本文主要是介绍D - Grid and Magnet,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

思路:标记一下磁铁周围的空地即可,每个连通块一定可以互相到达,我们dfs算出联通块的大小再加上该连通块周围的可达磁场区域即可。
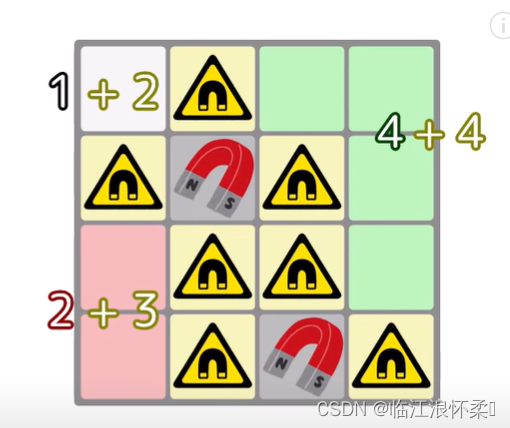
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
using ld = long double;int main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);int n, m;cin >> n >> m;vector vis(n, vector(m, false));vector<string> mp(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> mp[i];}const int dr[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};auto check = [&](int x, int y) {return (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m);};auto magnets = [&](int x, int y) {for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {int nx = x + dr[d][0], ny = y + dr[d][1];if (check(nx, ny) && mp[nx][ny] == '#') {return true;}}return false;};int tag = 0;vector vtag(n, vector(m, 0));auto dfs = [&](auto &&self, int x, int y) -> int {if (vis[x][y] || mp[x][y] == '#') {return 0;}if (magnets(x, y)) {if (vtag[x][y] == tag) {return 0;}vtag[x][y] = tag;return 1;}vis[x][y] = true;int res = 1;for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {int nx = x + dr[d][0], ny = y + dr[d][1];if (check(nx, ny)) {res += self(self, nx, ny);}}return res;};int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {++tag;ans = max(ans, dfs(dfs, i, j));}}cout << ans << '\n';return 0;
}
这篇关于D - Grid and Magnet的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!