部的指针。 ### calloc 用于 heap allocation。 他可以将数组中的每个单个条目初始化为 0。 ```c /* void *calloc(size_t nmemb, size_t size); */
### 常见误区 1.字节序仅适用于那些占有多个字节的值,对于 char c = 97,c == 0b01100001 在大端序和小端序中存储是一样的。 2.寄存器没有任何字节顺序的概念 3.数组和指针的顺序依旧一样。 - int a\[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 假设地址为 0x40 - &(a\[0]) == 0x40 && a\[0] == 1 ## 动态内存分配 ### malloc 接受一个参数也就是连续内存块的字节大小,但是它是未初始化的,返回一个指向分配开始的指针。如果分配失败了返回 NULL。 malloc 一般返回 void \*,所以我们要进行类型转换。 ```c int *p = (int *) malloc(n * sizeof(int)); ``` ### free 释放内存,需要传入一个指向分配的块头部的指针。 ### calloc 用于 heap allocation。 他可以将数组中的每个单个条目初始化为 0。 ```c /* void *calloc(size_t nmemb, size_t size); */
int *p = (int *)calloc(5, sizeof(int));
### 常见的内存错误
[What does the "bus error" message mean, and how does it differ from a segmentation fault?](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/212466/what-is-a-bus-error-is-it-different-from-a-segmentation-fault)
#### Segmentation Fault
尝试访问不允许的内存,比如内存访问越界、非法指针使用等。
#### Bus Error
当处理器无法尝试请求的内存访问,例如使用地址不满足对齐要求的处理器指令。
#### 使用未初始化的值
```c
void foo(int *p) {int j; /* 未初始化,是 garbage */*p = j;
}void bar() {int i = 10;foo(&i);printf("i = %d\n", i); /* i 现在包含 garbage */
}
使用不知道的内存
Using Memory You Don’t Own(1)
如果 head 为 NULL,则会引发 Seg Fault
typedef struct node {struct node* next;int val;
}Node;int findLastNodeValue(Node* head) {/* head 可能为 NULL */while(head->next != NULL) {head = head->next;}return ...
}
Using Memory You Don’t Own(2)
