本文主要是介绍Druid kafka-index supervisor启动流程分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言
在维护druid服务的过程中,我们的物化视图的supervisor状态总是发生异常,通过日志以及MR程序的情况来看,目前猜测是因为yarn资源问题导致的这一现状。虽然现在通过脚本监控的形式来保证物化视图supervisor异常时重新拉起而不会产生物化视图延迟(尤其是晚上发生异常)。但是不能明确为什么supervisor的执行流程。因此本着探究supervisor的心态,因为kafka-index supervisor比较成熟且经典,于是先研究下kafka-index supervisor先熟悉supervisor在代码中是一个怎样的形式存在的。
上图
先上一个启动supervisor的代码执行流程图。supervisor有一个管理器,是在启动overlord的时候创建的,即supervisor是被overlord管理的。supervisor管理器维护着druid服务中所有的supervisor服务并会将supervisor信息持久化到元数据库。overlord还会还会创建一个supervisor的资源请求入口,用于接收操作supervisor的RESTful请求。最终通过SupervisorResource的specPost方法接收创建supervisor的请求。

上代码
启动overlord服务, 执行overlord.sh 会携带overlord参数跳转到执行node.sh, 如下图是node.sh的主要执行步骤。

然后在代码中找到这个类,看一下是如何启动的?

上图中,在main函数中执行了run方法,而cli的build,获取的其实是clioverlord这个runnable。那么supervisorResource在CliOverlord中是如何实现的呢?通过注入的方式创建supervisorResource对象。
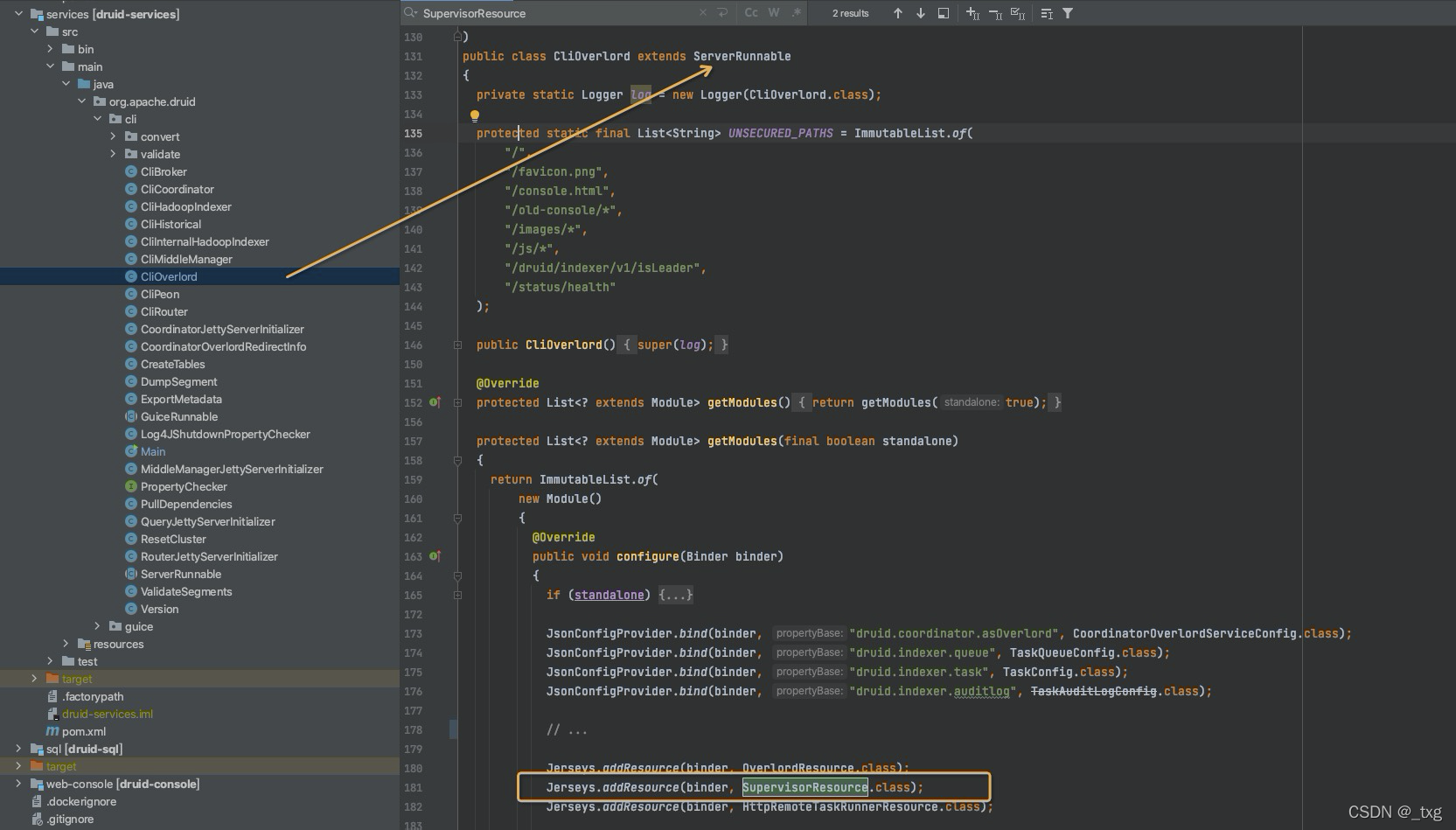
SupervisorResource是一个资源类,被@path注解,可以接收restful请求。外部发送一个创建supervisor的post请求,会路由的specPost方法上进行接下来的创建操作。
然后通过supervisorSpec进行创建supervisor并调用start()方法进行启动。其中supervisorSpec是注入的配置文件信息对象。在调用SupervisorResource的specPost请求的时候传入的参数。
@Path("/druid/indexer/v1/supervisor") // 表明SupervisorResource是个资源类, 并指定了URI访问路径,供RESTful请求
public class SupervisorResource
{@POST //用于接受post请求@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) // 它定义资源类或MessageBodyReader的方法可以生成的媒体类型@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) // 它定义资源类或MessageBodyWriter的方法可以生成的媒体类型public Response specPost(final SupervisorSpec spec, @Context final HttpServletRequest req){return asLeaderWithSupervisorManager(manager -> {Preconditions.checkArgument(spec.getDataSources() != null && spec.getDataSources().size() > 0,"No dataSources found to perform authorization checks");Access authResult = AuthorizationUtils.authorizeAllResourceActions(req,Iterables.transform(spec.getDataSources(), AuthorizationUtils.DATASOURCE_WRITE_RA_GENERATOR),authorizerMapper);if (!authResult.isAllowed()) {throw new ForbiddenException(authResult.toString());}manager.createAndStartSupervisorInternal(spec); // 调用创建supervisor的函数return Response.ok(ImmutableMap.of("id", spec.getId())).build();});}/*** 如果存在已经创建的supervisor则返回false, 如果创建新的supervisor则返回true*/private boolean createAndStartSupervisorInternal(SupervisorSpec spec, boolean persistSpec){String id = spec.getId();if (supervisors.containsKey(id)) {return false;}// 先进行插入基本信息到元数据库if (persistSpec) { // persistSpec 如果为true表示创建新的supervisor;如果为false表示启动supervisorManager的时候从元数据库中恢复supervisormetadataSupervisorManager.insert(id, spec);}Supervisor supervisor;try {supervisor = spec.createSupervisor();supervisor.start(); // 通过supervisorSpec创建完supervisor后进行启动}catch (Exception e) {// 为了保证事务,如果创建supervisor异常了则将元数据进行更新// Supervisor creation or start failed write tombstone only when trying to start a new supervisorif (persistSpec) {metadataSupervisorManager.insert(id, new NoopSupervisorSpec(null, spec.getDataSources()));}throw new RuntimeException(e);}supervisors.put(id, Pair.of(supervisor, spec));return true;}
}KafkaSupervisor的父类SeekableStreamSupervisor中的start()方法来启动supervisor。start()方法调用tryInit()方法来真正的启动一个supervisor。
1. supervisor线程会循环处理一个Notice类型的阻塞队列,Notice大概的内容包括运行task的notice、做checkpoint的notice、resetSuperviser的notice、shutdownSupervisor的notice。具体notice是如何添加到阻塞队列的、notice做了哪些事情在后期详细分享。
2. 在启动一个线程之前会先创建一个recordSupplier对象,即KafkaRecirdSupplier对象,这个类主要做的工作是关于处理kafka topic、kafka offset以及kakfa数据的类。比如kafka.poll() 进行获取数据,kafka.assign()和kafka.seek()方法进行处理partation和offset。
在追溯KafkaRecordSupplier这个类的时候,发现有三个地方在创建KafkaRecordSupplier对象。为什么一个kafkaSupervisor任务有三个对象,分别在做什么?后续会单独对KafkaRecordSupplier做分享。
@VisibleForTestingpublic void tryInit(){synchronized (stateChangeLock) {if (started) {log.warn("Supervisor was already started, skipping init");return;}if (stopped) {log.warn("Supervisor was already stopped, skipping init.");return;}try {// 这个地方创建了一个kafkarecordSupplier, 