本文主要是介绍whisper使用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
whisper使用
- 1. 直接调用 语音识别
- 2. 语种识别 whisper.detect_language()和whisper.decode()
- 3. 指定要识别的语种做语音识别
- **whisper 源码的transcribe函数**
- 函数解析
- 1. transcript.py
- 2. tokenizer.py
- 3. audio.py
- 4. __ init__.py
github: https://gitcode.com/openai/whisper/overview
1. 直接调用 语音识别
,transcribe()方法会读取整个文件,并使用一个30秒的滑动窗口对音频进行处理,对每个窗口进行自回归序列到序列的预测。
官网readme调用1
import whispermodel = whisper.load_model("base") # 加载模型
result = model.transcribe("audio.mp3") # 指定音频路径 识别
print(result["text"]) # 输出识别结果
load_model方法在__init__.py文件中有定义
{'text': ' 你一定會笑著說 二百克芝麻能力好耐架', 'segments': [{'id': 0, 'seek': 0, 'start': 0.0, 'end': 2.0, 'text': ' 你一定會笑著說', 'tokens': [50365, 10930, 24272, 6236, 11600, 19382, 4622, 50465], 'temperature': 0.0, 'avg_logprob': -0.5130815124511718, 'compression_ratio': 0.8253968253968254, 'no_speech_prob': 0.12529681622982025}, {'id': 1, 'seek': 0, 'start': 2.0, 'end': 5.5, 'text': ' 二百克芝麻能力好耐架', 'tokens': [50465, 220, 11217, 31906, 24881, 13778, 251, 38999, 8225, 13486, 2131, 4450, 238, 7360, 114, 50640], 'temperature': 0.0, 'avg_logprob': -0.5130815124511718, 'compression_ratio': 0.8253968253968254, 'no_speech_prob': 0.12529681622982025}], 'language': 'yue'}
2. 语种识别 whisper.detect_language()和whisper.decode()
以下是使用whisper.detect_language()和whisper.decode()的示例用法,这些方法提供对模型的更低级别访问。更低级别可以说是更底层的调用。
官网readme调用2
import whispermodel = whisper.load_model("base") # 加载预训练的语音识别模型,这里使用了名为"base"的模型。# load audio and pad/trim it to fit 30 seconds
audio = whisper.load_audio("audio.mp3")
audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio) # 对加载的音频进行填充或裁剪,使其适合30秒的滑动窗口处理。# make log-Mel spectrogram and move to the same device as the model
mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio).to(model.device)
# 将音频转换为对数梅尔频谱图,并将其移动到与模型相同的设备(如GPU)上进行处理。# detect the spoken language
_, probs = model.detect_language(mel) # 使用模型进行语言检测,返回检测到的语言和对应的概率。
# 打印检测到的语言,选取概率最高的语言作为结果。
print(f"Detected language: {max(probs, key=probs.get)}")# decode the audio
# 置解码的选项,如语言模型、解码器等。
options = whisper.DecodingOptions()
# 使用模型对音频进行解码,生成识别结果。
result = whisper.decode(model, mel, options)# print the recognized text
# 打印识别结果,即模型识别出的文本内容。
print(result.text)
3. 指定要识别的语种做语音识别
from whisper import load_model
from whisper.transcribe import transcribe
model = load_model(model_path, device=device)
# 指定model 音频路径 要识别的语言类型 yue--粤语
result = transcribe(model, audio_path, language="yue")
whisper 源码的transcribe函数
def transcribe(model: "Whisper",audio: Union[str, np.ndarray, torch.Tensor],*,verbose: Optional[bool] = None,temperature: Union[float, Tuple[float, ...]] = (0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0),compression_ratio_threshold: Optional[float] = 2.4,logprob_threshold: Optional[float] = -1.0,no_speech_threshold: Optional[float] = 0.6,condition_on_previous_text: bool = True,initial_prompt: Optional[str] = None,word_timestamps: bool = False,prepend_punctuations: str = "\"'“¿([{-",append_punctuations: str = "\"'.。,,!!??::”)]}、",clip_timestamps: Union[str, List[float]] = "0",hallucination_silence_threshold: Optional[float] = None,**decode_options,
