本文主要是介绍C++笔记:Hash Function 散列函数,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1. Hash Function 散列函数
- 简单的Hash实现:
class CustomerHash {
public:size_t operator()(const Customer& c) const {return hash<std::string>()(c.fname) + // first namehash<std::string>()(c.lname) + // last namehash<long>()(c.no);// 返回hash_code}
};
-
针对
Customer类对象,直接对其各个成员变量分别调用标准库中的hash函数,并将得到的哈希值相加。 -
虽然简单,但这种实现方式可能会导致哈希冲突(即不同对象可能产生相同的哈希值)。
-
改进的Hash实现:
class CustomerHash {
public:size_t operator()(const Customer& c) const {return hash_val(c.frame, c.lname, c.no);}
};
template <typename... Type>
inline size_t hash_val(const Type&... args){size_t seed = 0;hash_val(seed, args...);return seed; //seed最终就被视为hash code
}
- 顶层主函数:初始化
seed为0,调用hash_val递归处理所有参数,并返回最终的哈希值。
template <typename T, typename... Types>
inline void hash_val(size_t& seed, const T& val, const Type&... args){hash_combine(seed, val);hash_val(seed, args);
};
- 这是一个递归函数模板,它处理一个或多个参数:
- 首先,调用
hash_combine函数处理当前参数val并更新seed。 - 然后,递归调用自身处理剩余的参数。
- 首先,调用
template <typename T>
inline void hash_val(size_t& seed, const T& val){hash_combine(seed, val);
}
- 这是上面递归函数的终止版本,当没有更多参数时,只处理最后一个参数。
#include<functional>
template <typename T>
inline void hash_combine(size_t& seed, const T& val){seed ^= hash<T>()(val) + 0x9e3779b9 + (seed<<6) + (seed<<2);
}
-
结合当前的哈希值和传入的值来更新
seed,使用了一些常见的哈希组合技巧(例如魔数0x9e3779b9),以减少冲突。 -
以struct hash 偏特化的形式实现Hash function
- 在
std命名空间中特化hash结构体以支持MyString类型
- 在
namespace std {template<>struct hash<MyString> {size_t operator()(const MyString& s) const noexcept {return hash<string>()(s.get());}};
}
2. tuple
- 构造方式:
// 构造方式1
tuple<int, float, string> t1(41, 6.3, "nico");
cout << "t1: " << get<0>(t1) << " " << get<1>(t1) << " " << get<2>(t1) << endl;// 构造方式2
