本文主要是介绍Java开发工具类(JDK、Hutool、Guava),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- Java开发常用的工具类
- 1、JDK自带
- 程序读取控制台输入内容(调试程序或者学习的时候比较有用)
- Arrays工具类 数组转集合
- Collections 集合工具类 排序
- Collections 集合工具类 查找
- Lambda表达式 操作集合 收集、转map、分组
- 2、Apache 的 commons-lang3 和 commons-collections4
- 字符串和集合的工具类
- 3、Hutool
- 处理日期 cn.hutool.core.date.DateUnit
- 处理字符串 cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
- IO操作 (文件读取、复制、写入、压缩)
- 反射工具 cn.hutool.core.util.ReflectUtil
- 校验字段 (身份证、手机号、邮箱)
- 简单的外部配置信息获取
- 图片工具
- 加密解密
- 缓存
- 4、Guava
- 集合
- 缓存
- 5、其它工具类收集
- 金额转换成大写汉字
Java开发常用的工具类
1、JDK自带
程序读取控制台输入内容(调试程序或者学习的时候比较有用)
public static void main(String[] args) {try ( BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in))){String input;while ((input = reader.readLine()) != null){System.out.println(input);}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
或者
public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);String line = scanner.nextLine();while (line!=null) {System.out.println(line);line = scanner.nextLine();}}
Arrays工具类 数组转集合
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = Arrays.asList("123", "456", "789");System.out.println(list);// 注意 Arrays.asList 返回的集合是 静态内部类private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>// 并不支持集合修改操作 如果需要修改Arrays.asList转化的集合 需要再转成 java.util.List的实现list = new ArrayList<>(list); //比如 转成ArrayListlist.add("ok");System.out.println(list);}
Collections 集合工具类 排序
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("1哈士奇");list.add("2斗牛");list.add("3博美");list.add("4斗牛");list.add("5哈士奇");System.out.println("原始顺序:" + list);// 反转Collections.reverse(list);System.out.println("反转:" + list);// 洗牌,随机打乱Collections.shuffle(list);System.out.println("洗牌:" + list);// 自然升序Collections.sort(list);System.out.println("自然升序:" + list);// 交换 注意后两个参数是下标Collections.swap(list, 0,4);System.out.println("交换:" + list);// 自定义比较器Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String obj1, String obj2) {// 返回0 说明相等 大于0 说明obj1大 小于0 obj2大// 现在我想自定义排序 从小到大排 带哈士奇的就大 其余的都小if(obj1.equals(obj2)){return 0;}else if(obj1.contains("哈士奇")){return 1;}else {return -1;}}});System.out.println(list);}
Collections 集合工具类 查找
public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("1哈士奇");list.add("2斗牛");list.add("3博美");list.add("4斗牛");list.add("5哈士奇");System.out.println("集合数据:" + list);// 查找自然排序下的最大元素String max = Collections.max(list);System.out.println("最大: "+max);// 查找自然排序下的最小元素String min = Collections.min(list);System.out.println("最小: "+min);// 自定义比较器 返回最大元素String pomeranian = Collections.max(list, new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String obj1, String obj2) {// 返回0 说明相等 大于0 说明obj1大 小于0 obj2大// 现在我想自定义排序 从小到大排 带博美的就大 其余的都小if (obj1.equals(obj2)) {return 0;} else if (obj1.contains("博美")) {return 1;} else {return -1;}}});System.out.println("自定义排序下的最大元素: "+pomeranian);}
Lambda表达式 操作集合 收集、转map、分组