):"""Transcribe an audio file using WhisperParameters----------model: WhisperThe Whisper model instanceaudio: Union[str, np.ndarray, torch.Tensor]The path to the audio file to open, or the audio waveformverbose: boolWhether to display the text being decoded to the console. If True, displays all the details,If False, displays minimal details. If None, does not display anythingtemperature: Union[float, Tuple[float, ...]]Temperature for sampling. It can be a tuple of temperatures, which will be successively usedupon failures according to either `compression_ratio_threshold` or `logprob_threshold`.compression_ratio_threshold: floatIf the gzip compression ratio is above this value, treat as failedlogprob_threshold: floatIf the average log probability over sampled tokens is below this value, treat as failedno_speech_threshold: floatIf the no_speech probability is higher than this value AND the average log probabilityover sampled tokens is below `logprob_threshold`, consider the segment as silentcondition_on_previous_text: boolif True, the previous output of the model is provided as a prompt for the next window;disabling may make the text inconsistent across windows, but the model becomes less prone togetting stuck in a failure loop, such as repetition looping or timestamps going out of sync.word_timestamps: boolExtract word-level timestamps using the cross-attention pattern and dynamic time warping,and include the timestamps for each word in each segment.prepend_punctuations: strIf word_timestamps is True, merge these punctuation symbols with the next wordappend_punctuations: strIf word_timestamps is True, merge these punctuation symbols with the previous wordinitial_prompt: Optional[str]Optional text to provide as a prompt for the first window. This can be used to provide, or"prompt-engineer" a context for transcription, e.g. custom vocabularies or proper nounsto make it more likely to predict those word correctly.decode_options: dictKeyword arguments to construct `DecodingOptions` instancesclip_timestamps: Union[str, List[float]]Comma-separated list start,end,start,end,... timestamps (in seconds) of clips to process.The last end timestamp defaults to the end of the file.hallucination_silence_threshold: Optional[float]When word_timestamps is True, skip silent periods longer than this threshold (in seconds)when a possible hallucination is detectedReturns-------A dictionary containing the resulting text ("text") and segment-level details ("segments"), andthe spoken language ("language"), which is detected when `decode_options["language"]` is None."""dtype = torch.float16 if decode_options.get("fp16", True) else torch.float32if model.device == torch.device("cpu"):if torch.cuda.is_available():warnings.warn("Performing inference on CPU when CUDA is available")if dtype == torch.float16:warnings.warn("FP16 is not supported on CPU; using FP32 instead")dtype = torch.float32if dtype == torch.float32:decode_options["fp16"] = False# Pad 30-seconds of silence to