本文主要是介绍阿尔卡特笔试题目之二,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Part A是一些你的知识技能调查
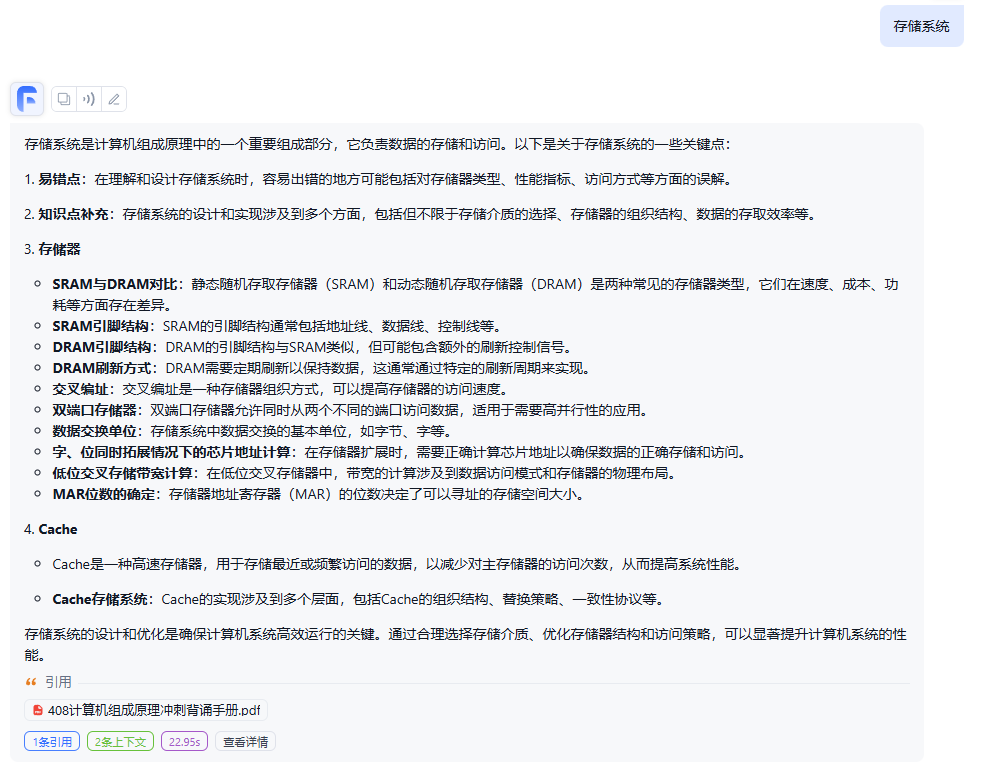
Part B全是通信方面的东西,不会做了,题目都没看完
Part C是Computer Sience的东西。
前3道是选择题,很easy
1、用A[1...n]模拟栈,A[n]是栈底,当A[T]是当前栈顶时,POP操作后,当然栈顶是什么http://blog.csdn.net/weiweitj/archive/2008/04/27/2336067.aspx
2、假设二叉树的根是为0层,那么第i层最多有几个节点?2^(k-1)
3、以下各项那项是结构化编程语言不允许的
a if-else b loop-while,for c goto d function
4、给出软件生存周期图
一个软件从定义到开发、使用和维护,直到最终被弃用,要经历一个漫长的时期,通常把软件经历的这个漫长的时期称为生存周期。软件生存周期一般可分为 以下阶段:问题定义、需求分析与可行性研究、设计、编码、测试、运行与维护。软件生存期也可以分为三个大的阶段:计划阶段。开发阶段和维护阶段。
5、C的Structure和C++ 的class的什么不同之处
初始化、默认继承权限、默认访问权限
6、什么是virtual函数,为什么使用virtual函数
7、填空完成ip v4协议表头
8、你认为造成软件 crash的主要原因是什么,怎么预防?
9、用C自己写一个string copy函数
 char * strcpy( char * strDest, const char * strSrc)
char * strcpy( char * strDest, const char * strSrc) {
{ assert(NULL != strDest);
assert(NULL != strDest);  assert(NULL != strSrc);
assert(NULL != strSrc); char *tmp= strDest;
char *tmp= strDest; while("0" != (*tmp++ = *strSrc++));
while("0" != (*tmp++ = *strSrc++));
10、写一个双向链表的插入函数(from luocong)
 template < typename T >
template < typename T >  inline int CDList < T > ::InsertBefore( const int pos, const T data)
inline int CDList < T > ::InsertBefore( const int pos, const T data) {
{ int i;
int i; int nRetPos;
int nRetPos; CNode<T> *pTmpNode;
CNode<T> *pTmpNode; CNode<T> *pNewNode;
CNode<T> *pNewNode;
 pNewNode = new CNode<T>;
pNewNode = new CNode<T>; if (NULL == pNewNode)
if (NULL == pNewNode) {
{ nRetPos = 0;
nRetPos = 0; goto Exit0;
goto Exit0; }
}
 pNewNode->data = data;
pNewNode->data = data;
 // if the list is empty, replace the head node with the new node.
