本文主要是介绍mysql的多表查询和子查询,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
多表查询:查询数据时,需要使用多张表来查询
多表查询分类:
1.内连接查询
2.外连接查询
3.子查询
笛卡尔积:
create table class
(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(10)
);
create table student
(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(10),class_id int,constraint FK_student_class_id foreign key(class_id) references class(id)
);insert into class(name) values ('清北班'),('冲刺班');
insert into student(name,class_id) values ('aaa',1),('bbb',1),('ccc',2),('ddd',2);-- 多表查询:查询所有学生信心和所属的班级
select student.id, student.name, class_id ,class.id, class.name from student,class;
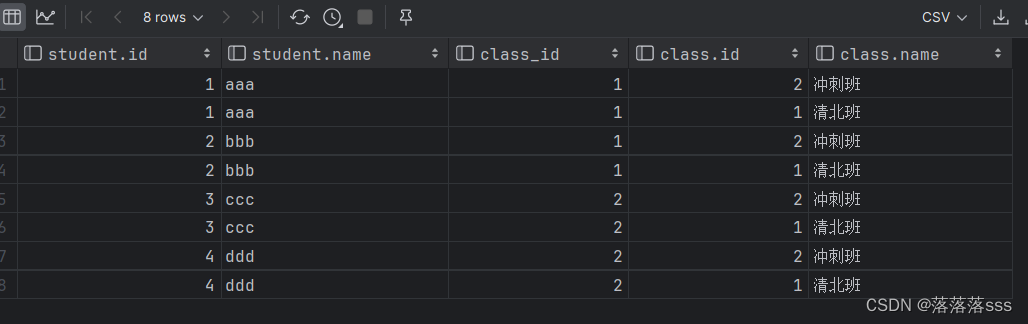
根据图片我们发现两张表相互查询,导致数据出现问题,这种问题叫笛卡尔积(多张表的每行数据进行了交叉查询)
解决方案:在进行多表查询时,消除笛卡尔积
查询时添加条件:主表.主表主键=从表.从表外键
select student.id, student.name, class_id ,class.id, class.name from student,class where class_id=class.id
order by student.id ASC; 
练习:查询id为1的学生一级班级信息
select student.id, student.name, class_id,class.id,class.name from student,class
where class_id=class.id -- 消除笛卡尔积
and student.id=1;内连接查询
1.内连接查询语法
内连接操作的目的是把多张表中互相关联的数据查询出来
1.隐式内连接
select 列名 from 左表,右表 where 从表.外键=主键.主键
2.显示内连接
select 列名 from 左表 [inner] join 右表 on 从表.外键=主键.主键
-- 查询 aaa 学生,并显示学生id,姓名,班级名
-- 语法1:
select student.id,student.name,class.name
from student,class
where class_id=class.id and student.name ='aaa';-- 语法2:
select student.id,student.name,class.name
from student inner join class
on student.class_id = class.id #消除笛卡尔积
-- on的优先级高于where
where student.name='aaa';-- 使用别名的用法
select s.id,s.name,c.name
from student AS s inner join class AS c
on s.class_id = c.id
where s.name='aaa';外连接查询
外连接查询有两种方式:
1.左外连接:左表中所有记录都出现在结果中,如果右表没有匹配的记录,使用null填充select 列名 from 左表 left join 右表 on 从表.外键=主表.主键2.右表连接:右表中所有记录都出现在结果中,如果左表没有匹配的记录,使用null填充
select 列名 from 左表 right join 右表 on 从表.外键=主表.主键
-- 这时候添加一个新班级,没有添加学生
insert into class (id, name) values (null,'补差班');
-- 查询,不会显示新班级
select c.name,s.id AS studentId,s.name
from class AS c inner join student AS s
on c.id = s.class_id;所以我们要使用外连接
select c.name,s.id AS studentId,s.name
from class AS c left join student AS s
on c.id = s.class_id;
子查询
根据子查询的结果,可以分为单行单列,多行单列,多行多列
单行单列
如果子查询时单行单列,父查询使用比较运算符 ><=
练习:
-- 查询学生id最大的学生信息
select
id, name
from student
where id=(select max(id) from student);
子查询 select max(id) from student 结果:

结果是单行单列,使用><=
-- 查询学生id大于bbb的id的学生信息
select
id,name
from student
where id>(select id from student where name='bbb');多行单列
如果子查询的结果是多行单列,可以认为是数组,父查询使用in,all.any关键字
| 关键字 | 说明 |
| in | 查询包含在in条件的所有数据 |
| all | 可以与> <号结合起来,分别表示大于或小于其中的所有数据为真 |
| any | 可以与> <号结合起来,分别表示大于或小于其中的任意一个数据为真 |
-- 查询 所有学生id>2的学生的班级信息
-- 1. 查询学生id>2的学生的班级id
select class_id from student where id>2;
-- 2.查询 所有学生id>2的学生的班级信息
select id, name from class
where id in (select class_id from student where id>2);select class_id from student where id>2;的结果是多行单列

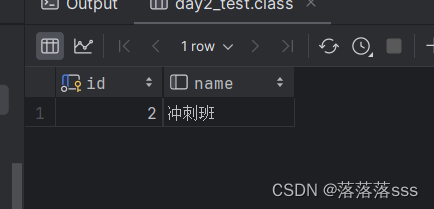
select id, name from class
where id in (select class_id from student where id>2);的结果
这篇关于mysql的多表查询和子查询的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




