本文主要是介绍OGG几何内核-BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge学习,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
OGG几何内核fork自OCCT 7.7.0,
BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge是几何内核的一个重要和基础的功能,也十分复杂,因为要支持line、circle、ellipse,parabola,hyperbola,circle,beziercurve,bsplinecurve。需要支持多种参数情况:
1、曲线。
2、曲线+始终长度。
3、曲线+始终角度。
4、曲线+两点。
5、曲线+面。
代码注释如下:
Provides methods to build edges.
The methods have the following syntax, where TheCurve is one of Lin, Circ, ...
Create(C : TheCurve)
Makes an edge on the whole curve. Add vertices on finite curves.
Create(C : TheCurve; p1,p2 : Real)
Make an edge on the curve between parameters p1 and p2. if p2 < p1 the edge will be REVERSED. If p1 or p2 is infinite the curve will be open in that direction. Vertices are created for finite values of p1 and p2.
Create(C : TheCurve; P1, P2 : Pnt from gp)
Make an edge on the curve between the points P1 and P2. The points are projected on the curve and the previous method is used. An error is raised if the points are not on the curve.
Create(C : TheCurve; V1, V2 : Vertex from TopoDS)
Make an edge on the curve between the vertices V1 and V2. Same as the previous but no vertices are created. If a vertex is Null the curve will be open in this direction.
class BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge : public BRepBuilderAPI_MakeShape
{
public:DEFINE_STANDARD_ALLOCStandard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge();Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Lin& L);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Lin& L, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Lin& L, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Lin& L, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Circ& L);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Circ& L, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Circ& L, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Circ& L, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Elips& L);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Elips& L, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Elips& L, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Elips& L, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Hypr& L);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Hypr& L, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Hypr& L, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Hypr& L, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Parab& L);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Parab& L, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Parab& L, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const