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Dog> list = new ArrayList<>();// 名称、爱好Dog dog1 = new Dog("秀逗", "吃骨头");Dog dog2 = new Dog("四眼", "吃馒头");Dog dog3 = new Dog("大黄", "吃骨头");Dog dog4 = new Dog("小黑", "吃馒头");Dog dog5 = new Dog("跳跳", "跳来跳去");list.add(dog1);list.add(dog2);list.add(dog3);list.add(dog4);list.add(dog5);System.out.println("集合数据:" + list);// 收集 集合中对象的某一个元素List<String> names = list.stream().map(Dog::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(names);// 转map 根据 集合中元素的 某个属性 准换成map集合 key是name属性 value是对象本身Map<String, Dog> dogMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Dog::getName, Function.identity(),(oldValue, newValue) -> oldValue));System.out.println(dogMap);// 分组 根据 hobby 分组Map<String, List<Dog>> dogGroup = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Dog::getHobby));System.out.println(dogGroup);}
2、Apache 的 commons-lang3 和 commons-collections4
<dependency><groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId><artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId><version>3.14.0</version>
</dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId><artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId><version>4.5.0-M1</version>
</dependency>
字符串和集合的工具类
判断字符串集合是否为空,字符串拼接,字符串填充
public static void main(String[] args) {// =============== 判断字符串String a = " ";// isNotBlank 如果字符串既非null又至少有一个非空白字符,则返回true;否则返回falseif(StringUtils.isNotBlank(a)){System.out.println("isNotBlank");}// isNotEmpty 如果字符串非null且长度大于0,则返回true;否则返回false。if(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(a)){System.out.println("isNotEmpty");}// 字符串拼接List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("秀逗", "大黄", "四眼");String join = StringUtils.join(list1, ",");System.out.println(join);// 字符串填充 如果不满多少位 就左填充 或者 右填充多少位String tt = "123";String leftPad = StringUtils.leftPad(tt, 6, "0");String rightPad = StringUtils.rightPad(tt, 6, "0");System.out.println(leftPad);System.out.println(rightPad);// =============== 判断集合List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("1", "2"));if(CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(list)){System.out.println("list集合不为空");}Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("1","1");if(MapUtils.isNotEmpty(map)){System.out.println("map集合不为空");}}
3、Hutool
Hutool官网https://www.hutool.cn
官方文档:https://doc.hutool.cn/pages/index/
Maven坐标
<dependency><groupId>cn.hutool</groupId><artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId><version>5.8.27</version>
</dependency>
下面这张图片来自 https://javabetter.cn/common-tool/hutool.html#_01%E3%80%81%E5%BC%95%E5%85%A5-hutool
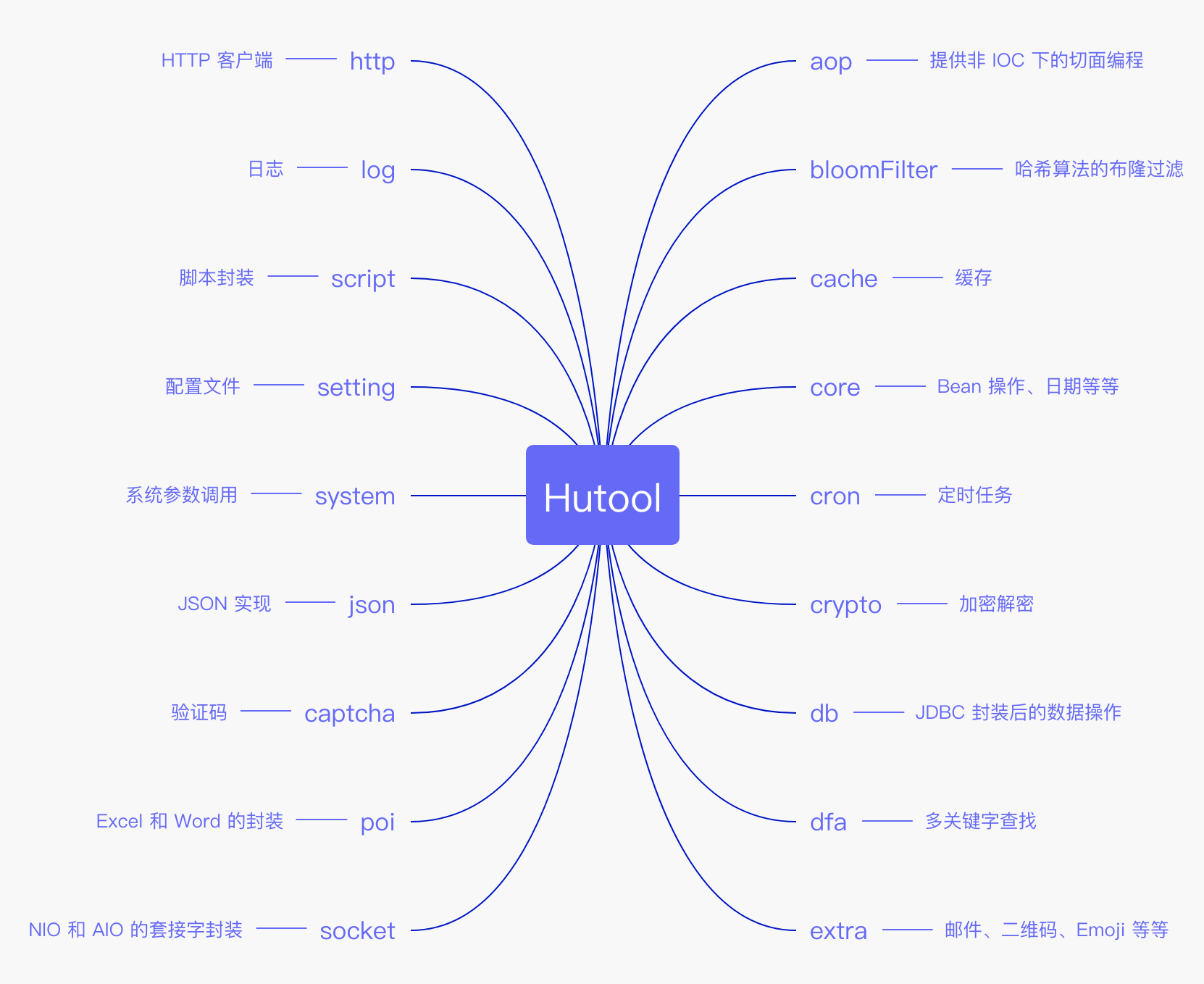
功能太多了,简单举几个常用的例子:
处理日期 cn.hutool.core.date.DateUnit