auto t2 = make_tuple(22, 44, "stacy");// 构造方式3
tuple<int,float,string> t3(77, 1.1, "more light");
int i1;
float f1;
stting s1;
tie(i1, f1, s1) = t3;
- 用例:
tuple<int, float, string> t(41, 6.3, "nico"); // 调用了构造函数
t.head() // 调用了head()函数,返回 41
t.tail() // 调用了tail()函数,返回 tuple<float, string>
t.tail().head() // 调用了tail()然后是head()函数,返回 6.3
t.tail().tail().head() // 调用了两次tail()然后是head()函数,返回 "nico"
&(t.tail()) // 调用了tail()函数,返回 tuple<float, string> 的引用
- 源码:
// 这是一个变长模板声明,表示tuple类可以接受任意数量和类型的模板参数
template<typename... Values> class tuple;
template<> class tuple<> {};
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
class tuple<Head, Tail...> : public tuple<Tail...>
{typedef tuple<Tail...> inherited;
public:tuple() {};tuple(Head v, Tail... vtail) : m_head(v), inheriter(vtail...) {}typename Head::type head() { return m_head;}inherited& tail { return *this;}
protected:Head m_head;
};
tuple<Head, Tail...>递归地继承了tuple<Tail...>,即剩下的参数组成的元组。tuple<int, float, string> : private tuple<float, string>tuple<float, string> : private tuple<string>tuple<string>
- 在
t.tail()中,调用tail()函数,tail()返回*this。此时,*this指向的对象类型是tuple<int, float, string>,但通过类型转换返回为inherited&,即tuple<float, string>&。 t.tail()会返回一个tuple<float, string>&(t.tail())会返回一个tuple<float, string>的引用
3. type traits
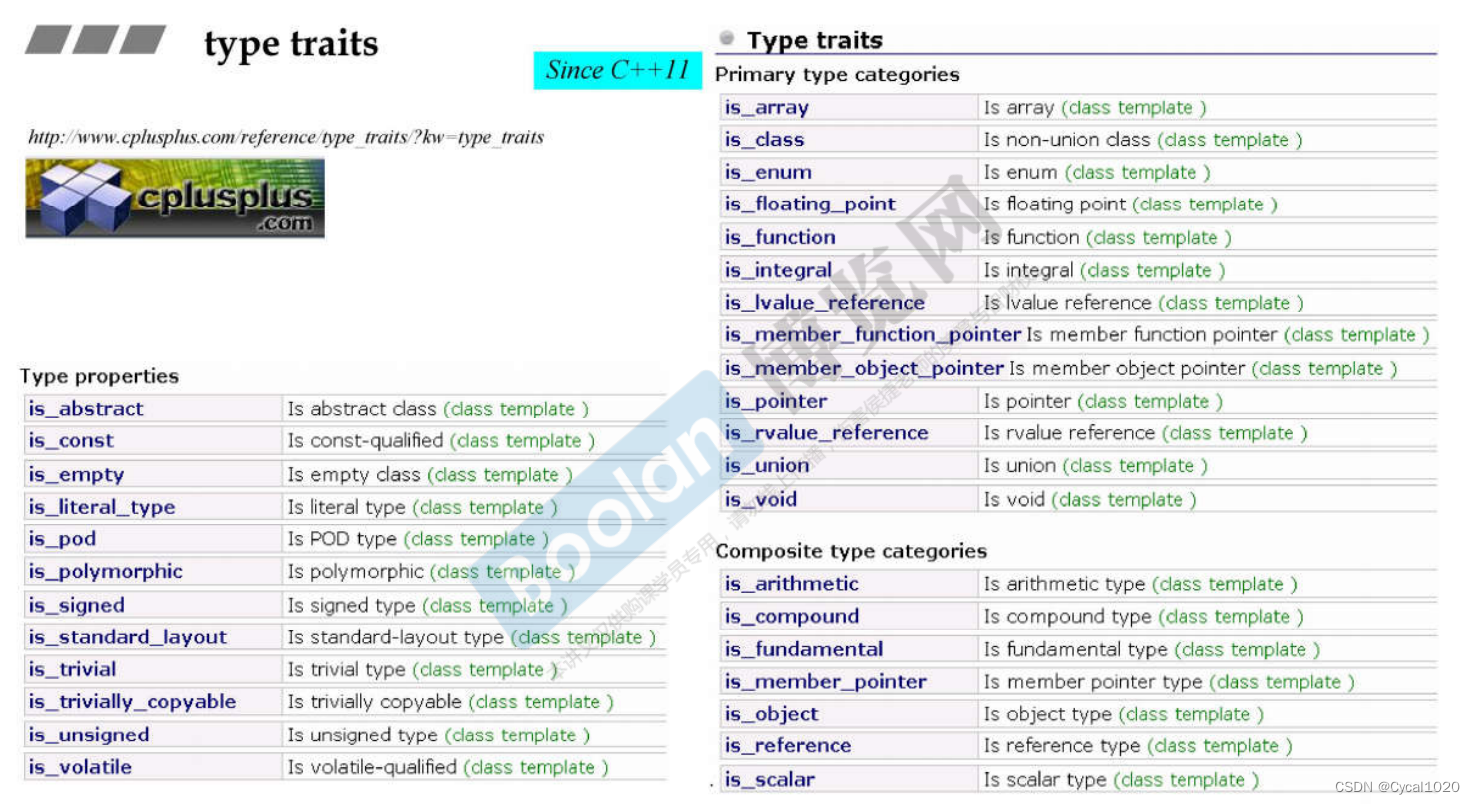

应用:
template <typename T>
void type_traits_output(const T&x)
{cout << "\\n type traits for type:" << typeid(T).name() << endl;cout << "is_void\\t" << is_void<T>::value << endl; // 0 or 1cout << "is_integral\\t" << is_integral<T>::value << endl; // 0 or 1...
}int i = 0;
double d = 0.0;
type_traits_output(i);
type_traits_output(d);
4. type traits中is_void的实现
为什么判断void时需要移除volatile和const限定符?