该对象是在setupRecordSupplier()方法中new的recordSupplier = setupRecordSupplier();// 向单线程池中提交一个线程, 这个线程运行supervisorexec.submit(() -> {try {// MAX_RUN_FREQUENCY_MILLIS 是任务的运行周期,默认是一秒long pollTimeout = Math.max(ioConfig.getPeriod().getMillis(), MAX_RUN_FREQUENCY_MILLIS);// 开一个循环执行, 所以supervisor的状态变更是需要加锁的,为了当其他线程stoped的时候是线程安全的while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() && !stopped) {// notices是一个阻塞的双端队列,存储Noticefinal Notice notice = notices.poll(pollTimeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);if (notice == null) {continue;}try {notice.handle();}catch (Throwable e) {stateManager.recordThrowableEvent(e);log.makeAlert(e, "SeekableStreamSupervisor[%s] failed to handle notice", dataSource).addData("noticeClass", notice.getClass().getSimpleName()).emit();}}}catch (InterruptedException e) {stateManager.recordThrowableEvent(e);log.info("SeekableStreamSupervisor[%s] interrupted, exiting", dataSource);}});firstRunTime = DateTimes.nowUtc().plus(ioConfig.getStartDelay());// 单独启动一个线程 将RunNotice添加到队列中,表示任务初次运行了scheduledExec.scheduleAtFixedRate(buildRunTask(),ioConfig.getStartDelay().getMillis(),Math.max(ioConfig.getPeriod().getMillis(), MAX_RUN_FREQUENCY_MILLIS),TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);scheduleReporting(reportingExec);started = true;log.info("Started SeekableStreamSupervisor[%s], first run in [%s], with spec: [%s]",dataSource,ioConfig.getStartDelay(),spec.toString());}catch (Exception e) {stateManager.recordThrowableEvent(e);if (recordSupplier != null) {recordSupplier.close();}initRetryCounter++;log.makeAlert(e, "Exception starting SeekableStreamSupervisor[%s]", dataSource).emit();throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}至此,kafka supervisor任务已经启动并持续运转起来了。下一篇会讲述supervisor如何管理task的,task是如何启动并运行的。
END
本篇只是对kafka supervisor的启动过程做了一个流程式的描述,限于篇幅其中有很多细节没有展开描述。主要目的是能够对supervisor在代码层次有一个直观的认识,揭开它神秘的面纱。
这篇关于Druid kafka-index supervisor启动流程分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







