本文主要是介绍Android单元测试/Ui测试+JaCoCo覆盖率统计,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Android单元测试/Ui测试+JaCoCo覆盖率统计
背景说明
-
单元测试
从源代码着手,对源码中的最小可测试单元进行检查和验证,在对源代码有较深的理解下,编写测试单元,工作量大,不管从编写单元测试用例再到用例的维护上,成本都会比较高,但是通过这种方式可靠性很强。 -
UI测试
从UI层面着手,对UI操作进行检查和验证,可以不需要对代码有深层次的了解,成本相对较低,工作量相对也低一些,但是可靠性相比之下会弱一点。 -
覆盖率的统计
我们有了多种测试方式,那么问题来了,这些测试的性能怎么样,是不是所有的代码都被测试过了?这时候就需要加入覆盖率的统计了,如果一个工程的待测数量为M,测试用例的数量为N,那么代码覆盖率F则为:
F=N/M
本文将介绍一个代码覆盖率的工具JaCoCo,通过这个工具,我们可以知道哪些方法被测试了,哪些方法没有被测试到。
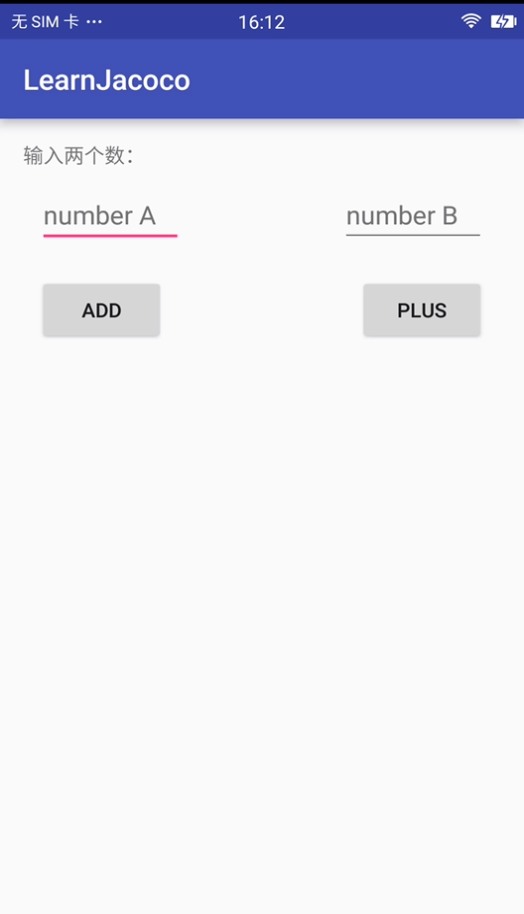
1. 先新建一个Android工程,大致的内容是有一个MainActivity,输入两个数,可以计算出二者相加、相乘的结果,并通过toast显示出计算结果。
- app界面如下:
- 源代码
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:id="@+id/activity_main"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="vertical"android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"tools:context="com.learn.learnjacoco.MainActivity"><TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="输入两个数:" /><RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_margin="10dp"android:orientation="horizontal"><EditText
android:hint="number A"android:id="@+id/edt_numA"android:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"android:inputType="number" /><EditText
android:hint="number B"android:id="@+id/edt_numB"android:layout_width="100dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_alignParentRight="true"android:inputType="number" /></RelativeLayout><RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_margin="10dp"><Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"android:onClick="add"android:text="add" /><Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_alignParentRight="true"android:onClick="plus"android:text="plus" /></RelativeLayout></LinearLayout>
MainActivity
package com.learn.learnjacoco;import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {public EditText edtNumA, edtNumB;int a, b;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);edtNumA = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edt_numA);edtNumB = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edt_numB);}public void add(View v) {if (getMyNum()) {String info = String.valueOf(MyUtils.add(a, b));Toast.makeText(this, "计算结果:" + info, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}else {Toast.makeText(this, "数字不合法", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}}public void plus(View v) {if (getMyNum()) {String info = String.valueOf(MyUtils.plus(a, b));Toast.makeText(this, "计算结果:" + info, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}else {Toast.makeText(this, "数字不合法", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}}public boolean getMyNum() {String aStr = edtNumA.getText().toString();String bStr = edtNumB.getText().toString();if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(aStr) && !TextUtils.isEmpty(bStr)) {a = Integer.parseInt(aStr);b = Integer.parseInt(bStr);return true;}return false;}