gp_Parab& L, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom_Curve)& L);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom_Curve)& L, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom_Curve)& L, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom_Curve)& L, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom_Curve)& L, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom_Curve)& L, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& L, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& L, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& L, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& L, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& L, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);//! The general method to directly create an edge is to give//! - a 3D curve C as the support (geometric domain) of the edge,//! - two vertices V1 and V2 to limit the curve (definition of the restriction of//! the edge), and//! - two real values p1 and p2 which are the parameters for the vertices V1 and V2//! on the curve.//! The curve may be defined as a 2d curve in the parametric space of a surface: a//! pcurve. The surface on which the edge is built is then kept at the level of the edge.//! The default tolerance will be associated with this edge.//! Rules applied to the arguments://! For the curve://! - The curve must not be a 'null handle'.//! - If the curve is a trimmed curve the basis curve is used.//! For the vertices://! - Vertices may be null shapes. When V1 or V2 is null the edge is open in the//! corresponding direction and the parameter value p1 or p2 must be infinite//! (remember that Precision::Infinite() defines an infinite value).//! - The two vertices must be identical if they have the same 3D location.//! Identical vertices are used in particular when the curve is closed.//! For the parameters://! - The parameters must be in the parametric range of the curve (or the basis//! curve if the curve is trimmed). If this condition is not satisfied the edge is not//! built, and the Error function will return BRepAPI_ParameterOutOfRange.//! - Parameter values must not be equal. If this condition is not satisfied (i.e.//! if | p1 - p2 | ) the edge is not built, and the Error function will return//! BRepAPI_LineThroughIdenticPoints.//! Parameter values are expected to be given in increasing order://! C->FirstParameter()//! - If the parameter values are given in decreasing order the vertices are switched,//! i.e. the "first vertex" is on the point of parameter p2 and the "second vertex" is//! on the point of parameter p1. In such a case, to keep the original intent of the//! construction, the edge will be oriented "reversed".//! - On a periodic curve the parameter values p1 and p2 are adjusted by adding or//! subtracting the period to obtain p1 in the parametric range of the curve, and p2]//! such that [ p1 , where Period is the period of the curve.//! - A parameter value may be infinite. The edge is open in the corresponding//! direction. However the corresponding vertex must be a null shape. If this condition//! is not satisfied the edge is not built, and the Error function will return//! BRepAPI_PointWithInfiniteParameter.//! - The distance between the vertex and the point evaluated on the curve with the//! parameter, must be lower than the precision of the vertex. If this condition is not//! satisfied the edge is not built, and the Error function will return//! BRepAPI_DifferentsPointAndParameter.