// if the list is empty, replace the head node with the new node. if (NULL == m_pNodeHead)
if (NULL == m_pNodeHead) {
{ pNewNode->prior = NULL;
pNewNode->prior = NULL; pNewNode->next = NULL;
pNewNode->next = NULL; m_pNodeHead = pNewNode;
m_pNodeHead = pNewNode; m_pNodeTail = pNewNode;
m_pNodeTail = pNewNode; nRetPos = 1;
nRetPos = 1; goto Exit1;
goto Exit1; }
}
 // is pos range valid?
// is pos range valid? ASSERT(1 <= pos && pos <= m_nCount);
ASSERT(1 <= pos && pos <= m_nCount);
 // insert before head node?
// insert before head node? if (1 == pos)
if (1 == pos) {
{ pNewNode->prior = NULL;
pNewNode->prior = NULL; pNewNode->next = m_pNodeHead;
pNewNode->next = m_pNodeHead; m_pNodeHead->prior = pNewNode;
m_pNodeHead->prior = pNewNode; m_pNodeHead = pNewNode;
m_pNodeHead = pNewNode; nRetPos = 1;
nRetPos = 1; goto Exit1;
goto Exit1; }
}
 // if the list is not empty and is not inserted before head node,
// if the list is not empty and is not inserted before head node, // seek to the pos of the list and insert the new node before it.
// seek to the pos of the list and insert the new node before it. pTmpNode = m_pNodeHead;
pTmpNode = m_pNodeHead; for (i = 1; i < pos; ++i)
for (i = 1; i < pos; ++i) {
{ pTmpNode = pTmpNode->next;
pTmpNode = pTmpNode->next; }
} pNewNode->next = pTmpNode;
pNewNode->next = pTmpNode; pNewNode->prior = pTmpNode->prior;
pNewNode->prior = pTmpNode->prior;
 pTmpNode->prior->next = pNewNode;
pTmpNode->prior->next = pNewNode; pTmpNode->prior = pNewNode;
pTmpNode->prior = pNewNode;
 // if tail node, must update m_pNodeTail
// if tail node, must update m_pNodeTail if (NULL == pNewNode->next)
if (NULL == pNewNode->next) {
{ m_pNodeTail = pNewNode;
m_pNodeTail = pNewNode; }
}
 nRetPos = pos;
nRetPos = pos;
 Exit1:
Exit1: ++m_nCount;
++m_nCount; Exit0:
Exit0: return nRetPos;
return nRetPos; }
} 
 template < typename T >
template < typename T >  inline int CDList < T > ::InsertAfter( const int pos, const T data)
inline int CDList < T > ::InsertAfter( const int pos, const T data) {
{ int i;
int i; int nRetPos;
int nRetPos; CNode<T> *pNewNode;
CNode<T> *pNewNode; CNode<T> *pTmpNode;
CNode<T> *pTmpNode;
 pNewNode = new CNode<T>;
pNewNode = new CNode<T>; if (NULL == pNewNode)
if (NULL == pNewNode) {
{ nRetPos = 0;
nRetPos = 0; goto Exit0;
goto Exit0; }
}
 pNewNode->data = data;
pNewNode->data = data;
 // if the list is empty, replace the head node with the new node.
// if the list is empty, replace the head node with the new node. if (NULL == m_pNodeHead)
if (NULL == m_pNodeHead) {
{ pNewNode->prior = NULL;
pNewNode->prior = NULL; pNewNode->next = NULL;
pNewNode->next = NULL; m_pNodeHead = pNewNode;
m_pNodeHead = pNewNode; m_pNodeTail = pNewNode;
m_pNodeTail = pNewNode; nRetPos = 1;
nRetPos = 1; goto Exit1;
goto Exit1; }
}
 // is pos range valid?
// is pos range valid? ASSERT(1 <= pos && pos <= m_nCount);
ASSERT(1 <= pos && pos <= m_nCount);
 // if the list is not empty,
// if the list is not empty, // seek to the pos of the list and insert the new node after it.
// seek to the pos of the list and insert the new node after it. pTmpNode = m_pNodeHead;
pTmpNode = m_pNodeHead; for (i = 1; i < pos; ++i)
for (i = 1; i < pos; ++i) {
{ pTmpNode = pTmpNode->next;
pTmpNode = pTmpNode->next; }
}
 pNewNode->next = pTmpNode->next;
pNewNode->next = pTmpNode->next; pNewNode->prior = pTmpNode;
pNewNode->prior = pTmpNode;
 // if NewNode's position is m_pNodeTail, update m_pNodeTail
// if NewNode's position is m_pNodeTail, update m_pNodeTail if (pTmpNode->next == m_pNodeTail)
if (pTmpNode->next == m_pNodeTail) {
{ m_pNodeTail->prior = pNewNode;
m_pNodeTail->prior = pNewNode; }
}
 pTmpNode->next = pNewNode;
pTmpNode->next = pNewNode;
 // if tail node, must update m_pNodeTail
// if tail node, must update m_pNodeTail if (NULL == pNewNode->next)
if (NULL == pNewNode->next) {
{ m_pNodeTail = pNewNode;
m_pNodeTail = pNewNode; }
}
 nRetPos = pos + 1;
nRetPos = pos + 1;
 Exit1:
Exit1: ++m_nCount;
++m_nCount; Exit0:
Exit0: return nRetPos;
return nRetPos; }
} 
Part D (optional)
给出你认为贝尔会感兴趣的topic
这篇关于阿尔卡特笔试题目之二的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!