public static void main(String[] args) {// 日期时间处理//============ 字符串转日期 ==============// 支持常见的格式// yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss// yyyy-MM-dd// HH:mm:ss// yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm// yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSSDateTime dateTime = DateUtil.parse("2024-05-01 12:00:00");System.out.println(dateTime);// 日期转字符串String format = DateUtil.format(dateTime, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");System.out.println(format);//========== 计算两个时间差 可以计算相差的 毫秒、秒、分钟、小时、天、星期String dateStr1 = "2024-05-01 12:00:00";String dateStr2 = "2024-05-05 15:00:00";DateTime date1 = DateUtil.parse(dateStr1);DateTime date2 = DateUtil.parse(dateStr2);// 计算相差多少天long betweenDay = DateUtil.between(date1, date2, DateUnit.DAY);System.out.println(betweenDay);// ========= 给定日期的开始时间 和最后时间 ===========String dateStrBegin = "2024-05-23";DateTime dateBegin = DateUtil.parse(dateStrBegin);DateTime beginOfDay = DateUtil.beginOfDay(dateBegin);System.out.println(DateUtil.format(beginOfDay,"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));String dateStrEnd = "2024-05-23";DateTime dateEnd = DateUtil.parse(dateStrEnd);DateTime endOfDay = DateUtil.endOfDay(dateEnd);System.out.println(DateUtil.format(endOfDay,"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));}
处理字符串 cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
public static void main(String[] args) {// ============= 字符串填充 =============String str = "秀逗喜欢吃{},也喜欢{}";String format = StrUtil.format(str, "骨头", "跑着玩");System.out.println(format);}
IO操作 (文件读取、复制、写入、压缩)
public static void main(String[] args) {// ============= 获取输入输出流 ==========BufferedInputStream inputStream = FileUtil.getInputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123.txt");BufferedOutputStream outputStream = FileUtil.getOutputStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123_copy.txt");// ============= 复制文件 ==========FileUtil.copy("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123.txt","C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123_copy.txt",true);// ============ 读取文件 ============List<String> list = FileUtil.readUtf8Lines("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123.txt");System.out.println(list);// ============ 写文件 ============List<String> lines = new ArrayList<>();lines.add("123");lines.add("456");lines.add("789");FileUtil.writeUtf8Lines(lines,"C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123.txt");// ============ 压缩文件 压缩成.zip格式 =============ZipUtil.zip("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\12333","C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\12333.zip");// ============ 解压文件 解压.zip格式压缩包 =============ZipUtil.unzip("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\12333.zip","C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\12333");}
反射工具 cn.hutool.core.util.ReflectUtil
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {// ================== 获取默认构造器Constructor<Dog> constructor = ReflectUtil.getConstructor(Dog.class);// ================== 获取对象Dog dog = ReflectUtil.newInstance(Dog.class);// ================== 获取全部字段Field[] fields = ReflectUtil.getFields(Dog.class);// ================== 获取某个字段Field name = ReflectUtil.getField(Dog.class, "name");// ================== 获取全部方法Method[] methods = ReflectUtil.getMethods(Dog.class);// ================== 获取某个方法Method eat = ReflectUtil.getMethod(Dog.class, "eat");// 执行某个方法ReflectUtil.invoke(ReflectUtil.newInstance(Dog.class), "bulk");}