the input audio, for slicingmel = log_mel_spectrogram(audio, model.dims.n_mels, padding=N_SAMPLES)content_frames = mel.shape[-1] - N_FRAMEScontent_duration = float(content_frames * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE)if decode_options.get("language", None) is None:if not model.is_multilingual:decode_options["language"] = "en"else:if verbose:print("Detecting language using up to the first 30 seconds. Use `--language` to specify the language")mel_segment = pad_or_trim(mel, N_FRAMES).to(model.device).to(dtype)_, probs = model.detect_language(mel_segment)decode_options["language"] = max(probs, key=probs.get)if verbose is not None:print(f"Detected language: {LANGUAGES[decode_options['language']].title()}")language: str = decode_options["language"]task: str = decode_options.get("task", "transcribe")tokenizer = get_tokenizer(model.is_multilingual,num_languages=model.num_languages,language=language,task=task,)if isinstance(clip_timestamps, str):clip_timestamps = [float(ts) for ts in (clip_timestamps.split(",") if clip_timestamps else [])]seek_points: List[int] = [round(ts * FRAMES_PER_SECOND) for ts in clip_timestamps]if len(seek_points) == 0:seek_points.append(0)if len(seek_points) % 2 == 1:seek_points.append(content_frames)seek_clips: List[Tuple[int, int]] = list(zip(seek_points[::2], seek_points[1::2]))punctuation = "\"'“¿([{-\"'.。,,!!??::”)]}、"if word_timestamps and task == "translate":warnings.warn("Word-level timestamps on translations may not be reliable.")def decode_with_fallback(segment: torch.Tensor) -> DecodingResult:temperatures = ([temperature] if isinstance(temperature, (int, float)) else temperature)decode_result = Nonefor t in temperatures:kwargs = {**decode_options}if t > 0:# disable beam_size and patience when t > 0kwargs.pop("beam_size", None)kwargs.pop("patience", None)else:# disable best_of when t == 0kwargs.pop("best_of", None)options = DecodingOptions(**kwargs, temperature=t)decode_result = model.decode(segment, options)needs_fallback = Falseif (compression_ratio_threshold is not Noneand decode_result.compression_ratio > compression_ratio_threshold):needs_fallback = True # too repetitiveif (logprob_threshold is not Noneand decode_result.avg_logprob < logprob_threshold):needs_fallback = True # average log probability is too lowif (no_speech_threshold is not Noneand decode_result.no_speech_prob > no_speech_threshold):needs_fallback = False # silenceif not needs_fallback:breakreturn decode_resultclip_idx = 0seek = seek_clips[clip_idx][0]input_stride = exact_div(N_FRAMES, model.dims.n_audio_ctx) # mel frames per output token: 2time_precision = (input_stride * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE) # time per output token: 0.02 (seconds)all_tokens = []all_segments = []prompt_reset_since = 0if initial_prompt is not None:initial_prompt_tokens = tokenizer.encode(" " + initial_prompt.strip())all_tokens.extend(initial_prompt_tokens)else:initial_prompt_tokens = []def new_segment(*, start: float, end: float, tokens: torch.Tensor, result: DecodingResult):tokens = tokens.tolist()text_tokens = [token for token in tokens if token < tokenizer.eot]return {"seek": seek,"start": start,"end": end,"text": tokenizer.decode(text_tokens),"tokens": tokens,"temperature": result.temperature,"avg_logprob": result.avg_logprob,"compression_ratio": result.compression_ratio,"no_speech_prob": result.no_speech_prob,}# show the progress bar when verbose is False (if True, transcribed text will be printed)with tqdm.tqdm(total=content_frames, unit="frames", disable=verbose is not False) as pbar:last_speech_timestamp = 0.0# NOTE: This loop is obscurely flattened to make the diff readable.# A later commit should turn this into a simpler nested loop.# for seek_clip_start, seek_clip_end in seek_clips:# while seek < seek_clip_endwhile clip_idx < len(seek_clips):seek_clip_start, seek_clip_end = seek_clips[clip_idx]if seek < seek_clip_start:seek = seek_clip_startif seek >= seek_clip_end:clip_idx += 1if clip_idx < len(seek_clips):seek = seek_clips[clip_idx][0]continuetime_offset = float(seek * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE)window_end_time = float((seek + N_FRAMES) * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE)segment_size = min(N_FRAMES, content_frames - seek, seek_clip_end - seek)mel_segment = mel[:, seek : seek + segment_size]segment_duration = segment_size * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATEmel_segment = pad_or_trim(mel_segment, N_FRAMES).to(model.device).to(dtype)decode_options["prompt"] = all_tokens[prompt_reset_since:]result: DecodingResult = decode_with_fallback(mel_segment)tokens = torch.tensor(result.tokens)if no_speech_threshold is not None:# no voice activity checkshould_skip = result.no_speech_prob > no_speech_thresholdif (logprob_threshold is not Noneand result.avg_logprob > logprob_threshold):# don't skip if the logprob is high enough, despite the no_speech_probshould_skip = Falseif should_skip:seek += segment_size # fast-forward to the next segment boundarycontinueprevious_seek = seekcurrent_segments = []# anomalous words are very long/short/improbabledef word_anomaly_score(word: dict) -> float:probability = word.get("probability", 0.0)duration = word["end"] - word["start"]score = 0.0if probability < 0.15:score += 1.0if duration < 0.133:score += (0.133 - duration) * 15if duration > 2.0:score += duration - 2.0return scoredef is_segment_anomaly(segment: Optional[dict]) -> bool:if segment is None or not segment["words"]:return Falsewords = [w for w in segment["words"] if w["word"] not in punctuation]words = words[:8]score = sum(word_anomaly_score(w) for w in words)return score >= 3 or score + 0.01 >= len(words)def next_words_segment(segments: List[dict]) -> Optional[dict]:return next((s for s in segments if s["words"]), None)timestamp_tokens: torch.Tensor = tokens.ge(tokenizer.timestamp_begin)single_timestamp_ending = timestamp_tokens[-2:].tolist() == [False, True]consecutive = torch.where(timestamp_tokens[:-1] & timestamp_tokens[1:])[0]consecutive.add_(1)if len(consecutive) > 0:# if the output contains two consecutive timestamp tokensslices = consecutive.tolist()if single_timestamp_ending:slices.append(len(tokens))last_slice = 0for current_slice in slices:sliced_tokens = tokens[last_slice:current_slice]start_timestamp_pos = (sliced_tokens[0].item() - tokenizer.timestamp_begin)end_timestamp_pos = (sliced_tokens[-1].item() - tokenizer.timestamp_begin)current_segments.append(new_segment(start=time_offset + start_timestamp_pos * time_precision,end=time_offset + end_timestamp_pos * time_precision,tokens=sliced_tokens,result=result,))last_slice = current_sliceif single_timestamp_ending:# single timestamp at the end means no speech after the last timestamp.seek += segment_sizeelse:# otherwise, ignore the unfinished segment and seek to the last timestamplast_timestamp_pos = (tokens[last_slice - 1].item() - tokenizer.timestamp_begin)seek += last_timestamp_pos * input_strideelse:duration = segment_durationtimestamps = tokens[timestamp_tokens.nonzero().flatten()]if (len(timestamps) > 0and timestamps[-1].item() != tokenizer.timestamp_begin):# no consecutive timestamps but it has a timestamp; use the last one.last_timestamp_pos = (timestamps[-1].item() - tokenizer.timestamp_begin)duration = last_timestamp_pos * time_precisioncurrent_segments.append(new_segment(start=time_offset,end=time_offset + duration,tokens=tokens,result=result,))seek += segment_sizeif word_timestamps:add_word_timestamps(segments=current_segments,model=model,tokenizer=tokenizer,mel=mel_segment,num_frames=segment_size,prepend_punctuations=prepend_punctuations,append_punctuations=append_punctuations,last_speech_timestamp=last_speech_timestamp,)if not single_timestamp_ending:last_word_end = get_end(current_segments)if last_word_end is not None and last_word_end > time_offset:seek = round(last_word_end * FRAMES_PER_SECOND)# skip silence before possible hallucinationsif hallucination_silence_threshold is not None:threshold = hallucination_silence_thresholdif not single_timestamp_ending:last_word_end = get_end(current_segments)if last_word_end is not None and last_word_end > time_offset:remaining_duration = window_end_time - last_word_endif remaining_duration > threshold:seek = round(last_word_end * FRAMES_PER_SECOND)else:seek = previous_seek + segment_size# if first segment might be a hallucination, skip leading silencefirst_segment = next_words_segment(current_segments)if first_segment is not None and is_segment_anomaly(first_segment):gap = first_segment["start"] - time_offsetif gap > threshold:seek = previous_seek + round(gap * FRAMES_PER_SECOND)continue# skip silence before any possible hallucination that is surrounded# by silence or more hallucinationshal_last_end = last_speech_timestampfor si in range(len(current_segments)):segment = current_segments[si]if not segment["words"]:continueif is_segment_anomaly(segment):next_segment = next_words_segment(current_segments[si + 1 :])if next_segment is not None:hal_next_start = next_segment["words"][0]["start"]else:hal_next_start = time_offset + segment_durationsilence_before = (segment["start"] - hal_last_end > thresholdor segment["start"] < thresholdor