假设你有一个类型是
const void或volatile void,这些类型本质上还是void类型,只是加了限定符。如果不去除这些限定符,直接判断类型是否为void,判断结果将会是错误的,因为const void和void在严格意义上是不同的类型。通过移除这些限定符,可以确保我们判断的基础类型是
void,而不是const void或volatile void。这确保了类型特性模板的准确性和一致性。
- 移除
volatile限定符:
// 如果类型不带volatile限定符,通用模板直接定义type为原始类型_Tp
template<typename _Tp>
struct remove_volatile {typedef _Tp type;
};// 如果类型带有volatile限定符,特化模板定义会去掉volatile限定符
template<typename _Tp>
struct remove_volatile<_Tp volatile> {typedef _Tp type;
};- 移除
const限定符:
template<typename _Tp>
struct remove_const {typedef _Tp type;
};template<typename _Tp>
struct remove_const<_Tp const> {typedef _Tp type;
};
- 移除
const和volatile限定符:
template<typename _Tp>
struct remove_cv {typedef typename remove_const<typename remove_volatile<_Tp>::type>::type type;
};
- 判断是否为
void类型:
template<typename>
struct __is_void_helper : public false_type {};template<>
struct __is_void_helper<void> : public true_type {};
- 最终的
is_void实现:
template<typename _Tp>
struct is_void : public __is_void_helper<typename remove_cv<_Tp>::type> {};
5. cout 标准输出流
ostream类是标准C++库中的输出流类,定义在<ostream>头文件中。这个类提供了多种运算符重载,以便将不同类型的数据输出到流中。
ostream& operator<<(char c) {// 输出一个字符return *this;
}ostream& operator<<(unsigned char c) {// 输出一个无符号字符return *this << static_cast<char>(c);
}ostream& operator<<(signed char c) {// 输出一个有符号字符return *this << static_cast<char>(c);
}ostream& operator<<(const char* s) {// 输出一个C风格字符串return *this;
}ostream& operator<<(const unsigned char* s) {// 输出一个无符号字符指针,转换为C风格字符串return *this << reinterpret_cast<const char*>(s);
}ostream& operator<<(const signed char* s) {// 输出一个有符号字符指针,转换为C风格字符串return *this << reinterpret_cast<const char*>(s);
}ostream& operator<<(const void* p) {// 输出一个指针return *this;
}ostream& operator<<(int n) {// 输出一个整数return *this;
}ostream& operator<<(unsigned int n) {// 输出一个无符号整数return *this;
}ostream& operator<<(long n) {// 输出一个长整数return *this;
}ostream& operator<<(unsigned long n) {// 输出一个无符号长整数return *this;
}
cout是一个全局的_IO_ostream_withassign对象,表示标准输出流。其继承自ostream,并提供赋值运算符的重载。
class _IO_ostream_withassign : public ostream {
public:_IO_ostream_withassign& operator=(ostream& os) {// 实现赋值操作// 允许将一个ostream对象赋值给_IO_ostream_withassign对象return *this;}_IO_ostream_withassign& operator=(_IO_ostream_withassign& rhs) {// 实现赋值操作return operator=(static_cast<ostream&>(rhs));}
};extern _IO_ostream_withassign cout;
6.moveable元素对于vector速度效能的影响
-
深拷贝:创建一个新对象,并复制所有的原始对象的数据,包括指向动态分配内存的指针。深拷贝确保新对象和原始对象独立,修改一个不会影响另一个。
// 拷贝构造函数 MyString(const MyString& other) {len = other.len;data = new char[len + 1]; // 为新对象开辟内存strcpy(data, other.data); // 将原对象的数据复制到新对象 }// 拷贝赋值运算符 MyString& operator=(const MyString& str) {if (this != &str) {if (_data) delete[] _data;_len = str._len;_init_data(str._data); // 复制数据}return *this; } -
浅拷贝:只复制对象的成员变量的值,包括指针的值。这意味着复制后的对象和原始对象共享同一块动态分配的内存。这可能会造成一个对象销毁时释放了共享的内存时,导致另一个对象访问无效内存。
MyString(const Mystring& other) {len = other.len;data = other.data; } -
移动语义(Move Semantics):通过转移指针操作将资源从一个对象转移到另一个对象,避免深拷贝。通过移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符实现。
#include <utility> class MyString { public:// 移动构造函数// data = other.data; 新对象直接使用原对象的指针。MyString(MyString&& other) noexcept: data(other.data), len(other.len) {other.data = nullptr; // 将原对象的指针设置为nullptr,防止原对象析构时释放内存other.len = 0;}// 移动赋值运算符MyString& operator=(MyString&& other) noexcept {if (this == &other) return *this;delete[] data;data = other.data;len = other.len;other.data = nullptr;other.len = 0;return *this;}// 析构函数~MyString() {++Dtor;if (_data) delete[] _data;}// 禁用拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值运算符MyString(const MyString& other) = delete;MyString& operator=(const MyString& other) = delete; -
具体示例
int main() {Mystring str1("Hello, world!");// 调用拷贝构造函数Mystring str2 = str1;cout << str2 << endl; // "Hello, world!"// 调用移动构造函数Mystring str3 = move(str1);cout << str3 << endl; // "Hello, world!"cout << str1 << endl; // 空,因为str1的资源已经转移
这篇关于C++笔记:Hash Function 散列函数的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