class Dog{private String name;private String hobby;public void eat(){System.out.println("狗喜欢吃骨头!");}public void bulk(){System.out.println("汪汪汪!");}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getHobby() {return hobby;}public void setHobby(String hobby) {this.hobby = hobby;}
}
校验字段 (身份证、手机号、邮箱)
public static void main(String[] args) {// =============== 校验身份证String right = "120222198412136012";String error = "340411199505250212999";System.out.println(IdcardUtil.isValidCard(right));System.out.println(IdcardUtil.isValidCard(error));// ============== 手机号boolean phone = PhoneUtil.isPhone("19905240696");System.out.println(phone);// ============== 邮箱boolean email = Validator.isEmail("123@qq.com");System.out.println(email);}
简单的外部配置信息获取
public static void main(String[] args) {// 初始化配置文件String settings = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\配置文件.txt";Setting setting = new Setting(settings);// 获取配置文件内信息String url = setting.get("url");String name = setting.get("name");System.out.println(url);System.out.println(name);}
图片工具
public static void main(String[] args) {// ========== 图片工具 =============// 压缩Img.from(FileUtil.file("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123\\dog.jpg")).setQuality(0.8)//压缩比率.write(FileUtil.file("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123\\dog_1.jpg"));// 添加水印ImgUtil.pressText(//FileUtil.file("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123\\dog.jpg"),FileUtil.file("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123\\dog_text.jpg"),"二哈", Color.WHITE, //文字new Font("黑体", Font.BOLD, 15), //字体0, //x坐标修正值。 默认在中间,偏移量相对于中间偏移0, //y坐标修正值。 默认在中间,偏移量相对于中间偏移0.8f//透明度:alpha 必须是范围 [0.0, 1.0] 之内(包含边界值)的一个浮点数字);// 剪裁ImgUtil.cut(FileUtil.file("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123\\dog.jpg"),FileUtil.file("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\123\\dog_text_2.jpg"),new Rectangle(0, 0, 259, 175)//裁剪的矩形区域);}
加密解密
public static void main(String[] args) {// ========== 加密工具 =============// 对称加密 解密AES aes = SecureUtil.aes();String s = aes.encryptHex("123456");System.out.println(s);String s1 = aes.decryptStr(s);System.out.println(s1);// 非对称加密RSA rsa = SecureUtil.rsa();// 公钥加密String s2 = rsa.encryptHex("123456", KeyType.PublicKey);System.out.println(s2);// 私钥解密String s3 = rsa.decryptStr(s2, KeyType.PrivateKey);System.out.println(s3);}
缓存