以下代码的问题在于该函数返回指向 result 的指针,而 result 是局部变量,在栈区创立,函数返回后该内存空间会被释放。这个指针也就指向了未知的东西。
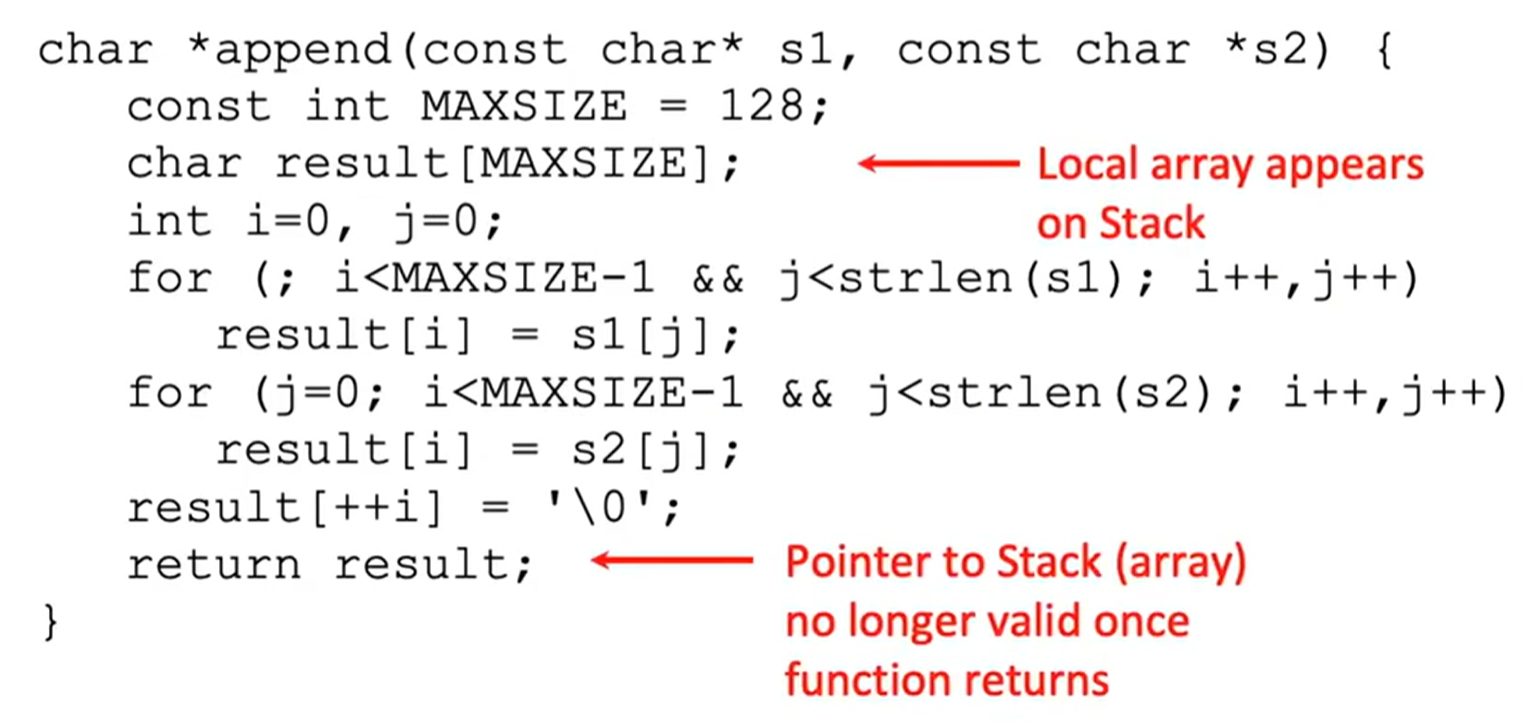
解决方法:使用动态内存分配,用 malloc 在堆上分配内存,这样即便函数返回,内存也仍然有效。
char *append(const char* s1, const char* s2) { const int MAXSIZE = 128; char* result = (char*)malloc(MAXSIZE * sizeof(char)); // 动态分配内存 if (result == NULL) { return NULL; // 检查内存分配是否成功 }...
Using Memory You Don’t Own(3)
strlen() 函数不会算上结尾的 ‘0’。

同时也要避免双重释放,比如
free(person);
free(person->name);
Using Memory You Haven’t Allocated

实际上这被称为 BUFFER OVERRUN or BUFFER OVERFLOW。
安全的版本:
#define ARR_LEN 1024
char buffer[ARR_LEN];int foo(char *str) {strncpy(buffer, str, ARR_LEN);
}
Memory Leaks

pi 是全局变量,所以 foo() 中的 pi 覆盖了 main 函数中,main() 函数内的指针就无法被释放。
创建 Linked List
struct Node {char *value; /* 字符串 */struct Node *next; /* 指向下一个节点的指针 */
} node;
Adding a Node to the List
s1 -> s2 -> s3 -> NULL
char *s1 = "start", *s2 = "middle", *s3 = "end";
struct node *theList = NULL;
theList = addNode(s3, theList);
theList = addNode(s2, theList);
theList = addNode(s1, theList);
这些字符串实际上存储在静态区。
node *addNode(char *s, node *list) {node *new = (node *) malloc(sizeof(NodeStuct));new->value = (char *) malloc(strlen(s) + 1); /* '\0' 的存在 */strcpy(new->value, s);new->next = list;return new;
}
Removing a Node from the List
Delete/free the first node
node *deleteNode(node *list) {node *temp = list->next;free(list->value);free(list);return temp;
}
这篇关于cs61C | lecture4的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!