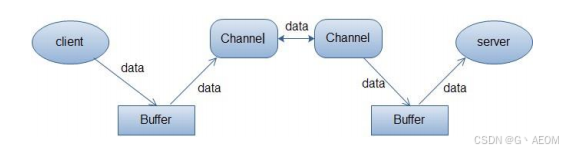
本文主要是介绍NIO - MappedByteBuffer,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
*MappedByteBuffer的创建
在FileChannel上调用map方法 返回一个MappedByteBuffer对象
- public MappedByteBuffer map(MapMode mode, long position, long size)
1.READ_ONLY 只读映射模式
2.READ_WRITE 读/写映射模式
3.PRIVATE 通过put方法对MappedByteBuffer的修改 不会修改到磁盘文件 只是虚拟内存的修改
*MappedByteBuffer在父类ByteBuffer的基础上 新增的几个方法
1.fore缓冲区在READ_WRITE模式下,此方法对缓冲区所做的内容更改强制写入文件
2.load:将缓冲区的内容载入物理内存,并返回该缓冲区的引用
3.isLoaded:判断缓冲区的内容是否在物理内存,如果在则返回true,否则返回false
- private final static Charset charset = Charset.forName("GBK");
- /**
- * 读文件
- * <br>------------------------------<br>
- * @param path
- * @return
- * @throws IOException
- */
- private static String read(String path) throws IOException {
- if (path == null || path.length() == 0) return null;
- FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path);
- FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
- MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, fileChannel.size());
- fileInputStream.close();
- fileChannel.close();
- String str = charset.decode(mappedByteBuffer).toString();
- mappedByteBuffer = null;
- return str;
- }
- /**
- * 追加内容
- * <br>------------------------------<br>
- * @param path
- * @param str
- * @return
- * @throws IOException
- */
- private static MappedByteBuffer append(String path, String str) throws IOException {
- if (str == null || str.length() == 0) return null;
- RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(path, "rw");
- FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
- byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
- long size = fileChannel.size() + bytes.length;
- MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, size);
- fileChannel.close();
- randomAccessFile.close();
- int position = mappedByteBuffer.limit() - bytes.length;
- mappedByteBuffer.position(position);
- mappedByteBuffer.put(bytes);
- mappedByteBuffer.force();
- mappedByteBuffer.flip();
- return mappedByteBuffer;
- }
- /**
- * 文件复制
- * <br>------------------------------<br>
- * @param srcfilePath
- * @param targetPath
- * @throws IOException
- */
- private static void copy(String srcfilePath, String targetPath) throws IOException {
- File file = new File(targetPath);
- if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
- file.mkdirs();
- }
- RandomAccessFile inRandomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(srcfilePath, "r");
- FileChannel inFileChannel = inRandomAccessFile.getChannel();
- MappedByteBuffer inMappedByteBuffer = inFileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inFileChannel.size());
- inRandomAccessFile.close();
- inFileChannel.close();
- RandomAccessFile outRandomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(targetPath, "rw");
- FileChannel outFileChannel = outRandomAccessFile.getChannel();
- MappedByteBuffer outMappedByteBuffer = outFileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inMappedByteBuffer.capacity());
- outMappedByteBuffer.put(inMappedByteBuffer);
- outMappedByteBuffer.force();
- outRandomAccessFile.close();
- outFileChannel.close();
- outMappedByteBuffer.flip();
- }
- /**
- * 不会更新到文件 只会更新虚拟内存
- * <br>------------------------------<br>
- * @param path
- * @param str
- * @return
- * @throws IOException
- */
- private static MappedByteBuffer doTestPrivateMode(String path, String str) throws IOException {
- if (str == null || str.length() == 0) return null;
- RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(path, "rw");
- FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
- byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
- long size = fileChannel.size() + bytes.length;
- MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = fileChannel.map(MapMode.PRIVATE, 0, size);
- mappedByteBuffer.put(bytes);
- fileChannel.close();
- randomAccessFile.close();
- mappedByteBuffer.flip();
- System.out.println(charset.decode(mappedByteBuffer));
- return mappedByteBuffer;
- }
这篇关于NIO - MappedByteBuffer的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!