本文主要是介绍力扣437. 路径总和 III,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Problem: 437. 路径总和 III
文章目录
- 题目描述
- 思路
- 复杂度
- Code
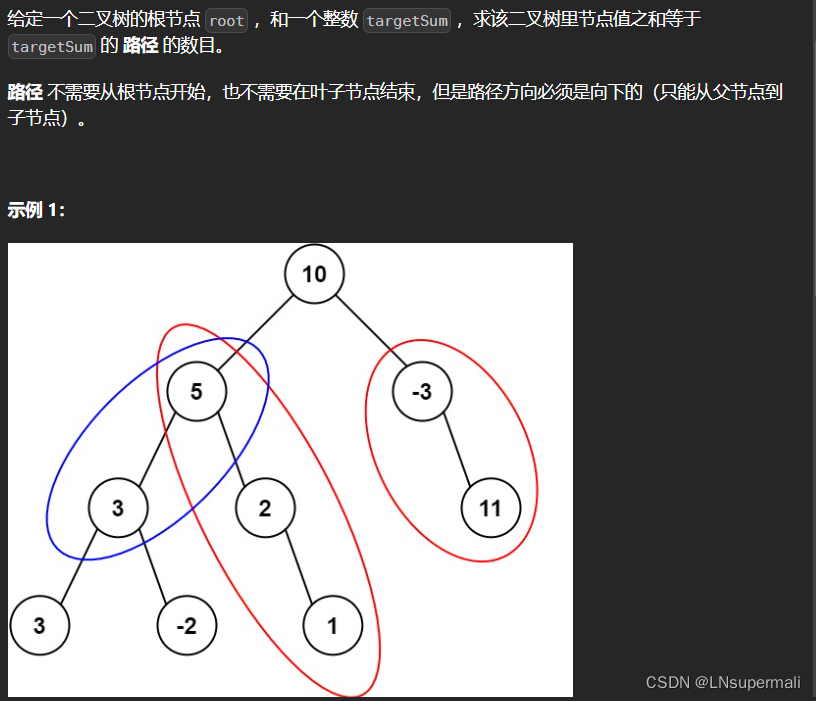
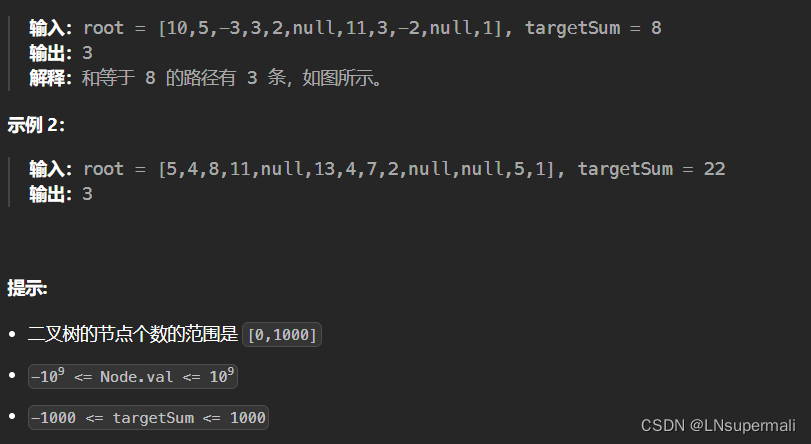
题目描述
思路
1.定义int类型函数rootSum(root, targetSum),用于求取每一个节点等于目标函数的路径数:
1.1.易知rootSum(root, targetSum)求出的数量等于rootSum(root.left, targetSum - value)求出的数量加上rootSum(root.right, targetSum - value)求出的数量,其中value是当前遍历到的节点的节点值
1.2.若当前的value值等于targetSum,则所求的路径总和加一;
2.在pathSum函数中实现对每一个节点调用rootSum函数得出最终的路劲总和数
复杂度
时间复杂度:
O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2);其中 n n n为二叉树节点的个数
空间复杂度:
O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
Code
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {/*** Path Sum III** @param root The root of binary tree* @param targetSum The target number* @return int*/public int pathSum(TreeNode root, long targetSum) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int res = rootSum(root, targetSum);res += pathSum(root.left, targetSum);res += pathSum(root.right, targetSum);return res;}/*** Find the sum of the target paths of each node** @param root The root of binary tree* @param targetSum The target number* @return int*/public int rootSum(TreeNode root, long targetSum) {int res = 0;if (root == null) {return 0;}int value = root.val;if (value == targetSum) {res++;}res += rootSum(root.left, targetSum - value);res += rootSum(root.right, targetSum - value);return res;}
}
这篇关于力扣437. 路径总和 III的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!