本文主要是介绍Android触屏分发机制(二),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
上一篇博客 Android触屏分发机制(一) http://blog.csdn.net/u010429311/article/details/50978987
在上一篇博客中讲到了Button的点击事件处理,即View的点击事件是如何分发的,那么这篇文章更深入的理解触屏分发机制,讲述ViewGroup是如何实现的。大家可能都知道各种布局如RelativeLayout,LinearLayout都是继承自ViewGroup,简单来说它是View的集合,就像一个RelativeLayout包含了许多控件一样。其关系如图所示。
关于ViewGroup和View的具体信息,可以在百度里找到大量的资料。
回到正题,ViewGroup是如何实现触屏分发机制的呢?同样,先做一个测试:
Button btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View v) {Log.i(TAG, "on click");}});
RelativeLayout layout = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout);layout.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {@Overridepublic boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {Log.i(TAG, "layout on touch");return false;}});当我们分别点击Button和Button外的空白处时,分别输出了两个结果:
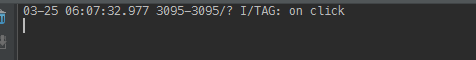
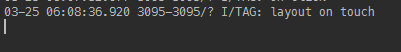
我们可以看到,当点击按钮时layout的onTouch事件并没有执行!为什么作为ViewGroup的RelativeLayout没有执行onTouch事件呢?上一节讲到了当按钮点击时会执行其dispatchTouchEvent()方法,同样我们可以看看ViewGroup是如何实现其dispatchTouchEvent()方法的:
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {//省略一部分final boolean intercepted;if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;if (!disallowIntercept) {intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed} else {intercepted = false;}} else {// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down// so this view group continues to intercept touches.intercepted = true;}// If intercepted, start normal event dispatch. Also if there is already// a view that is handling the gesture, do normal event dispatch.if (intercepted || mFirstTouchTarget != null) {ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);}// Check for cancelation.final boolean canceled = resetCancelNextUpFlag(this)|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL;// Update list of touch targets for pointer down, if needed.final boolean split = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_SPLIT_MOTION_EVENTS) != 0;TouchTarget newTouchTarget = null;boolean alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = false;if (!canceled && !intercepted) {// If the event is targeting accessiiblity focus we give it to the// view that has accessibility focus and if it does not handle it// we clear the flag and dispatch the event to all children as usual.// We are looking up the accessibility focused host to avoid keeping// state since these events are very rare.View childWithAccessibilityFocus = ev.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()? findChildWithAccessibilityFocus() : null;if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex(); // always 0 for downfinal int idBitsToAssign = split ? 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex): TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS;// Clean up earlier touch targets for this pointer id in case they// have become out of sync.removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToAssign);final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {final float x = ev.getX(actionIndex);final float y = ev.getY(actionIndex);// Find a child that can receive the event.