本文主要是介绍gpio_desc()的分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Linux下GPIO驱动(三) ----gpio_desc()的分析
上篇最后提出的疑问是结构体gpio_chip中的成员函数set等是怎么实现的,在回答之前先介绍下gpio_desc这个结构体。
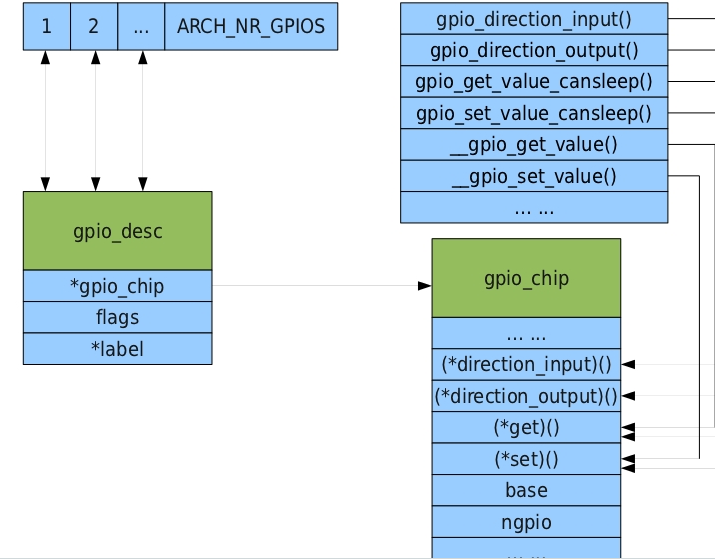
如上图所示,右上方部分为GPIO驱动对其它驱动提供的GPIO操作接口,其对应的右下方部分为GPIO硬件操作接口,也就是说对外提供的接口最终会一一对应的对硬件GPIO进行操作。
再来看左边部分,左上方部分为一全局数组,记录各个GPIO的描述符,即对应左下方的gpio_desc结构体,其中gpio_chip指向硬件层的GPIO,flags为一标志位,用来指示当前GPIO是否已经占用,当用gpio_request申请GPIO资源时,flags位就会置位,当调用gpio_free释放GPIO资源时,flags就会清零。label是一个字符串指针,用来作说明。
在软件上,我们首先通过函数gpiochip_add注册一个gpio_chip对应的gpio_desc到全局数组gpio描述符中。其中,一个描述符对应一个GPIO,所以如果我们要使用多个GPIO,那么就在gpio_chip结构体的ngpio指定个数,base为起始的GPIO号。
//每个引脚分配一个gpio_desc数据结构
struct gpio_desc {struct gpio_chip *chip;unsigned long flags;
};

/*** struct gpio_chip - abstract a GPIO controller* @label: for diagnostics* @dev: optional device providing the GPIOs* @owner: helps prevent removal of modules exporting active GPIOs* @request: optional hook for chip-specific activation, such as* enabling module power and clock; may sleep* @free: optional hook for chip-specific deactivation, such as* disabling module power and clock; may sleep* @direction_input: configures signal "offset" as input, or returns error* @get: returns value for signal "offset"; for output signals this* returns either the value actually sensed, or zero* @direction_output: configures signal "offset" as output, or returns error* @set: assigns output value for signal "offset"* @to_irq: optional hook supporting non-static gpio_to_irq() mappings;* implementation may not sleep* @dbg_show: optional routine to show contents in debugfs; default code* will be used when this is omitted, but custom code can show extra* state (such as pullup/pulldown configuration).* @base: identifies the first GPIO number handled by this chip; or, if* negative during registration, requests dynamic ID allocation.* @ngpio: the number of GPIOs handled by this controller; the last GPIO* handled is (base + ngpio - 1).* @can_sleep: flag must be set iff get()/set() methods sleep, as they* must while accessing GPIO expander chips over I2C or SPI* @names: if set, must be an array of strings to use as alternative* names for the GPIOs in this chip. Any entry in the array* may be NULL if there is no alias for the GPIO, however the* array must be @ngpio entries long. A name can include a single printk* format specifier for an unsigned int. It is substituted by the actual* number of the gpio.** A gpio_chip can help platforms abstract various sources of GPIOs so* they can all be accessed through a common programing interface.* Example sources would be SOC controllers, FPGAs, multifunction* chips, dedicated GPIO expanders, and so on.** Each chip controls a number of signals, identified in method calls* by "offset" values in the range 0..(@ngpio - 1). When those signals* are referenced through calls like gpio_get_value(gpio), the offset* is calculated by subtracting @base from the gpio number.*/
struct gpio_chip {
//这些函数实现在arch\arm\mach-s5pv210\gpiolib.c const char *label;struct device *dev;struct module *owner;int (*request)(struct gpio_chip *chip,unsigned offset);void (*free)(struct gpio_chip *chip,unsigned offset);int (*direction_input)(struct gpio_chip *chip,unsigned offset);int (*get)(struct gpio_chip *chip,unsigned offset);int (*direction_output)(struct gpio_chip *chip,unsigned offset, int value);int (*set_debounce)(struct gpio_chip *chip,unsigned offset, unsigned debounce);void (*set)(struct gpio_chip *chip,unsigned offset, int value);int (*to_irq)(struct gpio_chip *chip,unsigned offset);void (*dbg_show)(struct seq_file *s,struct gpio_chip *chip);int base;u16 ngpio;const char *const *names;unsigned can_sleep:1;unsigned exported:1;
};

