本文主要是介绍音视频开发19 FFmpeg 视频解码- 将 h264 转化成 yuv,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
视频解码过程

FFmpeg流程
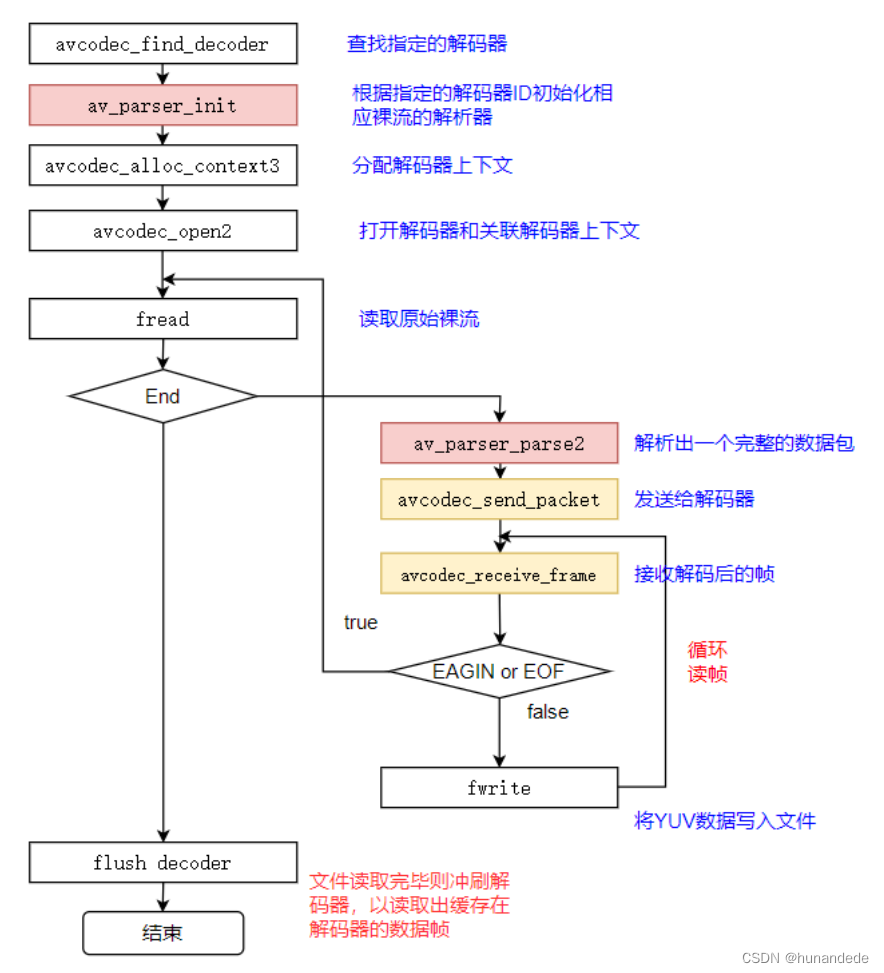
这里的流程是和音频的解码过程一样的,不同的只有在存储YUV数据的时候的形式
存储YUV 数据
如果知道YUV 数据的格式
前提:这里我们打开的h264文件,默认是YUV420P 格式的,
我们可以通过 AVFrame->frame 获得,获得的值如果是视频就 是 AVPixelFormat。
我们可以通过 AVPixelFormat ,知道该视频的编码是啥?
在正常情况下,我们需要判断AVPixelFormat是那种类型,当前代码中并没有判断是因为我们默认使用的YUV420P,那么怎么存储这个YUV420P呢?
