本文主要是介绍hdu Swipe Bo(bfs+状态压缩)错了多次的题,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Swipe Bo
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1549 Accepted Submission(s): 315
The main character of this game is a square blue tofu called Bo. We can swipe up / down / left / right to move Bo up / down / left / right. Bo always moves in a straight line and nothing can stop it except a wall. You need to help Bo find the way out.
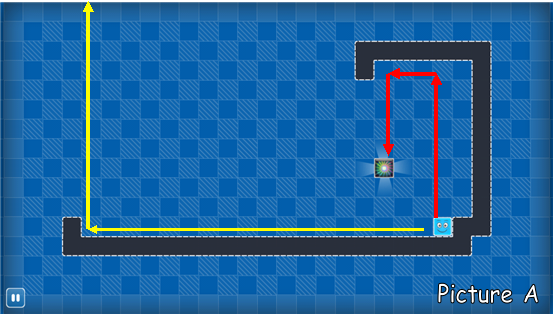
The picture A shows that we needs three steps to swipe Bo to the exit (swipe up, swipe left, swipe down). In a similar way, we need only two steps to make Bo disappear from the world (swipe left, swipe up)!
Look at the picture B. The exit is locked, so we have to swipe Bo to get all the keys to unlock the exit. When Bo get all the keys, the exit will unlock automatically .The exit is considered inexistent if locked. And you may notice that there are some turning signs, Bo will make a turn as soon as it meets a
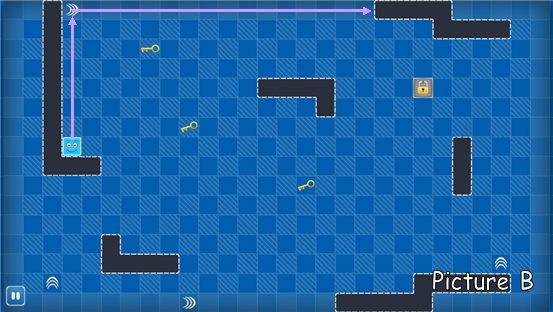
turning signs. For example, if we swipe Bo up, it will go along the purple line.
Now, your task is to write a program to calculate the minimum number of moves needed for us to swipe Bo to the exit.
The first line of each test case contains two integers N and M (1≤N, M≤200), which denote the sizes of the map. The next N lines give the map’s layout, with each line containing M characters. A character is one of the following: '#': represents the wall; 'S' represents the start point of the Bo; 'E' represents the exit; '.' represents an empty block; ‘K’ represents the key, and there are no more than 7 keys in the map; 'L','U','D','R' represents the turning sign with the direction of left, up, down, right.
5 6 ###### #....# .E...# ..S.## .##### 5 6 ###### #....# .....# SEK.## .##### 5 6 ###### #....# ....K# SEK.## .##### 5 6 ###### #....# D...E# S...L# .#####
3 2 7 -1
题意:有一个迷宫,包含墙、空白格子、起点S、终点E、方向格子(LRUD)和钥匙K。要求如下:
(1)每次转弯只能在碰到墙壁时(每次转弯的选择和初始时从S出发的方向选择均称为一次操作);
(2)对于方向格子,若到达该格子,不管周围是不是墙,必须转向该格子指示的方向(这个不算一次操作);
(3)若迷宫中没有钥匙存在,则求出S到E的最少操作次数;若有钥匙,则必须先遍历到每个钥匙之后才能去E(在这个过程中可以经过E也就是E不算做障碍)。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;const int N = 225;
const int inf = 1<<29;
struct node{int x,y,sta,stp;
};
int n,m,k;
char mapt[N][N];
int K[N][N];
bool vist[N][N][1<<7];
int dir[4][2]={0,-1,0,1,-1,0,1,0};int judge1(node& now,int &e){int flag=0;if(now.x<0||now.x>=n||now.y<0||now.y>=m)return 0;if(mapt[now.x][now.y]!='#'){if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='L')e=0,flag=1;else if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='R')e=1,flag=1;else if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='U')e=2,flag=1;else if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='D')e=3,flag=1;else if(mapt[now.x][now.y]=='K')now.sta|=(1<<K[now.x][now.y]);if(flag&&vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta])return 0;else if(flag) vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta]=1; //固定方向的位置,可以直接标记return 1;}else //遇到墙,退一格,在当前位置停止{now.x-=dir[e][0];now.y-=dir[e][1];return 2;}}
int bfs(int sx,int sy){queue<node>q;node now,pre;for(int i=0; i<n; i++)for(int j=0; j<m; j++)for(int sta=0; sta<(1<<k); sta++)vist[i][j][sta]=0;now.x=sx,now.y=sy,now.sta=0,now.stp=0;q.push(now);vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta]=1;while(!q.empty()){pre=q.front(); q.pop();pre.stp++;for(int te=0; te<4; te++){int e=te;now=pre;while(1){ //找到一个停止点,或不能走,或走过了,则跳出now.x+=dir[e][0];now.y+=dir[e][1];int flag=judge1(now,e);if(flag==0)break;if(flag==1&&mapt[now.x][now.y]=='E'&&now.sta==(1<<k)-1){return now.stp;}if(flag==2){if(vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta])break;vist[now.x][now.y][now.sta]=1;q.push(now);break;}}}}return -1;
}
int main()
{int sx,sy;while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)>0){k=0;for(int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%s",mapt[i]);for(int j=0; j<m; j++)if(mapt[i][j]=='S')sx=i,sy=j;else if(mapt[i][j]=='K')K[i][j]=k++;}printf("%d\n",bfs(sx,sy));}
}
这篇关于hdu Swipe Bo(bfs+状态压缩)错了多次的题的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