}
MyUtils
package com.learn.learnjacoco;public class MyUtils {public static int add(int a, int b) {return (a + b);}public static int plus(int a, int b) {return (a * b);}
}以上完成了之后,先试运行一下,保证app能正常运行起来。
2. 编写单元测试
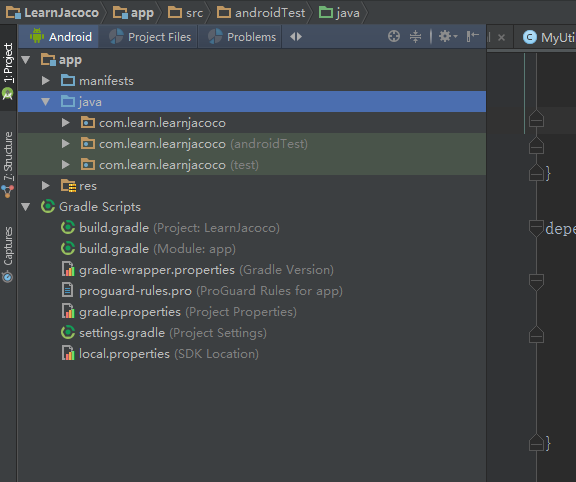
将视图切换到Android视图,如下:
可以看到com.learn.learnjacoco有三个,第一个存放工程的源码,后面两个放的是测试代码,分别为androidTest和test,这里顺带说明一下,androidTest一般存放的是和Android相关的测试,比如需要用到context等时候应该把测试放到该包下,而test对应的是Java相关的测试,也android无关的应该放到此包下。我们直接使用AndroidTest的包。
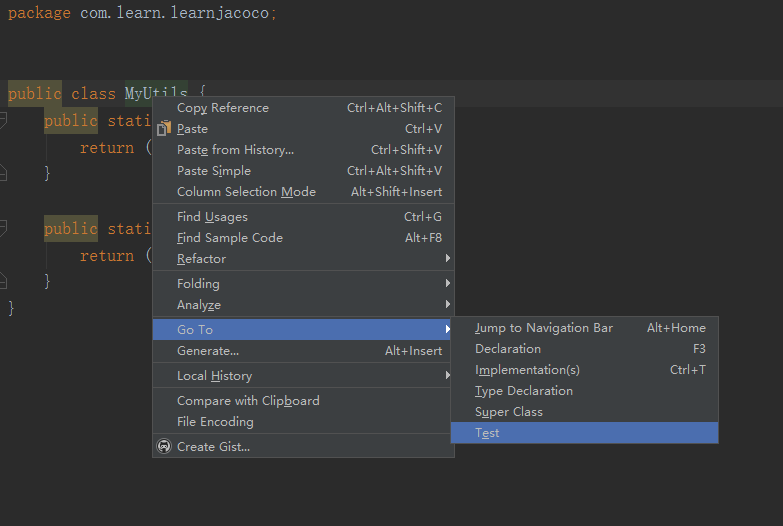
打开MyUtils.java,对着类名右键,Go to – Test – CreateNewTest – 把要测试的方法打上勾 – 选择存放在AndroidTest包下,如图:
补充MyUtilsTest的内容如下:
package com.learn.learnjacoco;import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;public class MyUtilsTest {@Testpublic void add() throws Exception {Assert.assertEquals(3,MyUtils.add(1,2));}@Testpublic void plus() throws Exception {Assert.assertEquals(30,MyUtils.plus(10,3));}}3. 编写UI测试
这里我们使用robotium编写UI测试用例(你也可以使用uiautomator去编写,效果是一样的),首先,我们需要配置gradle(app),添加robotium的依赖。
dependencies {...androidTestCompile 'com.jayway.android.robotium:robotium-solo:5.1'
}接下来,在androidTest包下,我们创建一个MainActivity的测试类,内容如下:
package com.learn.learnjacoco;import android.test.ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2;import com.robotium.solo.Solo;import junit.framework.Assert;public class MainActivityTest extends ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2 {private Solo solo;private MainActivity mActivity;public MainActivityTest() {super(MainActivity.class);}@Overridepublic void setUp() throws Exception {super.setUp();solo = new Solo(getInstrumentation(), getActivity());mActivity = (MainActivity) getActivity();}@Overridepublic void tearDown() throws Exception {super.tearDown();}public void testInputA() throws Exception {solo.enterText(mActivity.edtNumA, "10");Assert.assertEquals("10", mActivity.edtNumA.getText().toString());}public void testInputB() throws Exception {solo.enterText(mActivity.edtNumB, "3");Assert.assertEquals("3", mActivity.edtNumB.getText().toString());}
}
4. 运行connectedAndroidTest
在Android Studio的右侧垂直栏中,有一个小的gradle图标,点开,如下图(如果没有内容,可以点击刷新):
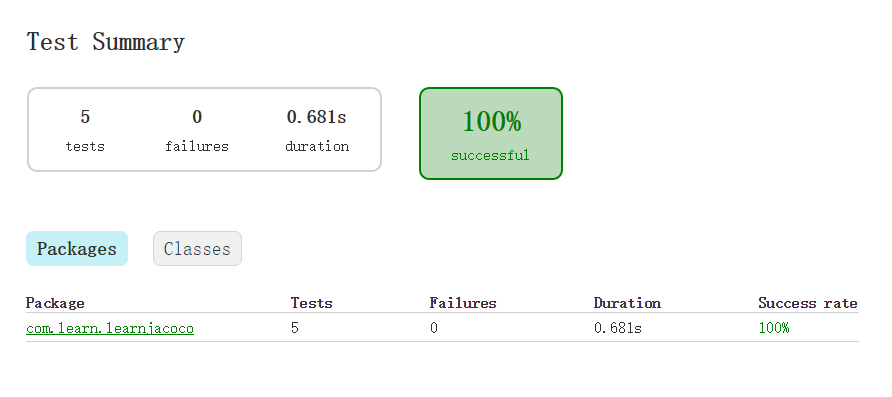
运行完毕之后,进入到工程目录 $app\build\reports\androidTests\connected下,打开index.xml,这个文件中会存放这本次测试的结果,即使测试不通过,也会保留错误信息,如下图:
这篇关于Android单元测试/Ui测试+JaCoCo覆盖率统计的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!