首先我们这里要明白,一个AVFrame就是一张图片,假设AVframe 我们存储的是322 * 356 ,322并不是16的整倍数,322/16 = 20......2 也就是说一行会有2个字节的剩余
那么这个剩余的2个字节,怎么办呢?会多给14个字节和剩余的2个字节 结合起来。
因此如果我们用和音频类似的写法: fwrite(frame->data[0], 1, frame->width * frame->height, outfile) 去写,就会有问题,因为要保证这里 width是16的整倍数
这时候就要用到 ffmpeg 的AVFrame给我们提供的 linesize[x]了,
核心代码
// 一般H264默认为 AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, 具体怎么强制转为 AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P 在音视频合成输出的时候讲解// frame->linesize[1] 因为有字节对齐的问题。// 这里先回顾一下 音频的处理方式,在交错模式的时候,使用的 声道数*每个声道有多少个音频样本 * 每个样本占用多少个字节,这是因为音频上 没有字节对齐的问题//字节对齐问题的根本是因为 ,对于一张 322 * 356 的图片来说 ,322并不是16的整倍数,322/16 = 20......2 也就是说一行会有2个字节的剩余//那么这个剩余的2个字节,怎么办呢?会多给14个字节和剩余的2个字节 结合起来。//因此如果我们用和音频类似的写法: fwrite(frame->data[0], 1, frame->width * frame->height, outfile) 去写,就会有问题,因为要保证这里 width是16的整倍数//这时候就要用到 ffmpeg 的AVFrame给我们提供的 linesize[x]了,// uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:
// 指向实际的帧数据的指针数组。
// 对于视频帧,这通常是图像平面(如YUV中的Y、U、V平面)。
// 对于音频帧,这通常是音频通道的数据指针。// int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:
// 每一行(视频)或每一个音频通道(音频)的大小。
// 对于视频,这通常是图像宽度的字节数。如果图像的宽度 除以 16 有余数,则这个值会凑成16的倍数。
// 对于音频,这通常是这个通道的字节数大小。 在交错模式下: 理论上等于 声道数 * 每个声道有多少个音频样本 * 每个样本占用多少个字节
// 但是,测试发现,在第一个AVFrame包和最后一个 AVframe的时候,linesize[0]的值 比 声道数 * 每个声道有多少个音频样本 * 每个样本占用多少个字节 大于64.//了解了linesize[]的意义,对于一个avframe,就是包含了一帧,就是一张图片,//YUV420P的存储方式是这样的 YYYYYYYYUUVV
// 那么对于 一张 YUV420P (322 * 120)的图片来看,有多少个Y 呢?多少个U,多少个V呢?
// Y的个数为:有 120行,一行一行的存储,每一行的实际大小为322, 但是存储322个Y后,就结束了吗?没有 ,因为有字节对齐问题,因此每次存储完322后,还要跳过14个字节,也就是实际大小为linesize[0],//我们先将Y全部存储完毕。//再存储U,U的个数是多少呢?这里要回头看一下YUV420P存储结构图,这里只是结论:宽高均是Y的一半,因此这里要注意存储U的写法//V的存储和U是一样的。// 正确写法 linesize[]代表每行的字节数量,所以每行的偏移是linesize[],但是真正存储的值 Y 是宽度,for(int j=0; j<frame->height; j++)fwrite(frame->data[0] + j * frame->linesize[0], 1, frame->width, outfile);for(int j=0; j<frame->height/2; j++)fwrite(frame->data[1] + j * frame->linesize[1], 1, frame->width/2, outfile);for(int j=0; j<frame->height/2; j++)fwrite(frame->data[2] + j * frame->linesize[2], 1, frame->width/2, outfile);// 错误写法 用source.200kbps.766x322_10s.h264测试时可以看出该种方法是错误的// 写入y分量
// fwrite(frame->data[0], 1, frame->width * frame->height, outfile);//Y
// // 写入u分量
// fwrite(frame->data[1], 1, (frame->width) *(frame->height)/4,outfile);//U:宽高均是Y的一半
// // 写入v分量
// fwrite(frame->data[2], 1, (frame->width) *(frame->height)/4,outfile);//V:宽高均是Y的一半AVCodecParser说明
avcodec_send_packet
avcodec_receive_frame
所有的代码
/**
* @projectName 07-05-decode_audio
* @brief 解码音频,主要的测试格式aac和mp3
* @author Liao Qingfu
* @date 2020-01-16
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>#include <libavutil/frame.h>
#include <libavutil/mem.h>#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>#define VIDEO_INBUF_SIZE 20480
#define VIDEO_REFILL_THRESH 4096static char err_buf[128] = {0};
static char* av_get_err(int errnum)
{av_strerror(errnum, err_buf, 128);return err_buf;
}static void print_video_format(const AVFrame *frame)
{printf("width: %u\n", frame->width);printf("height: %u\n", frame->height);printf("format: %u\n", frame->format);// 格式需要注意
}static void decode(AVCodecContext *dec_ctx, AVPacket *pkt, AVFrame *frame,FILE *outfile)