public static void main(String[] args) {// =============== 缓存// =========== FIFO(first in first out) 先进先出策略。// 元素不停的加入缓存直到缓存满为止,当缓存满时,清理过期缓存对象,清理后依旧满则删除先入的缓存(链表首部对象)。Cache<String,String> fifoCache = CacheUtil.newFIFOCache(3);//加入元素,每个元素可以设置其过期时长,DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis()代表每秒对应的毫秒数,在此为3秒fifoCache.put("key1", "value1", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);fifoCache.put("key2", "value2", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);fifoCache.put("key3", "value3", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);//由于缓存容量只有3,当加入第四个元素的时候,根据FIFO规则,最先放入的对象将被移除fifoCache.put("key4", "value4", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);//value1为nullString value1 = fifoCache.get("key1");// =========== LFU(least frequently used) 最少使用率策略。// 根据使用次数来判定对象是否被持续缓存(使用率是通过访问次数计算),// 当缓存满时清理过期对象,清理后依旧满的情况下清除最少访问(访问计数最小)// 的对象并将其他对象的访问数减去这个最小访问数,以便新对象进入后可以公平计数。Cache<String, String> lfuCache = CacheUtil.newLFUCache(3);//通过实例化对象创建//LFUCache<String, String> lfuCache = new LFUCache<String, String>(3);lfuCache.put("key1", "value1", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);lfuCache.get("key1");//使用次数+1lfuCache.put("key2", "value2", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);lfuCache.put("key3", "value3", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);lfuCache.put("key4", "value4", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);//由于缓存容量只有3,当加入第四个元素的时候,根据LRU规则,最少使用的将被移除(2,3被移除)String value2 = lfuCache.get("key2");//nullString value3 = lfuCache.get("key3");//null// =========== LRU (least recently used)最近最久未使用缓存。根据使用时间来判定对象是否被持续缓存,// 当对象被访问时放入缓存,当缓存满了,最久未被使用的对象将被移除。// 此缓存基于LinkedHashMap,因此当被缓存的对象每被访问一次,这个对象的key就到链表头部。// 这个算法简单并且非常快,他比FIFO有一个显著优势是经常使用的对象不太可能被移除缓存。// 缺点是当缓存满时,不能被很快的访问。Cache<String, String> lruCache = CacheUtil.newLRUCache(3);//通过实例化对象创建//LRUCache<String, String> lruCache = new LRUCache<String, String>(3);lruCache.put("key1", "value1", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);lruCache.put("key2", "value2", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);lruCache.put("key3", "value3", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);lruCache.get("key1");//使用时间推近lruCache.put("key4", "value4", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 3);//由于缓存容量只有3,当加入第四个元素的时候,根据LRU规则,最少使用的将被移除(2被移除)String value_2 = lruCache.get("key");//null// =========== 定时缓存,对被缓存的对象定义一个过期时间,当对象超过过期时间会被清理。// 此缓存没有容量限制,对象只有在过期后才会被移除。//创建缓存,默认4毫秒过期TimedCache<String, String> timedCache = CacheUtil.newTimedCache(4);//实例化创建//TimedCache<String, String> timedCache = new TimedCache<String, String>(4);timedCache.put("key1", "value1", 1);//1毫秒过期timedCache.put("key2", "value2", DateUnit.SECOND.getMillis() * 5);timedCache.put("key3", "value3");//默认过期(4毫秒)//启动定时任务,每5毫秒清理一次过期条目,注释此行首次启动仍会清理过期条目timedCache.schedulePrune(5);//等待5毫秒ThreadUtil.sleep(5);//5毫秒后由于value2设置了5毫秒过期,因此只有value2被保留下来String value_1 = timedCache.get("key1");//nullString value__2 = timedCache.get("key2");//value2//5毫秒后,由于设置了默认过期,key3只被保留4毫秒,因此为nullString value_3 = timedCache.get("key3");//null//取消定时清理timedCache.cancelPruneSchedule();}
4、Guava
Guava是Google开源的一个Java库,它包含了很多Google核心库中使用的基础工具和高性能原语。