//! Other edge constructions//! - The parameter values can be omitted, they will be computed by projecting the//! vertices on the curve. Note that projection is the only way to evaluate the//! parameter values of the vertices on the curve: vertices must be given on the curve,//! i.e. the distance from a vertex to the curve must be less than or equal to the//! precision of the vertex. If this condition is not satisfied the edge is not built,//! and the Error function will return BRepAPI_PointProjectionFailed.//! - 3D points can be given in place of vertices. Vertices will be created from the//! points (with the default topological precision Precision::Confusion()).//! Note://! - Giving vertices is useful when creating a connected edge.//! - If the parameter values correspond to the extremities of a closed curve,//! points must be identical, or at least coincident. If this condition is not//! satisfied the edge is not built, and the Error function will return//! BRepAPI_DifferentPointsOnClosedCurve.//! - The vertices or points can be omitted if the parameter values are given. The//! points will be computed from the parameters on the curve.//! The vertices or points and the parameter values can be omitted. The first and last//! parameters of the curve will then be used.//!//! Auxiliary methodsStandard_EXPORT BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& L, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom_Curve)& C);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom_Curve)& C, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom_Curve)& C, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom_Curve)& C, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom_Curve)& C, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom_Curve)& C, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& C, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& C, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& C, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& C, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2);Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& C, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const gp_Pnt& P1, const gp_Pnt& P2, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);//! Defines or redefines the arguments for the construction of an edge.//! This function is currently used after the empty constructor BRepAPI_MakeEdge().Standard_EXPORT void Init (const Handle(Geom2d_Curve)& C, const Handle(Geom_Surface)& S, const TopoDS_Vertex& V1, const TopoDS_Vertex& V2, const Standard_Real p1, const Standard_Real p2);protected:private:BRepLib_MakeEdge myMakeEdge;};从最后几行代码,结合可以发现,BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge是BRepLib_MakeEdge的包装,实际功能由BRepLib_MakeEdge实现。
为了能更深入理解BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge,可以研究分析一下测试命令mkedge的代码。
static Standard_Integer mkedge(Draw_Interpretor& di, Standard_Integer n, const char** a)