{int ret;/* send the packet with the compressed data to the decoder */ret = avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, pkt);if(ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN)){fprintf(stderr, "Receive_frame and send_packet both returned EAGAIN, which is an API violation.\n");}else if (ret < 0){fprintf(stderr, "Error submitting the packet to the decoder, err:%s, pkt_size:%d\n",av_get_err(ret), pkt->size);return;}/* read all the output frames (infile general there may be any number of them */while (ret >= 0){// 对于frame, avcodec_receive_frame内部每次都先调用ret = avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, frame);if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)return;else if (ret < 0){fprintf(stderr, "Error during decoding\n");exit(1);}static int s_print_format = 0;if(s_print_format == 0){s_print_format = 1;print_video_format(frame);}printf("video frame data = %f \n", (frame->width) * (frame->height) * 1.5);printf("frame->line[0] = %d \n",frame->linesize[0]);printf("frame->line[1] = %d \n",frame->linesize[1]);printf("frame->line[2] = %d \n",frame->linesize[2]);printf("frame->pkt_size = %d \n",frame->pkt_size);// 一般H264默认为 AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, 具体怎么强制转为 AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P 在音视频合成输出的时候讲解// frame->linesize[1] 因为有字节对齐的问题。// 这里先回顾一下 音频的处理方式,在交错模式的时候,使用的 声道数*每个声道有多少个音频样本 * 每个样本占用多少个字节,这是因为音频上 没有字节对齐的问题//字节对齐问题的根本是因为 ,对于一张 322 * 356 的图片来说 ,322并不是16的整倍数,322/16 = 20......2 也就是说一行会有2个字节的剩余//那么这个剩余的2个字节,怎么办呢?会多给14个字节和剩余的2个字节 结合起来。//因此如果我们用和音频类似的写法: fwrite(frame->data[0], 1, frame->width * frame->height, outfile) 去写,就会有问题,因为要保证这里 width是16的整倍数//这时候就要用到 ffmpeg 的AVFrame给我们提供的 linesize[x]了,// uint8_t *data[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:
// 指向实际的帧数据的指针数组。
// 对于视频帧,这通常是图像平面(如YUV中的Y、U、V平面)。
// 对于音频帧,这通常是音频通道的数据指针。// int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS]:
// 每一行(视频)或每一个音频通道(音频)的大小。
// 对于视频,这通常是图像宽度的字节数。如果图像的宽度 除以 16 有余数,则这个值会凑成16的倍数。
// 对于音频,这通常是这个通道的字节数大小。 在交错模式下: 理论上等于 声道数 * 每个声道有多少个音频样本 * 每个样本占用多少个字节
// 但是,测试发现,在第一个AVFrame包和最后一个 AVframe的时候,linesize[0]的值 比 声道数 * 每个声道有多少个音频样本 * 每个样本占用多少个字节 大于64.//了解了linesize[]的意义,对于一个avframe,就是包含了一帧,就是一张图片,//YUV420P的存储方式是这样的 YYYYYYYYUUVV
// 那么对于 一张 YUV420P (322 * 120)的图片来看,有多少个Y 呢?多少个U,多少个V呢?
// Y的个数为:有 120行,一行一行的存储,每一行的实际大小为322, 但是存储322个Y后,就结束了吗?没有 ,因为有字节对齐问题,因此每次存储完322后,还要跳过14个字节,也就是实际大小为linesize[0],//我们先将Y全部存储完毕。//再存储U,U的个数是多少呢?这里要回头看一下YUV420P存储结构图,这里只是结论:宽高均是Y的一半,因此这里要注意存储U的写法//V的存储和U是一样的。// 正确写法 linesize[]代表每行的字节数量,所以每行的偏移是linesize[],但是真正存储的值 Y 是宽度,for(int j=0; j<frame->height; j++)fwrite(frame->data[0] + j * frame->linesize[0], 1, frame->width, outfile);for(int j=0; j<frame->height/2; j++)fwrite(frame->data[1] + j * frame->linesize[1], 1, frame->width/2, outfile);for(int j=0; j<frame->height/2; j++)fwrite(frame->data[2] + j * frame->linesize[2], 1, frame->width/2, outfile);// 错误写法 用source.200kbps.766x322_10s.h264测试时可以看出该种方法是错误的// 写入y分量
// fwrite(frame->data[0], 1, frame->width * frame->height, outfile);//Y
// // 写入u分量
// fwrite(frame->data[1], 1, (frame->width) *(frame->height)/4,outfile);//U:宽高均是Y的一半
// // 写入v分量
// fwrite(frame->data[2], 1, (frame->width) *(frame->height)/4,outfile);//V:宽高均是Y的一半}
}
// 注册测试的时候不同分辨率的问题
// 提取H264: ffmpeg -i source.200kbps.768x320_10s.flv -vcodec libx264 -an -f h264 source.200kbps.768x320_10s.h264
// 提取MPEG2: ffmpeg -i source.200kbps.768x320_10s.flv -vcodec mpeg2video -an -f mpeg2video source.200kbps.768x320_10s.mpeg2
// 播放:ffplay -pixel_format yuv420p -video_size 768x320 -framerate 25 source.200kbps.768x320_10s.yuv
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{const char *outfilename;const char *filename;const AVCodec *codec;AVCodecContext *codec_ctx= NULL;AVCodecParserContext *parser = NULL;int len = 0;int ret = 0;FILE *infile = NULL;FILE *outfile = NULL;// AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE 在输入比特流结尾的要求附加分配字节的数量上进行解码uint8_t inbuf[VIDEO_INBUF_SIZE + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE];uint8_t *data = NULL;size_t data_size = 0;AVPacket *pkt = NULL;AVFrame *decoded_frame = NULL;// if (argc <= 2)
// {
// fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <input file> <output file>\n", argv[0]);
