本文主要是介绍asyncionetworkxFuncAnimation学习--动态显示计算图的运行情况,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
asyncio&networkx&FuncAnimation学习--动态显示计算图的运行情况
- 一.效果
- 二.代码
一.目的
1.动态显示计算图的运行状态(点或边是否已完成)
二.步骤:
1.定义计算图
2.asyncio 并行计算
3.networkx 显示计算图
4.FuncAnimation 动态更新
三.依赖:
conda install pygraphviz
一.效果
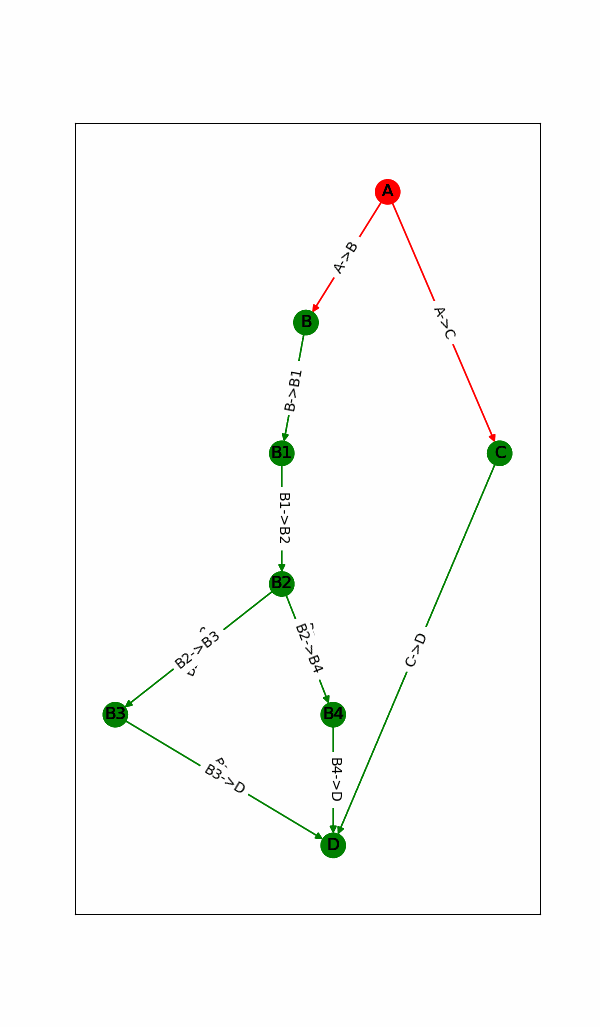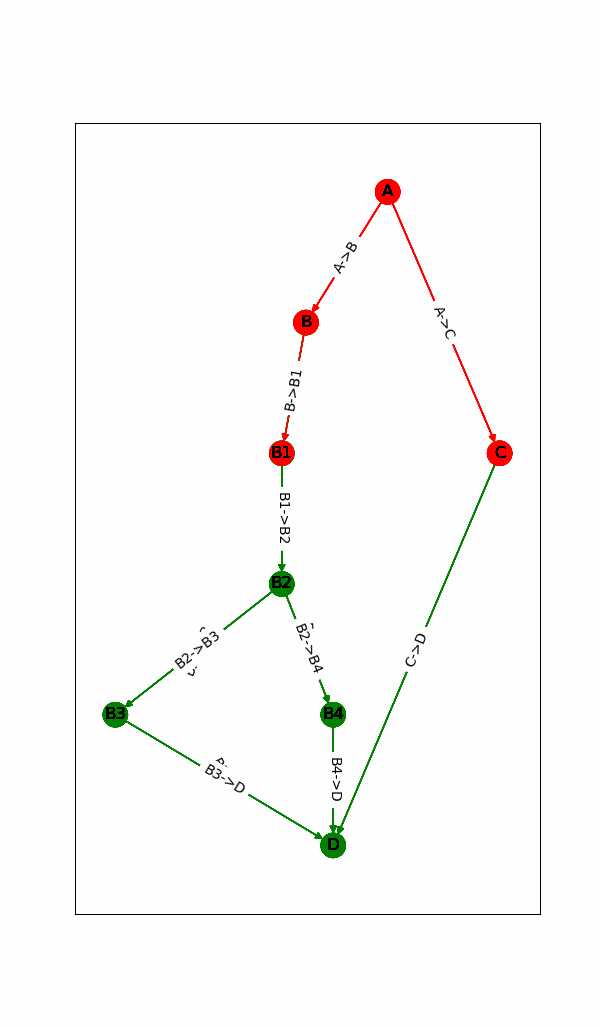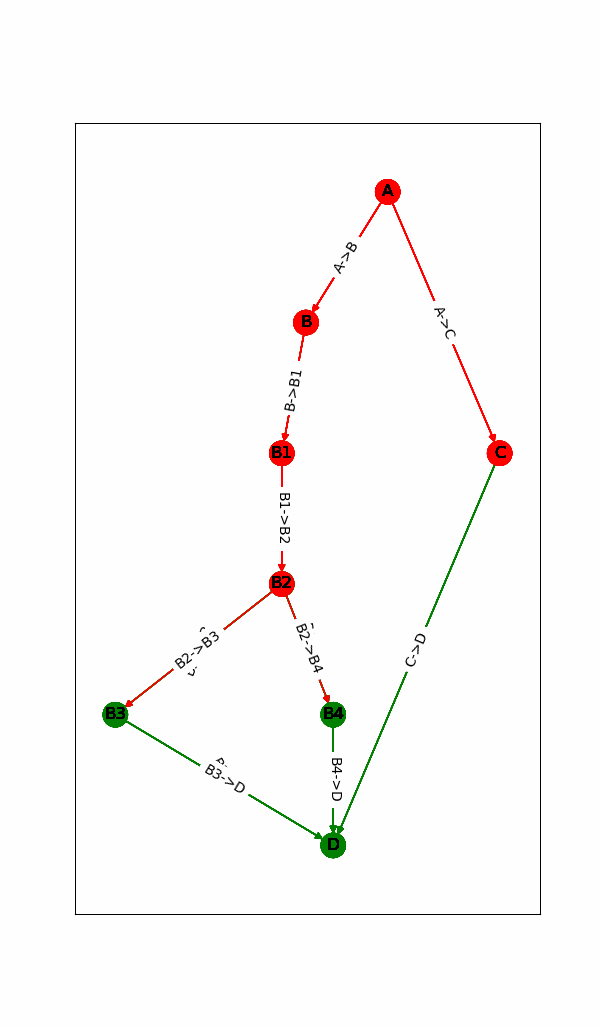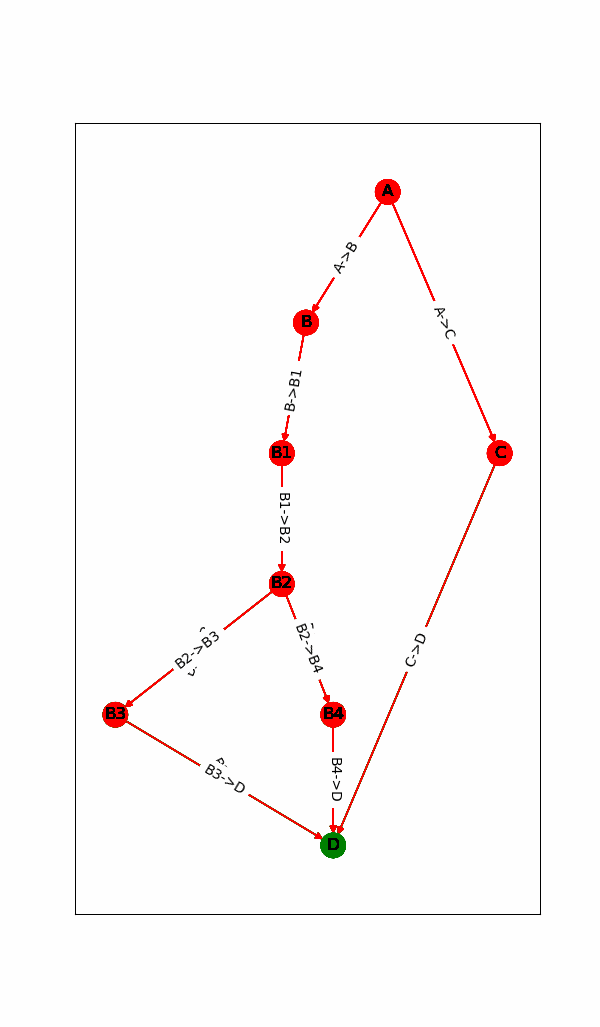
二.代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-'''
一.目的
1.动态显示计算图的运行状态(点或边是否已完成)
二.步骤:
1.定义计算图
2.asyncio 并行计算
3.networkx 显示计算图
4.FuncAnimation 动态更新
三.依赖:
conda install pygraphviz
'''import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import asyncio
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
import asyncio
import datetime
import numpy as np
import threading
from io import BytesIO
from PIL import Imageclass Node:'''节点信息'''event_man = {}node_refs = {} def __init__(self, name, inputs,callback) -> None:self.name = nameself.event_man = Node.event_manself.callback = callbackself.node_refs = Node.node_refsself.event_man[self.name] = Noneself.node_refs[self.name] = inputsself.delay = np.random.randint(1, 5)async def run(self):# 等待上游节点for ev in self.node_refs[self.name]:await self.event_man[ev].wait()self.callback((ev, self.name), "edge")# 模拟耗时await asyncio.sleep(self.delay)# 