本文主要是介绍LeetCode刷题记(四):91~120题,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
91. 解码方法
一条包含字母 A-Z 的消息通过以下映射进行了 编码 :
'A' -> "1" 'B' -> "2" ... 'Z' -> "26"
要 解码 已编码的消息,所有数字必须基于上述映射的方法,反向映射回字母(可能有多种方法)。例如,"11106" 可以映射为:
"AAJF",将消息分组为(1 1 10 6)"KJF",将消息分组为(11 10 6)
注意,消息不能分组为 (1 11 06) ,因为 "06" 不能映射为 "F" ,这是由于 "6" 和 "06" 在映射中并不等价。
给你一个只含数字的 非空 字符串 s ,请计算并返回 解码 方法的 总数 。
题目数据保证答案肯定是一个 32 位 的整数。
示例 1:
输入:s = "12" 输出:2 解释:它可以解码为 "AB"(1 2)或者 "L"(12)。
示例 2:
输入:s = "226" 输出:3 解释:它可以解码为 "BZ" (2 26), "VF" (22 6), 或者 "BBF" (2 2 6) 。
示例 3:
输入:s = "06" 输出:0 解释:"06" 无法映射到 "F" ,因为存在前导零("6" 和 "06" 并不等价)。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 100s只包含数字,并且可能包含前导零。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int numDecodings(string s) {int n = s.size();vector<int> dp(n + 1);dp[0] = 1;dp[1] = s[0] == '0' ? 0 : 1;for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {int oneDigit = stoi(s.substr(i - 1, 1));int twoDigits = stoi(s.substr(i - 2, 2));if(oneDigit >= 1 && oneDigit <= 9) {dp[i] += dp[i - 1];}if(twoDigits >= 10 && twoDigits <= 26) {dp[i] += dp[i - 2];}} return dp[n];}
};int main() {string s;cin >> s;Solution solution;cout << solution.numDecodings(s) << endl;return 0;
}92. 反转链表Ⅱ
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
示例 1:
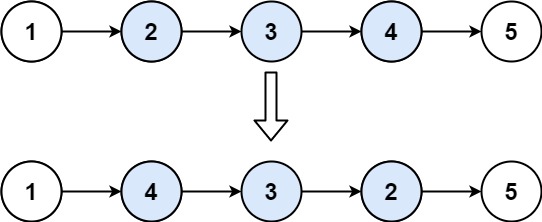
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4 输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1 输出:[5]
提示:
- 链表中节点数目为
n 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
进阶: 你可以使用一趟扫描完成反转吗?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {if(head == NULL) {return head;}ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);dummy->next = head;ListNode* pre = dummy;for(int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++) {pre = pre->next;}ListNode* curr = pre->next;ListNode* next;for(int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {next = curr->next;curr->next = next->next;next->next = pre->next;pre->next = next;}return dummy->next;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode *head = NULL;ListNode *current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = current->next;}if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}return head;
}void printList(ListNode *head) {ListNode *current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {ListNode *head = createList();int left, right;cin >> left >> right;Solution solution;ListNode * result = solution.reverseBetween(head, left, right);printList(result);return 0;}93. 复原IP地址
有效 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 '.' 分隔。
- 例如:
"0.1.2.201"和"192.168.1.1"是 有效 IP 地址,但是"0.011.255.245"、"192.168.1.312"和"192.168@1.1"是 无效 IP 地址。
给定一个只包含数字的字符串 s ,用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能的有效 IP 地址,这些地址可以通过在 s 中插入 '.' 来形成。你 不能 重新排序或删除 s 中的任何数字。你可以按 任何 顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "25525511135" 输出:["255.255.11.135","255.255.111.35"]
示例 2:
输入:s = "0000" 输出:["0.0.0.0"]
示例 3:
输入:s = "101023" 输出:["1.0.10.23","1.0.102.3","10.1.0.23","10.10.2.3","101.0.2.3"]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 20s仅由数字组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) {vector<string> result;if(s.size() < 4 || s.size() > 12) { // 长度要求 return result;}backtrack(s, 0, 0, "", result);return result;}void backtrack(string s, int start, int partNum, string current, vector<string>& result) {if(start == s.size() && partNum == 4) {result.push_back(current);return;}if(s.size() - start > (4 - partNum) * 3) { // 剩下的长度超过了限制 return;}for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { // 尝试将当前部分加入IP地址中并继续递归处理剩余部分 if(start + i > s.size()) {break;}string part = s.substr(start, i);if(isValidPart(part)) {string newCurrent = current.empty() ? part : current + "." + part;backtrack(s, start + i, partNum + 1, newCurrent, result);}}}bool isValidPart(const string& s) {if(s.size() > 1 && s[0] == '0') {return false;}int num = stoi(s);return num >= 0 && num <= 255;}
};int main() {string s;cin >> s;Solution solution;vector<string> result = solution.restoreIpAddresses(s);cout << "[";for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "\"" << result[i] << "\"";} else {cout << "\"" << result[i] << "\", ";}}cout << "]";return 0;
}94. 二叉树的中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例 1:
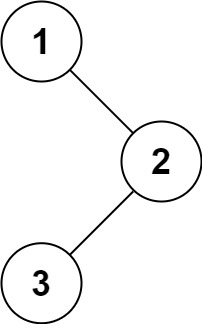