// exit(0);
// }
// filename = argv[1];
// outfilename = argv[2];filename = "D:/AllInformation/qtworkspacenew/07-06-decode_video/source.200kbps.768x320_10s.h264";outfilename = "D:/AllInformation/qtworkspacenew/07-06-decode_video/source.200kbps.768x320_10s.yuv";//我们这里 768x320_10s 是使用的 YUV420p格式,那么一张图片的大小应该为 768*320*1.5 = 368640 bit = 46080 bytes = 45 kb//我们这里计算这个,就是为了查看是否 avframe 的大小.log如下,因为768除以16是没有余数的,因此这里没有字节对齐问题,
// video frame data = 368640.000000
// frame->line[0] = 768
// frame->line[1] = 384
// frame->line[2] = 384// filename = "D:/AllInformation/qtworkspacenew/07-06-decode_video/source.200kbps.766x322_10s.h264";
// outfilename = "D:/AllInformation/qtworkspacenew/07-06-decode_video/source.200kbps.766x322_10s.yuv";//我们这里 766x322_10s 是使用的 YUV420p格式,那么一张图片的大小应该为 766*322*1.5 = 369,978 bit = 46247.25 bytes 约等于 45.16 kb//我们这里计算这个,就是为了查看是否 avframe 的大小 。log如下,说明在766除以16有余数的case下,是有字节对齐的问题存在的,因此在存储这个文件的pcm时候,要注意使用到 linesize[x]// video frame data = 369978.000000
// frame->line[0] = 768
// frame->line[1] = 384
// frame->line[2] = 384printf("aaa\n");pkt = av_packet_alloc();enum AVCodecID video_codec_id = AV_CODEC_ID_H264;if(strstr(filename, "264") != NULL){video_codec_id = AV_CODEC_ID_H264;}else if(strstr(filename, "mpeg2") != NULL){video_codec_id = AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO;}else{printf("default codec id:%d\n", video_codec_id);}// 查找解码器codec = avcodec_find_decoder(video_codec_id); // AV_CODEC_ID_H264if (!codec) {fprintf(stderr, "Codec not found\n");exit(1);}// 获取裸流的解析器 AVCodecParserContext(数据) + AVCodecParser(方法)parser = av_parser_init(codec->id);if (!parser) {fprintf(stderr, "Parser not found\n");exit(1);}// 分配codec上下文codec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);if (!codec_ctx) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate audio codec context\n");exit(1);}// 将解码器和解码器上下文进行关联if (avcodec_open2(codec_ctx, codec, NULL) < 0) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not open codec\n");exit(1);}// 打开输入文件infile = fopen(filename, "rb");if (!infile) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not open %s\n", filename);exit(1);}// 打开输出文件outfile = fopen(outfilename, "wb");if (!outfile) {av_free(codec_ctx);exit(1);}// 读取文件进行解码data = inbuf;data_size = fread(inbuf, 1, VIDEO_INBUF_SIZE, infile);while (data_size > 0){if (!decoded_frame){if (!(decoded_frame = av_frame_alloc())){fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate audio frame\n");exit(1);}}ret = av_parser_parse2(parser, codec_ctx, &pkt->data, &pkt->size,data, data_size,AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE, 0);if (ret < 0){fprintf(stderr, "Error while parsing\n");exit(1);}data += ret; // 跳过已经解析的数据data_size -= ret; // 对应的缓存大小也做相应减小if (pkt->size)decode(codec_ctx, pkt, decoded_frame, outfile);if (data_size < VIDEO_REFILL_THRESH) // 如果数据少了则再次读取{memmove(inbuf, data, data_size); // 把之前剩的数据拷贝到buffer的起始位置data = inbuf;// 读取数据 长度: VIDEO_INBUF_SIZE - data_sizelen = fread(data + data_size, 1, VIDEO_INBUF_SIZE - data_size, infile);if (len > 0)data_size += len;}}/* 冲刷解码器 */pkt->data = NULL; // 让其进入drain modepkt->size = 0;decode(codec_ctx, pkt, decoded_frame, outfile);fclose(outfile);fclose(infile);avcodec_free_context(&codec_ctx);av_parser_close(parser);av_frame_free(&decoded_frame);av_packet_free(&pkt);printf("main finish, please enter Enter and exit\n");return 0;
}
播放测试:
ffplay -pixel_format yuv420p -video_size 768x320 -framerate 25
source.200kbps.768x320_10s.yuv分离H264或mpeg2video视频格式数据
提取H264:
提取MPEG2:
FFmpeg命令查找-f 后面的格式
这篇关于音视频开发19 FFmpeg 视频解码- 将 h264 转化成 yuv的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






