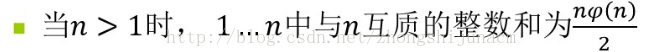本文主要是介绍HDU 2588 GCD GCD问题总结,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
GCD(一)
题目:
The greatest common divisor GCD(a,b) of two positive integers a and b,sometimes written (a,b),is the largest divisor common to a and b,For example,(1,2)=1,(12,18)=6.
(a,b) can be easily found by the Euclidean algorithm. Now Carp is considering a little more difficult problem:
Given integers N and M, how many integer X satisfies 1<=X<=N and (X,N)>=M.
求满足题目要求的x个数。
算法:
直接筛选会超时,根据题目给出的不等式特点GCD(x,N) >= M 可以知道满足题目要求的一定是N的因子而且必须大于等于M(想想为什么?解体关键)。所以,只要枚举N的大于等于M的因子就可以了。因为,在10^9内最多的因子数不超过30个。所以,总时间是O(30*loglogn)接近常数。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;typedef __int64 LL;
const int MOD = 1000000007;int euler_phi(int n){int k = (int)sqrt(n + 0.5);int ans = n;for(int i = 2;i <= k;++i) if(0 == n % i){ans = ans / i * (i - 1);while(0 == n % i) n /= i;}if(n > 1) ans = ans / n * (n - 1);return ans;
}LL getFact(int n,int m){LL res = 0;int k = sqrt(n + 0.5);int tmp;for(int i = 1;i <= k;++i){if(0 == n % i){tmp = n / i;if(i >= m) res += euler_phi(n / i);if(tmp >= m && i != tmp) res += euler_phi(n / tmp);}}return res;
}int main()
{int T,n,m;scanf("%d",&T);while(T--){scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);if(n == 1 && m == 1){puts("1");continue;}printf("%I64d\n",getFact(n,m));}return 0;
}
GCD(二)
题目:
给你一个数N,使得在1~N之间能够找到x使得x满足gcd( x , N ) >= M,求解gcd(x,N)的和。
算法:
由上题的知识可以知道,1...N的互质个数为欧拉函数值且其gcd只能是N的因子。所以,对于N = x * y。我们只要
求出x在y内的互质个数就好了,结果乘以x就是gcd = x的和了.
证明:
SUM(gcd = x ) = 1*x + 2*x + 3*x ..... y*x
所以,当gcd = x的时候只要求出y的欧拉函数值就好了。
而一个数的因子又可以在sqrt(N)内求出。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;typedef long long LL;int euler_phi(int n){int m = sqrt(n + 0.5);int ans = n;for(int i = 2;i <= m;++i) if(0 == n % i){ans = ans / i * (i - 1);while(0 == n % i) n /= i;}if(n > 1) ans = ans / n * (n - 1);return ans;
}LL solve(int n,int m){LL res = 0;int k = sqrt(n + 0.5);for(int i = 1;i <= k;++i){if(0 == n % i){if(i >= m)res += i * euler_phi(n / i);if(i != n / i && n / i >= m)res += n / i * euler_phi(i);}}return res;
}int main()
{int n,m;while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){printf("%lld\n",solve(n,m));}return 0;
}
GCD(三)
题目:
The greatest common divisor GCD(a,b) of two positive integers a and b,sometimes written (a,b),is the largest divisor common to a and b,For example,(1,2)=1,(12,18)=6.
(a,b) can be easily found by the Euclidean algorithm. Now Carp is considering a little more difficult problem:
Given integers N and M,please answer sum of X satisfies 1<=X<=N and (X,N)>=M.
算法:
跟GCD(一)不同的是这题求得是满足gcd(x,n) >= m ,x的和。而由欧拉函数中的一个定理可以知道
所以,只要SUM(n = x * y) = y*α(y) / 2 * x
因为要的是x的和,而我们是在把X先进行X / x处理的所以最后要在乘回上x得到原值。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;typedef long long LL;
const int MOD = 1000000007;int euler_phi(int n){int k = (int)sqrt(n + 0.5);int ans = n;for(int i = 2;i <= k;++i) if(0 == n % i){ans = ans / i * (i - 1);while(0 == n % i) n /= i;}if(n > 1) ans = ans / n * (n - 1);return ans;
}LL getFact(int n,int m){LL res = 0;int k = sqrt(n + 0.5);LL tmp;for(int i = 1;i <= k;++i){if(0 == n % i){tmp = n / i;if(i >= m){LL t1 = tmp * euler_phi(tmp) / 2 % MOD;t1 = t1 ? t1 : 1;res = (res + t1 * i) % MOD;}if(tmp >= m && i != tmp) {LL t1 = i * euler_phi(i) / 2 % MOD;t1 = t1 ? t1 : 1;res = (res + t1 * tmp) % MOD;}}}return res >= MOD ? res%MOD : res;
}int main()
{int T,n,m;scanf("%d",&T);while(T--){scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);printf("%lld\n",getFact(n,m));}return 0;
}
这篇关于HDU 2588 GCD GCD问题总结的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!