Guava的目标是提高Java程序员的生产力,特别是通过减少常见的编程任务中的 boilerplate code(样板代码),同时引入一些Java标准库中没有的功能和改进已有的功能。
Guava主要特性包括:
①、集合(Collections): Guava提供了丰富的不可变集合(Immutable Collections)、多值映射(Multimap)、双向映射(BiMap)、表(Table)等数据结构,以及强大的集合操作工具类,如Iterables、Lists、Sets等,这些都大大增强了Java集合框架的功能。
②、缓存(Cache): 提供了一个强大且可自定义的缓存实现——Cache,支持多种缓存淘汰策略(如基于容量、基于时间等),使得在Java中实现高性能缓存变得更加简单。
③、并发(Concurrency): Guava提供了并发工具类,比如ListenableFuture用于异步编程,以及一些并发工具方法,帮助开发者更安全、高效地处理并发问题。
④、字符串处理(Strings): 扩展了Java的字符串处理能力,提供了更多方便的方法,如字符串连接、前缀判断、后缀移除等。
⑤、原生类型支持(Primitives): Guava对Java基本类型提供了丰富的支持,包括基本类型的数组操作、集合转换等,提高了处理基本类型数据的效率。
⑥、函数式编程支持(Functional Programming): 包括函数接口(Function、Predicate等)和流式操作,尽管不如Java 8引入的Stream API那样全面,但提供了基础的函数式编程支持。
⑦、校验器(Validators): 用于数据验证,提供了一套可组合的校验规则,方便构建复杂的校验逻辑。
⑧、I/O操作: 简化了文件读写操作,提供了基于流的读写工具类,以及一些实用的I/O工具方法。
⑨、范围(Range): 用于表示和操作数值范围,简化区间判断逻辑。
⑩、事件总线(EventBus): 一种发布/订阅模式的通信机制,用于解耦应用程序的不同部分,简化组件间的通信。
引入Maven坐标:
<dependency><groupId>com.google.guava</groupId><artifactId>guava</artifactId><version>33.2.0-jre</version>
</dependency>
示例:
只举一些常用的集合和缓存的例子 ,更多的内容可以去 Guava的在线文档内学习
Guava在线文档-英文版https://tool.oschina.net/apidocs/apidoc?api=guava
集合
public static void main(String[] args) {// ============== 创建快速初始化的集合ArrayList<String> arrayList = Lists.newArrayList("123", "456", "789");// ============== 不可变集合ImmutableList<String> immutableList = ImmutableList.of("1", "2");
// immutableList.add("2"); // 报异常 java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException// 把可变集合转换成不可变集合ImmutableList<String> immutableList1 = ImmutableList.copyOf(arrayList);// ============== Multiset// 可以把 Multiset 看成 没有元素顺序限制的ArrayList// 存储结构 Map<E, Integer>,键为元素,值为计数Multiset<String> multiset = HashMultiset.create();multiset.add("1");multiset.add("1");multiset.add("2");multiset.add("3");System.out.println("1的个数:" + multiset.count("1"));System.out.println("multiset内元素的个数:" + multiset.size());System.out.println("multiset内不重复元素的集合:" + multiset.elementSet());// ============== MultiMap// 类似分组操作 一个key 可以对应一个集合 集合里面有多个值// 常用的接口 ListMultimap 和 SetMultimapMultimap<String,String> multimap = ArrayListMultimap.create();multimap.put("1","1");multimap.put("1","2");multimap.put("3","3");multimap.putAll("3",Lists.newArrayList("A","B","C","D"));Collection<String> strings = multimap.get("1");System.out.println(strings);Map<String, Collection<String>> asMap = multimap.asMap();System.out.println("asMap视图:"+ Joiner.on(";").withKeyValueSeparator("=").join(asMap));// ============== BiMap// 可以根据key查询value 也可以根据value查询key// 保证值是唯一的BiMap<String, String> biMap = HashBiMap.create();biMap.put("1","秀逗");biMap.put("2","四眼");String value = biMap.get("1");String key = biMap.inverse().get("秀逗");System.out.println(value);System.out.println(key);// biMap.put("3","秀逗"); // 报错 java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: value already present: 秀逗biMap.forcePut("3","秀逗"); // 强制替换 会覆盖已有的映射关系System.out.println(biMap);}
缓存
说到缓存马上想到的可能是Redis这类缓存数据库,实际上JVM内存缓存也是实现缓存的一种手段。
那么用 JVM本地内存缓存 有什么优势呢?