触发下游节点self.callback(f"{self.name}", "node")self.event_man[self.name].set()if __name__ == "__main__":G = nx.DiGraph()node_colors = {}edge_colors = {}semaphore = threading.Semaphore(0)def event_callback(name, event):print(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%H:%M:%S.%f"), name)# 修改节点或边的颜色if event == "node":node_colors[name] = "red"elif event == "edge":edge_colors[name] = "red"semaphore.release()graph_nodes = []graph_nodes.append(Node("A", [], event_callback))graph_nodes.append(Node("B", ["A"], event_callback))graph_nodes.append(Node("B1", ["B"], event_callback))graph_nodes.append(Node("B2", ["B1"], event_callback))graph_nodes.append(Node("B3", ["B2"], event_callback))graph_nodes.append(Node("B4", ["B2"], event_callback))graph_nodes.append(Node("C", ["A"], event_callback))graph_nodes.append(Node("D", ["B4", "B3", "C"], event_callback))# 添加节点for x in graph_nodes:G.add_node(x.name, name=x.name, color="green")# 添加边for k, v in Node.node_refs.items():for j in v:G.add_edge(j, k, name=f"{j}->{k}", color="green")# 设置layoutfor layer, nodes in enumerate(nx.topological_generations(G)):for node in nodes:G.nodes[node]["layer"] = layer#pos = nx.multipartite_layout(G, subset_key="layer")pos = nx.nx_agraph.pygraphviz_layout(G, prog='dot') #垂直布局node_labels = nx.get_node_attributes(G, 'name')edge_labels = nx.get_edge_attributes(G, 