下面分析gpio_desc中成员chip的成员函数的实现:

__init int s5pv210_gpiolib_init(void)//在Linux初始化期间,此函数就执行了
{struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip = s5pv210_gpio_4bit;int nr_chips = ARRAY_SIZE(s5pv210_gpio_4bit);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < nr_chips; i++, chip++) {if (chip->config == NULL)chip->config = &gpio_cfg;if (chip->base == NULL)chip->base = S5PV210_BANK_BASE(i);}samsung_gpiolib_add_4bit_chips(s5pv210_gpio_4bit, nr_chips);return 0;
}


void __init samsung_gpiolib_add_4bit_chips(struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip,int nr_chips)
{for (; nr_chips > 0; nr_chips--, chip++) {samsung_gpiolib_add_4bit(chip);s3c_gpiolib_add(chip);}
}


void __init samsung_gpiolib_add_4bit(struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip)
{chip->chip.direction_input = samsung_gpiolib_4bit_input;chip->chip.direction_output = samsung_gpiolib_4bit_output;chip->pm = __gpio_pm(&s3c_gpio_pm_4bit);
}


__init void s3c_gpiolib_add(struct s3c_gpio_chip *chip)
{struct gpio_chip *gc = &chip->chip;int ret;BUG_ON(!chip->base);BUG_ON(!gc->label);BUG_ON(!gc->ngpio);spin_lock_init(&chip->lock);// 初始化s3c_gpio_chip的自旋锁
if (!gc->direction_input)gc->direction_input = s3c_gpiolib_input;//chip->direction_inputif (!gc->direction_output)gc->direction_output = s3c_gpiolib_output;//chip->direction_outputif (!gc->set)gc->set = s3c_gpiolib_set;//chip->set此处就回答了上篇的疑问if (!gc->get)gc->get = s3c_gpiolib_get;//chip->get#ifdef CONFIG_PMif (chip->pm != NULL) {if (!chip->pm->save || !chip->pm->resume)printk(KERN_ERR "gpio: %s has missing PM functions\n",gc->label);} elseprintk(KERN_ERR "gpio: %s has no PM function\n", gc->label);
#endif/* gpiochip_add() prints own failure message on error. */ret = gpiochip_add(gc);if (ret >= 0)s3c_gpiolib_track(chip);
}


/*** gpiochip_add() - register a gpio_chip* @chip: the chip to register, with chip->base initialized* Context: potentially before irqs or kmalloc will work** Returns a negative errno if the chip can't be registered, such as* because the chip->base is invalid or already associated with a* different chip. Otherwise it returns zero as a success code.** When gpiochip_add() is called very early during boot, so that GPIOs* can be freely used, the chip->dev device must be registered before* the gpio framework's arch_initcall(). Otherwise sysfs initialization* for GPIOs will fail rudely.** If chip->base is negative, this requests dynamic assignment of* a range of valid GPIOs.*/
int gpiochip_add(struct gpio_chip *chip) // 在gpio_desc[]中分配空间,并链接chip结构;注册一个gpio_chip对应的gpio_desc到全局数组gpio描述符中
{unsigned long flags;int status = 0;unsigned id;int base = chip->base;if ((!gpio_is_valid(base) || !gpio_is_valid(base + chip->ngpio - 1))&& base >= 0) {status = -EINVAL;goto fail;}spin_lock_irqsave(&gpio_lock, flags);if (base < 0) {base = gpiochip_find_base(chip->ngpio);// 这个函数在gpiolib.c中,在gpio_desc[]中分配chip->ngpio个空间(从最后往前分配),返回第一个indexif (base < 0) {status = base;goto unlock;}chip->base = base;}/* these GPIO numbers must not be managed by another gpio_chip */for (id = base; id < base + chip->ngpio; id++) {if (gpio_desc[id].chip != NULL) {status = -EBUSY;break;}}if (status == 0) {// 分配到空间,正常情况下for (id = base; id < base + chip->ngpio; id++) {gpio_desc[id].chip = chip;// 这里将gpio_desc与s3c_gpio_chip联系起来,他们的chip成员指向的是同一个数据结构
/* REVISIT: most hardware initializes GPIOs as* inputs (often with pullups enabled) so power* usage is minimized. Linux code should set the* gpio direction first thing; but until it does,* we may expose the wrong direction in sysfs.*/gpio_desc[id].flags = !chip->direction_input? (1 << FLAG_IS_OUT): 0;}}unlock:spin_unlock_irqrestore(&gpio_lock, flags);if (status == 0)status = gpiochip_export(chip);
fail:/* failures here can mean systems won't boot... */if (status)pr_err("gpiochip_add: gpios %d..%d (%s) failed to register\n",chip->base, chip->base + chip->ngpio - 1,chip->label ? : "generic");return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(gpiochip_add);
这篇关于gpio_desc()的分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