segment["start"] - time_offset < 2.0)silence_after = (hal_next_start - segment["end"] > thresholdor is_segment_anomaly(next_segment)or window_end_time - segment["end"] < 2.0)if silence_before and silence_after:seek = round(max(time_offset + 1, segment["start"])* FRAMES_PER_SECOND)if content_duration - segment["end"] < threshold:seek = content_framescurrent_segments[si:] = []breakhal_last_end = segment["end"]last_word_end = get_end(current_segments)if last_word_end is not None:last_speech_timestamp = last_word_endif verbose:for segment in current_segments:start, end, text = segment["start"], segment["end"], segment["text"]line = f"[{format_timestamp(start)} --> {format_timestamp(end)}] {text}"print(make_safe(line))# if a segment is instantaneous or does not contain text, clear itfor i, segment in enumerate(current_segments):if segment["start"] == segment["end"] or segment["text"].strip() == "":segment["text"] = ""segment["tokens"] = []segment["words"] = []all_segments.extend([{"id": i, **segment}for i, segment in enumerate(current_segments, start=len(all_segments))])all_tokens.extend([token for segment in current_segments for token in segment["tokens"]])if not condition_on_previous_text or result.temperature > 0.5:# do not feed the prompt tokens if a high temperature was usedprompt_reset_since = len(all_tokens)# update progress barpbar.update(min(content_frames, seek) - previous_seek)return dict(text=tokenizer.decode(all_tokens[len(initial_prompt_tokens) :]),segments=all_segments,language=language,)
函数解析
1. transcript.py
kimichat:
这段代码是一个Python脚本,它使用了Whisper模型来进行音频转录。Whisper是一个由OpenAI开发的大型语音识别模型,能够处理多种语言和任务。以下是代码的主要功能和组件的逐行解释:
1-7行:导入了所需的库和模块,包括argparse(命令行参数解析)、os(操作系统交互)、traceback(错误跟踪)、warnings(警告信息)、numpy(科学计算)、torch(PyTorch深度学习库)、tqdm(进度条显示)。
9-14行:定义了一些常量和辅助函数,如FRAMES_PER_SECOND(每秒帧数)、HOP_LENGTH(帧跳跃长度)、N_FRAMES(每个音频段的帧数)、N_SAMPLES(音频样本数)、SAMPLE_RATE(采样率)等。
16-25行:定义了log_mel_spectrogram函数,用于将音频信号转换为Mel频率倒谱系数,这是语音识别中常用的特征表示方法。
27-36行:定义了pad_or_trim函数,用于对音频信号进行填充或裁剪,以匹配模型所需的输入长度。
38-55行:定义了transcribe函数,它是脚本的核心,负责加载音频、预处理、使用Whisper模型进行转录,并返回转录结果。它接受多种参数,如verbose(是否显示详细信息)、temperature(采样温度)、compression_ratio_threshold(压缩比阈值)等,这些参数影响转录过程和结果。
57-82行:在transcribe函数中,首先检查设备类型和数据类型(是否使用半精度浮点数),然后对音频进行预处理,包括检测语言、加载tokenizer、处理音频剪辑时间戳等。
84-131行:实现了一个循环,用于处理音频文件的每个剪辑段,进行转录,并更新进度条。
133-174行:在transcribe函数中,还实现了对转录结果的处理,包括添加单词时间戳、处理可能的幻觉(hallucination)和沉默段。
176-198行:定义了cli函数,它使用argparse解析命令行参数,并调用transcribe函数来处理音频文件。
200-206行:在cli函数中,根据用户输入的参数,加载了Whisper模型,并设置了输出格式和目录。
208-213行:实现了对每个音频文件的循环处理,调用transcribe函数进行转录,并将结果写入到文件中。
215-218行:最后,如果这个脚本作为主程序运行,它将执行cli函数,开始命令行界面。
整体来看,这个脚本提供了一个完整的命令行界面,允许用户指定音频文件、模型、输出格式和其他参数,以执行音频转录任务。它使用了Whisper模型的强大功能,能够处理多种语言和语音识别任务。
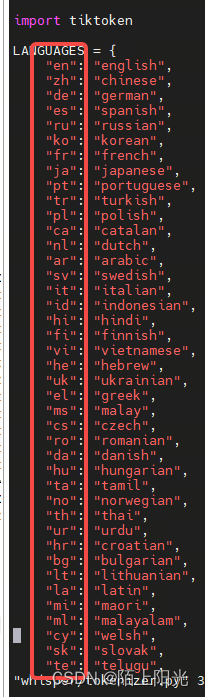
2. tokenizer.py
根据缩写指定要识别的语言
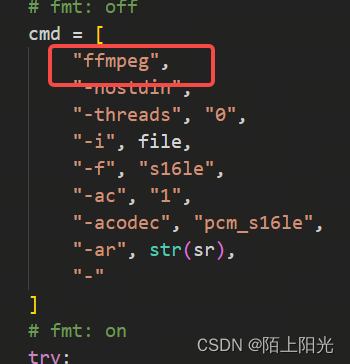
3. audio.py
处理音频用到了ffmpeg命令行工具,在运行环境要安装上ffmpeg命令行工具。
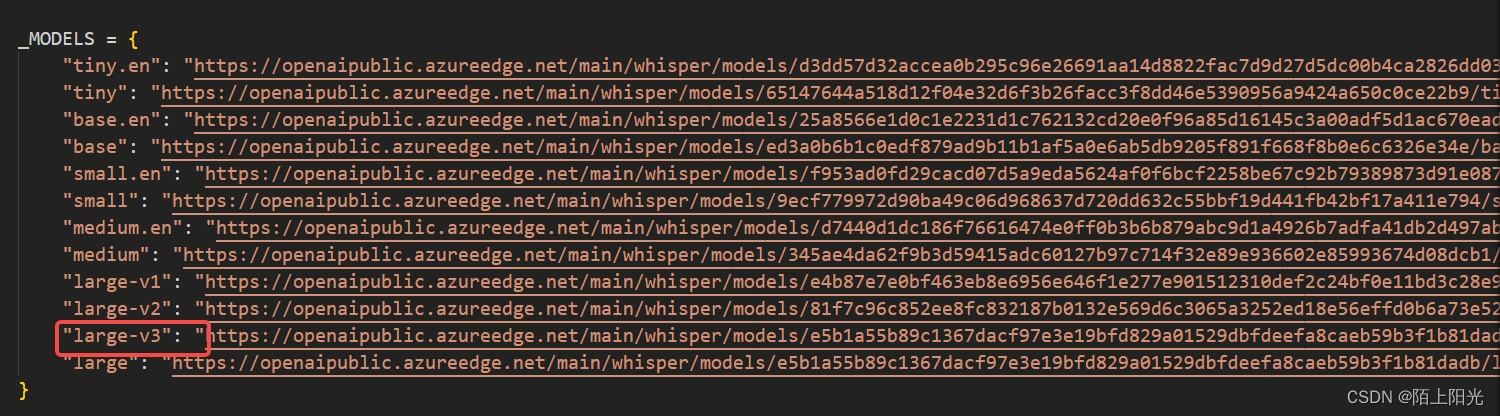
4. __ init__.py
指定要调用的模型, 可以把模型先下载到本地,直接指定模型路径加载本地模型。
grep -H “example” * 匹配内容的同时输出被匹配的文件名。
这篇关于whisper使用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