// Scan children from front to back.final ArrayList<View> preorderedList = buildOrderedChildList();final boolean customOrder = preorderedList == null&& isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled();final View[] children = mChildren;for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {final int childIndex = customOrder? getChildDrawingOrder(childrenCount, i) : i;final View child = (preorderedList == null)? children[childIndex] : preorderedList.get(childIndex);// If there is a view that has accessibility focus we want it// to get the event first and if not handled we will perform a// normal dispatch. We may do a double iteration but this is// safer given the timeframe.if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != null) {if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != child) {continue;}childWithAccessibilityFocus = null;i = childrenCount - 1;}if (!canViewReceivePointerEvents(child)|| !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) {ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);continue;}newTouchTarget = getTouchTarget(child);if (newTouchTarget != null) {// Child is already receiving touch within its bounds.// Give it the new pointer in addition to the ones it is handling.newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign;break;}resetCancelNextUpFlag(child);if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {// Child wants to receive touch within its bounds.mLastTouchDownTime = ev.getDownTime();if (preorderedList != null) {// childIndex points into presorted list, find original indexfor (int j = 0; j < childrenCount; j++) {if (children[childIndex] == mChildren[j]) {mLastTouchDownIndex = j;break;}}} else {mLastTouchDownIndex = childIndex;}mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX();mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY();newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;break;}// The accessibility focus didn't handle the event, so clear// the flag and do a normal dispatch to all children.ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);}if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear();}//省略一部分}已经省略一部分了,代码还是有点长。我们看到第9行中这句代码
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev)中的 onInterceptTouchEvent()方法,该方法很简单:
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {return false;}Intercept为“拦截的意思”,顾名思义,我们可以联想到分发事件的拦截。经过测试,可以知道,到返回值为true时,拦截分发,点击RelativeLayout中的Button无法响应,只输出了RelativeLayout的onTouch事件。了解了这个方法后,我们继续回到之前的dispatchTouchEvent()方法:
我们看到34行: if (!canceled && !intercepted),当onInterceptTouchEvent()方法返回false时,可通过该条件,然后跳到65行里的for循环,该循坏是遍历ViewGroup中所有的子ViewGroup或是View,找到用户所点击的View,并在第89行赋值newTouchTarget = getTouchTarget(child)。
之后我们在跳到98行的 if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign))这个条件语句,再看看 idispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)这个方法实现方式:
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {final boolean handled;// Canceling motions is a special case. We don't need to perform any transformations// or filtering. The important part is the action, not the contents.final int oldAction = event.getAction();if (cancel || oldAction == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) {event.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL);if (child == null) {handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);} else {handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(event);}event.setAction(oldAction);return handled;}//省略一部分 }
幸运!我们终于在第13行中看到了child.dispatchTouchEvent(event)这句话,明显如果找到了点击控件child不为null,执行该语句。即回到了上一节所讲的View的dispatchTouchEvent()方法的触屏分发机制。
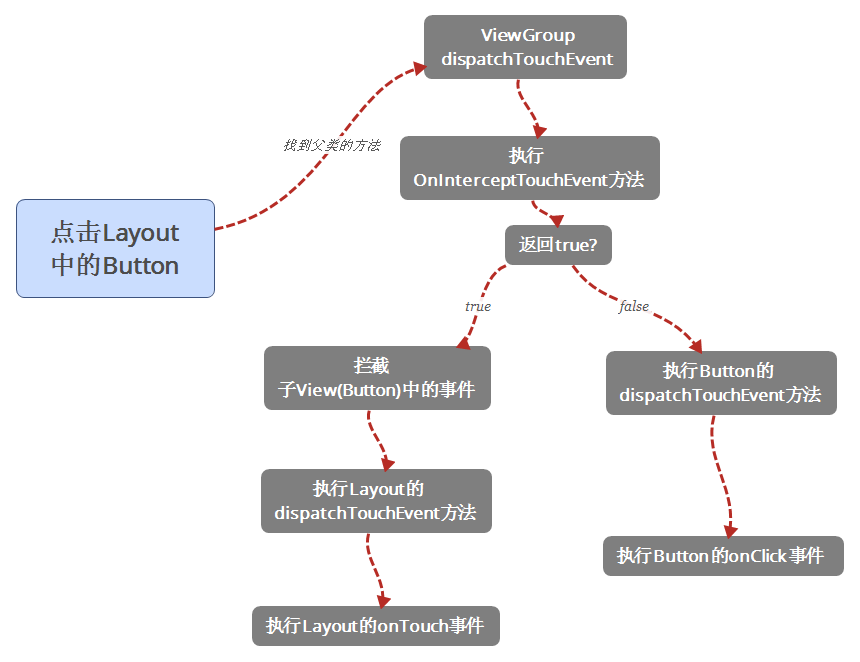
至此,ViewGroup的触屏分发机制也清晰了。最后,画个图总结一下:
这篇关于Android触屏分发机制(二)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!