{if (n < 3) return 1;Handle(Geom_Curve) C = DrawTrSurf::GetCurve(a[2]);Handle(Geom2d_Curve) C2d = DrawTrSurf::GetCurve2d(a[2]);if (C.IsNull() && C2d.IsNull()) {//std::cout << a[2] << " is not a curve" << std::endl;di << a[2] << " is not a curve\n";return 1;}TopoDS_Edge edge;if (n == 3) {if (!C.IsNull()) edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(C);else edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge2d(C2d);}else {Handle(Geom_Surface) S;Standard_Integer i = 0;if (!C2d.IsNull()) {S = DrawTrSurf::GetSurface(a[3]);if (!S.IsNull()) i = 1;}TopoDS_Shape aLocalShape(DBRep::Get(a[3+i],TopAbs_VERTEX));TopoDS_Vertex V1 = TopoDS::Vertex(aLocalShape);
// TopoDS_Vertex V1 = TopoDS::Vertex(DBRep::Get(a[3+i],TopAbs_VERTEX));if (n == 5+i) {if (V1.IsNull()) {if (!C.IsNull()) edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(C,Draw::Atof(a[3]),Draw::Atof(a[4]));else if (S.IsNull()) edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge2d(C2d,Draw::Atof(a[3]),Draw::Atof(a[4]));elseedge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(C2d,S,Draw::Atof(a[4]),Draw::Atof(a[5]));}else {aLocalShape = DBRep::Get(a[4+i],TopAbs_VERTEX);TopoDS_Vertex V2 = TopoDS::Vertex(aLocalShape);
// TopoDS_Vertex V2 = TopoDS::Vertex(DBRep::Get(a[4+i],TopAbs_VERTEX));if (!C.IsNull()) edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(C,V1,V2);else if (S.IsNull()) edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge2d(C2d,V1,V2);elseedge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(C2d,S,V1,V2);}} else if (n == 7+i) {aLocalShape = DBRep::Get(a[5+i],TopAbs_VERTEX);TopoDS_Vertex V2 = TopoDS::Vertex(aLocalShape);
// TopoDS_Vertex V2 = TopoDS::Vertex(DBRep::Get(a[5+i],TopAbs_VERTEX));if (!C.IsNull()) edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(C,V1,V2,Draw::Atof(a[4]),Draw::Atof(a[6]));else if (S.IsNull()) edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge2d(C2d,V1,V2,Draw::Atof(a[4]),Draw::Atof(a[6]));else edge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(C2d,S,V1,V2,Draw::Atof(a[5]),Draw::Atof(a[7]));}elsereturn 1;}DBRep::Set(a[1],edge);return 0;
}以下是各种曲线生成及参数测试:
vertex a 0 0 0
vertex b 6 0 0
vertex c 6 1 0
vertex d 6 0 0
edge l a b
mkcurve curve1 l
mkedge l1 curve1 1 2
mkedge l2 curve1 a b
mkedge l3 curve1 a c
mkedge l4 curve1 a dcircle c 0 0 0 10
mkedge c1 c 0 pi/4
mkedge c1 c 0 pi/2
mkedge c1 c 0 pi
mkedge c1 c 0 2*pi
mkedge c1 c 0 2pi
mkedge c1 c -pi pi
mkedge c1 c -pi/2 0mkedge e1 a bparabola w1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 50
mkedge p1 w1 -100 100beziercurve w2 5 0 0 0 20 0 0 20 5 0 25 10 0 10 20 0
mkedge b1 w2
mkedge b1 w2 0 0.5
mkedge b1 w2 0 0.9
mkedge b1 w2 0 1
mkedge b1 w2 0 2bsplinecurve w3 3 2 -1.0 4 1.0 4 0 0 0 1 2 10 0 1 4 6 0 1 10 0 0 1
mkedge b2 w3
mkedge b2 w3 0 0.5通过这些测试命令,可以观察看到线的方向,以及OCCT对不同类型的线生成的edge的处理方式不同。
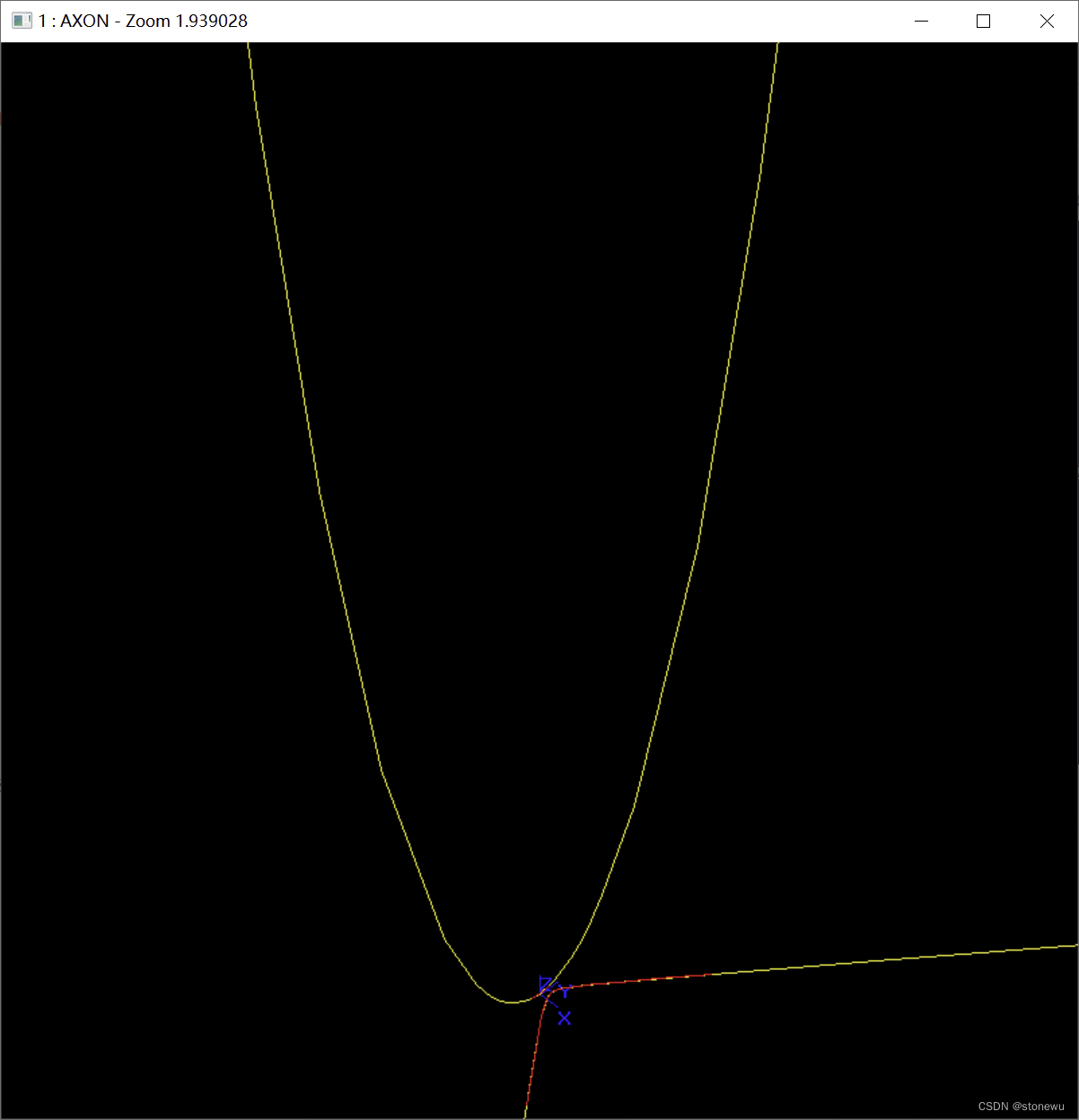
抛物线和双曲线:
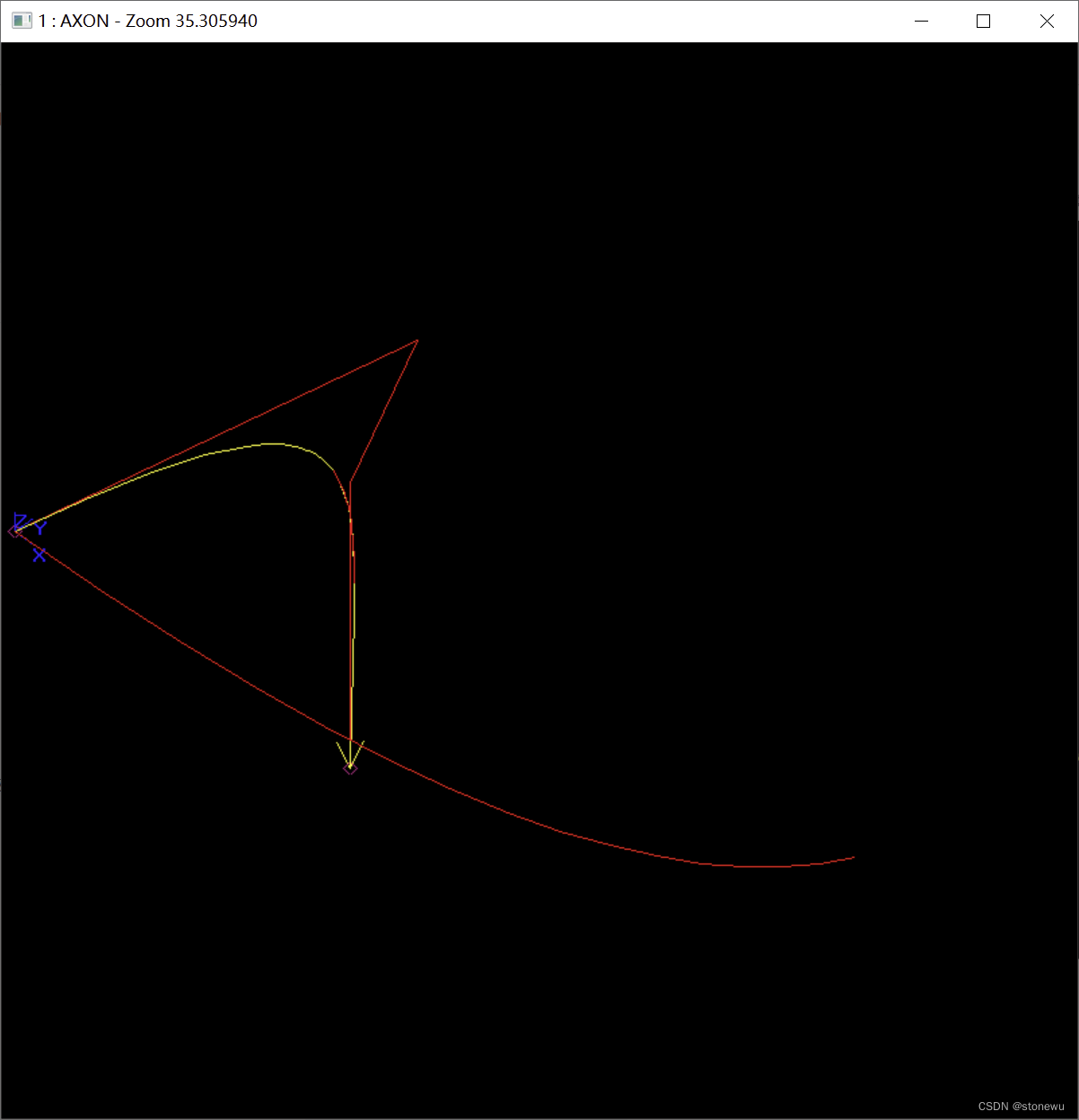
beziercurve和bsplinecurve
这篇关于OGG几何内核-BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge学习的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







