本文主要是介绍Reachability算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1.算法描述
Reachability在 Wikipedia中的定义是这样的:In graph theory, reachability refers to the ability to get from one vertex to another within a graph. We say that a vertex s can reach a vertex t (or that t is reachable from s) if there exists a sequence of adjacent vertices (i.e. a path) which starts with s and ends with t.Reachability是很有用的算法,比如说判断两地是否可达,社交网络中两人是否认识等。Reachability算法的思想很简单:从起始结点找其邻结点是否包含目的结点,如果不包含,继续找其邻结点的邻结点。以此类推,直到所有结点访问完。
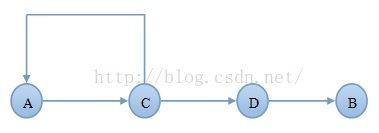
但是,上述描述有一个小问题,如下图:
假设起始结点是A点,目的结点是B点。
第一步,A点不是目的结点B,找A的邻结点C,
第二步,C点不是目的结点B,找C的邻结点A、D,
第三步,A点不是目的结点B,找A的邻结点C,
……………………
现在问题就出来了,必须对结点的访问与否进行检查。
因此,Reachability算法步骤是:
- 起始点就是目的点,则可达且算法结束;
- 把当前结点标记为visited,找其邻结点,并判断邻结点是否包含目的结点;
- 重复第二步,直到找到目的结点,或者所有结点访问完。
In an undirected graph, it is sufficient to identify the connected components, as any pair of vertices in such a graph can reach each other if and only if they belong to the same connected component. The connected components of a graph can be identified in linear time. The remainder of this article focuses on reachability in a directed graph setting.
所以,在Reachability算法还可以按照Connected Components算法思路,因此也就可以按照Connected Components中矩阵实现方法,用矩阵的幂的并集来实现Reachability算法。具体操作可以参照基于矩阵实现的Connected Components算法。
2.算法实现
由于矩阵实现的方法和Connected Components算法类似,所以这里就只介绍非矩阵实现的代码:def reachability(graph, srcVertex, dstVertex):
# reachable = FalsecheckNode = []checkNode.append(srcVertex)while not(len(checkNode) == 0):currentVertex = checkNode.pop()if(currentVertex == dstVertex):return Trueelse:neighborIds = graph.get(currentVertex)size = len(neighborIds)for i in range(size):checkNode.append(neighborIds[i])return Falseif __name__ == "__main__":graph = {0: [1, 2], 1: [2, 3], 2: [3], 3: [4], 4: []}print(reachability(graph, 4, 1))
这篇关于Reachability算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!