本文主要是介绍【经典排序算法】堆排序(精简版),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
什么是堆排序:
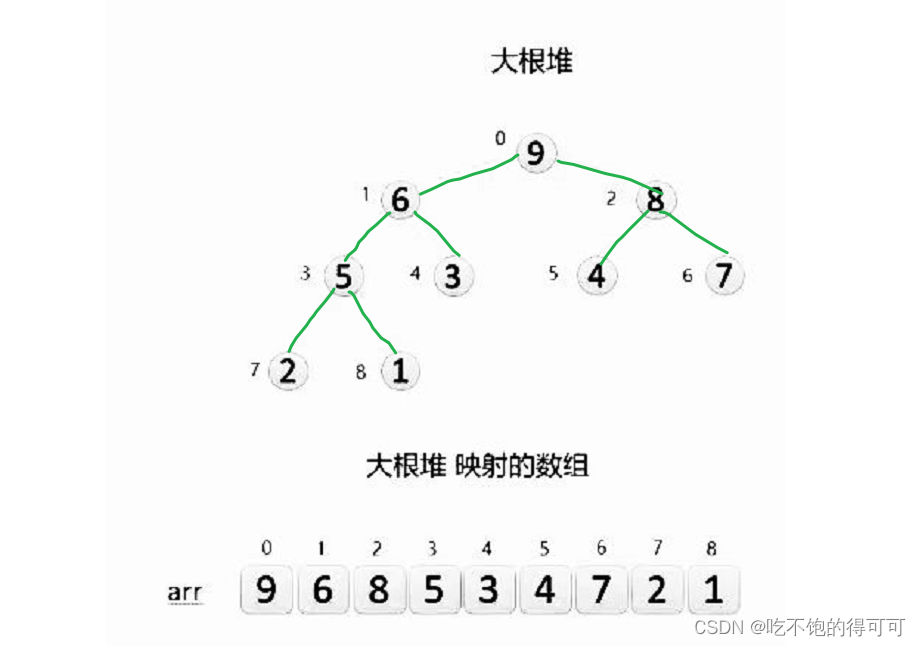
在我看来,堆排序中最重要的是向上调整和向下调整算法。
堆排序是基于这两个算法来进行的。
向上调整算法:
目的:
当向堆中插入新元素时,为了维护堆的性质,需要对该元素进行向上调整。向上调整法就是从新插入的节点开始,通过与其父节点的比较和交换,确保该节点的值不大于(对于大根堆)或不小于(对于小根堆)其父节点的值。
//以大堆为例
void Adjustup(int* a, int child)
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){if (a[child] > a[parent])swap(a[child], a[parent]);elsebreak;child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}
}向下调整算法:
目的:
当向堆中插入新元素时,为了维护堆的性质,需要对该元素进行向上调整。向上调整法就是从新插入的节点开始,通过与其父节点的比较和交换,确保该节点的值不大于(对于大根堆)或不小于(对于小根堆)其父节点的值。
//向下调整算法
//大堆为例
void Adjustdown(int* a, int parent, int n)//n是数组a的元素个数
{int child = 2 * parent + 1;while (child < n){if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1]){++child;}if (a[child] > a[parent]){swap(a[child], a[parent]);}elsebreak;parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}
}需要注意的是对堆进行向上向下调整算法是要确保堆左子树和右子树是大堆/小堆。
下面我们来实现一下堆排序的完整代码:
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{int tmp = *x;*x = *y;*y = tmp;
}
//以大堆为例
void Adjustup(int* a, int child)
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){if (a[child] > a[parent])swap(a[child], a[parent]);elsebreak;child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}
}
//向下调整算法
//大堆为例
void Adjustdown(int* a, int parent, int n)//n是数组a的元素个数
{int child = 2 * parent + 1;while (child < n){if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1]){++child;}if (a[child] > a[parent]){swap(a[child], a[parent]);}elsebreak;parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}
}
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
{//首先利用向上调整算法建一个大堆(即父节点>=子节点的完全二叉树二叉树)for (int i = 1;i < n;i++){Adjustup(a, i);}int end = n - 1;while (end > 0){swap(a[0], a[end]);Adjustdown(a, 0, end);--end;}
}上述堆排序代码是针对数组升序编写的,这里就不写降序的代码了,降序的堆排序和升序的如出一辙。
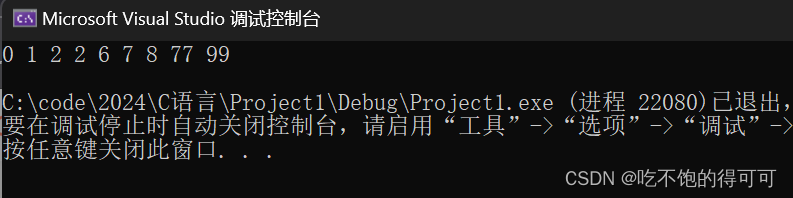
试验结果如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{int arr[] = { 77,99,2,1,2,8,6,7,0 };HeapSort(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));for (auto e : arr){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
这篇关于【经典排序算法】堆排序(精简版)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