- ①、性能优势: 对于小规模或访问极为频繁的数据,JVM本地缓存(如Guava Cache)由于省去了网络通信的开销,能够提供更低的访问延迟。数据直接存储在应用的内存中,使得读写速度极快。
- ②、缓存分级策略: 在一些大型系统中,可能会采用多级缓存策略,即首先查询本地JVM缓存(如Guava Cache),未命中时再查询Redis等分布式缓存,最后才是数据库。这种策略可以进一步提升数据访问速度,减少数据库系统的压力。
有优势就有劣势:
- ①、数据存放在本机的内存,未持久化到硬盘,应用重启数据会丢失
- ②、单机缓存,容量有限
- ③、多个实例部署应用会出现缓存数据不一致的问题
com.google.common.cache.Cache示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用 CacheBuilder 构建JVM缓存// expireAfterWrite 设置缓存项在写入后3秒后过期。// .initialCapacity(1): 指定缓存的初始容量为1。// .maximumSize(2): 设置缓存的最大容量为2。当缓存项的数量超过这个限制时,// 根据Guava的默认实现(LRU,最近最少使用策略),最不常使用的条目会被移除以腾出空间给新的条目// .removalListener(...): 添加一个缓存移除监听器。每当有条目从缓存中移除时// (无论是因为过期、容量达到上限还是显式删除),都会调用这个监听器的方法。Cache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS).initialCapacity(1).maximumSize(2).removalListener((RemovalListener<String, String>) notification ->System.out.println(notification.getKey() + "移除了,value:" + notification.getValue())).build();// getIfPresent(key):从现有的缓存中获取,如果缓存中有key,则返回value,如果没有则返回nullString value = cache.getIfPresent("1");System.out.println(value); //nullcache.put("1", "秀逗");cache.put("2", "四眼");cache.put("3", "大黄");System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("1"));System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("2"));System.out.println(cache.getIfPresent("3"));}
使用Guava Cache时需要注意的事项:(需要深入研究)
-
①、明确缓存目的: 在设计缓存之前,明确其目的是提高读取速度、减少数据库负载还是其他。这将帮助你决定合适的缓存策略。
-
②、选择合适的缓存淘汰策略:
使用.expireAfterWrite或.expireAfterAccess根据业务需求设置过期时间。
结合.maximumSize设置缓存最大容量,采用LRU(最近最少使用)或FIFO(先进先出)等淘汰策略。
线程安全:Guava Cache天生线程安全,但确保在访问和更新缓存时逻辑正确,避免不必要的锁竞争。 -
③、监听器的合理使用: 利用.removalListener监听缓存项移除事件,可以进行日志记录、资源清理等工作,但注意不要在监听器中执行耗时操作,以免影响性能。
-
④、弱引用与软引用: 根据应用场景,适当使用.weakKeys()、.weakValues()或.softValues()来控制缓存项的生命周期,尤其是在内存敏感的应用中。
-
⑤、统计与监控: 启用统计功能(.recordStats())来监控缓存命中率、加载次数等指标,帮助分析缓存效率,适时调整策略。
-
⑥、异步加载与刷新: 对于耗时的缓存项加载,可以使用.loadingCache并结合.refreshAfterWrite来异步刷新缓存,避免阻塞主线程。
-
⑦、避免过度缓存: 不是所有数据都适合缓存,特别是频繁变化、占用大量内存或访问频率很低的数据。合理评估并选择真正能带来性能提升的数据进行缓存。
-
⑧、资源管理: 当不再需要缓存时,通过.cleanUp()手动清理资源,或者确保应用关闭时能正确释放缓存资源。
5、其它工具类收集
金额转换成大写汉字
public class MoneyUtil {/** 大写数字 */private static final String[] NUMBERS = { "零", "壹", "贰", "叁", "肆", "伍","陆", "柒", "捌", "玖" };/** 整数部分的单位 */private static final String[] IUNIT = { "元", "拾", "佰", "仟", "万", "拾", "佰","仟", "亿", "拾", "佰", "仟", "万", "拾", "佰", "仟" };/** 小数部分的单位 */private static final String[] DUNIT = { "角", "分", "厘" };/*** 得到大写金额。