'name')node_colors = nx.get_node_attributes(G, 'color')edge_colors = nx.get_edge_attributes(G, 'color')async def graph_forward(nodes):global node_colorsglobal edge_colorsnode_colors = nx.get_node_attributes(G, 'color')edge_colors = nx.get_edge_attributes(G, 'color')for k in Node.event_man.keys():Node.event_man[k] = asyncio.Event() await asyncio.gather(*[asyncio.create_task(x.run()) for x in nodes])fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,12))snapshots = []def fig_update(data):semaphore.acquire() #有事件触发才更新nx.draw_networkx_labels(G, pos, labels=node_labels)nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G, pos, edge_labels=edge_labels)nx.draw_networkx(G, pos,nodelist=node_colors.keys(),node_color=node_colors.values(),edgelist=edge_colors.keys(),edge_color=edge_colors.values())# 截图buf = BytesIO()plt.savefig(buf, format='png')buf.seek(0)pil_image = Image.open(buf)snapshots.append(pil_image)ani = FuncAnimation(fig, fig_update, interval=100)def trigger(snapshots):while True:asyncio.run(graph_forward(graph_nodes))# 保存gifsnapshots[1].save("out.gif",save_all=True,append_images=snapshots[2:],duration=500,loop=0)print("Finished")breakt=threading.Thread(target=trigger, args=(snapshots,))t.setDaemon(True)t.start()plt.show()
这篇关于asyncionetworkxFuncAnimation学习--动态显示计算图的运行情况的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