*/public static String toChinese(String str) {str = str.replaceAll(",", "");// 去掉","String integerStr;// 整数部分数字String decimalStr;// 小数部分数字// 初始化:分离整数部分和小数部分if (str.indexOf(".") > 0) {integerStr = str.substring(0, str.indexOf("."));decimalStr = str.substring(str.indexOf(".") + 1);} else if (str.indexOf(".") == 0) {integerStr = "";decimalStr = str.substring(1);} else {integerStr = str;decimalStr = "";}// integerStr去掉首0,不必去掉decimalStr的尾0(超出部分舍去)if (!integerStr.equals("")) {integerStr = Long.toString(Long.parseLong(integerStr));if (integerStr.equals("0")) {integerStr = "";}}// overflow超出处理能力,直接返回if (integerStr.length() > IUNIT.length) {System.out.println(str + ":超出处理能力");return str;}int[] integers = toArray(integerStr);// 整数部分数字boolean isMust5 = isMust5(integerStr);// 设置万单位int[] decimals = toArray(decimalStr);// 小数部分数字return getChineseInteger(integers, isMust5)+ getChineseDecimal(decimals);}/*** 整数部分和小数部分转换为数组,从高位至低位*/private static int[] toArray(String number) {int[] array = new int[number.length()];for (int i = 0; i < number.length(); i++) {array[i] = Integer.parseInt(number.substring(i, i + 1));}return array;}/*** 得到中文金额的整数部分。*/private static String getChineseInteger(int[] integers, boolean isMust5) {StringBuffer chineseInteger = new StringBuffer("");int length = integers.length;for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {// 0出现在关键位置:1234(万)5678(亿)9012(万)3456(元)// 特殊情况:10(拾元、壹拾元、壹拾万元、拾万元)String key = "";if (integers[i] == 0) {if ((length - i) == 13)// 万(亿)(必填)key = IUNIT[4];else if ((length - i) == 9)// 亿(必填)key = IUNIT[8];else if ((length - i) == 5 && isMust5)// 万(不必填)key = IUNIT[4];else if ((length - i) == 1)// 元(必填)key = IUNIT[0];// 0遇非0时补零,不包含最后一位if ((length - i) > 1 && integers[i + 1] != 0)key += NUMBERS[0];}chineseInteger.append(integers[i] == 0 ? key: (NUMBERS[integers[i]] + IUNIT[length - i - 1]));}return chineseInteger.toString();}/*** 得到中文金额的小数部分。*/private static String getChineseDecimal(int[] decimals) {StringBuffer chineseDecimal = new StringBuffer("");for (int i = 0; i < decimals.length; i++) {// 舍去3位小数之后的if (i == 3)break;chineseDecimal.append(decimals[i] == 0 ? "": (NUMBERS[decimals[i]] + DUNIT[i]));}return chineseDecimal.toString();}/*** 判断第5位数字的单位"万"是否应加。*/private static boolean isMust5(String integerStr) {int length = integerStr.length();if (length > 4) {String subInteger = "";if (length > 8) {// 取得从低位数,第5到第8位的字串subInteger = integerStr.substring(length - 8, length - 4);} else {subInteger = integerStr.substring(0, length - 4);}return Integer.parseInt(subInteger) > 0;} else {return false;}}// public static void main(String[] args) {
// MoneyUtil moneyUtil = new MoneyUtil();
// System.out.println(moneyUtil.toChinese("520"));
// }}
这篇关于Java开发工具类(JDK、Hutool、Guava)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