输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[1]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> s;vector<int> v;TreeNode* rt = root;while(rt || s.size()) {while(rt) {s.push(rt);rt = rt->left;}rt = s.top(); s.pop();v.push_back(rt->val);rt = rt->right;}return v;}
};// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;vector<int> result = solution.inorderTraversal(root);for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << result[i] << " ";}return 0;
}95. 不同的二叉搜索树Ⅱ
给你一个整数 n ,请你生成并返回所有由 n 个节点组成且节点值从 1 到 n 互不相同的不同 二叉搜索树 。可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
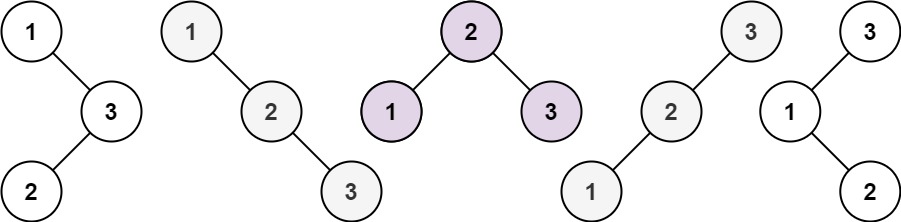
输入:n = 3 输出:[[1,null,2,null,3],[1,null,3,2],[2,1,3],[3,1,null,null,2],[3,2,null,1]]
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= n <= 8
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode* right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:vector<TreeNode*> helper(int start, int end) {vector<TreeNode*> trees;if (start > end) {trees.push_back(NULL);return trees;}for (int i = start; i <= end; ++i) {vector<TreeNode*> leftSubtrees = helper(start, i - 1);vector<TreeNode*> rightSubtrees = helper(i + 1, end);for (TreeNode* left : leftSubtrees) {for (TreeNode* right : rightSubtrees) {TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(i);root->left = left;root->right = right;trees.push_back(root);}}}return trees;}vector<TreeNode*> generateTrees(int n) {if (n == 0) {return {};}return helper(1, n);}
};void printTree(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {return;}cout << root->val << " ";printTree(root->left);printTree(root->right);
}int main() {int n;cin >> n;Solution solution;vector<TreeNode*> result = solution.generateTrees(n);for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";TreeNode* tree = result[i];printTree(tree);if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "], ";}}
}96. 不同的二叉搜索树
给你一个整数 n ,求恰由 n 个节点组成且节点值从 1 到 n 互不相同的 二叉搜索树 有多少种?返回满足题意的二叉搜索树的种数。
示例 1:

输入:n = 3 输出:5
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:1
提示:
1 <= n <= 19
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode* right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};/* class Solution {public:vector<TreeNode*> helper(int start, int end) {vector<TreeNode*> trees;if (start > end) {trees.push_back(NULL);return trees;}for (int i = start; i <= end; ++i) {vector<TreeNode*> leftSubtrees = helper(start, i - 1);vector<TreeNode*> rightSubtrees = helper(i + 1, end);for (TreeNode* left : leftSubtrees) {for (TreeNode* right : rightSubtrees) {TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(i);root->left = left;root->right = right;trees.push_back(root);}}}return trees;}int numTrees(int n) {if (n == 0) {return {};}vector<TreeNode*> trees = helper(1, n);return trees.size();}
}; */class Solution {public:int numTrees(int n) {// 动态规划// 从2开始遍历到n,对于每个节点数量i,再遍历1到i作为根节点的情况,// 计算左子树和右子树的种数乘积,并累加到当前节点数量的种数中。vector<int> dp(n + 1, 0);dp[0] = 1;dp[1] = 1;for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i - j];}}return dp[n];}
};int main() {int n;cin >> n;Solution solution;cout << solution.numTrees(n);return 0;
}97. 交错字符串
给定三个字符串 s1、s2、s3,请你帮忙验证 s3 是否是由 s1 和 s2 交错 组成的。
两个字符串 s 和 t 交错 的定义与过程如下,其中每个字符串都会被分割成若干 非空
子字符串:
s = s1 + s2 + ... + snt = t1 + t2 + ... + tm|n - m| <= 1- 交错 是
s1 + t1 + s2 + t2 + s3 + t3 + ...或者t1 + s1 + t2 + s2 + t3 + s3 + ...
注意:a + b 意味着字符串 a 和 b 连接。
示例 1:
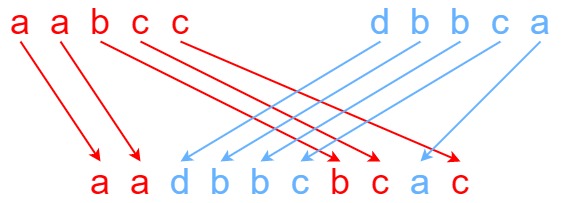
输入:s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbcbcac" 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbbaccc" 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:s1 = "", s2 = "", s3 = "" 输出:true
提示:
0 <= s1.length, s2.length <= 1000 <= s3.length <= 200s1、s2、和s3都由小写英文字母组成
进阶:您能否仅使用 O(s2.length) 额外的内存空间来解决它?
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:bool isInterleave(string s1, string s2, string s3) {int m = s1.length(), n = s2.length();if(m + n != s3.length()) {return false;}vector<vector<bool>> dp(m + 1, vector<bool>(n + 1, false));dp[0][0] = true;for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] && s1[i - 1] == s3[i - 1];}for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1] && s2[j - 1] == s3[j - 1];}for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {dp[i][j] = (dp[i - 1][j] && s1[i - 1] == s3[i + j - 1]) ||(dp[i][j - 1] && s2[j - 1] == s3[i + j - 1]);}}return dp[m][n];}
};int main() {string s1, s2, s3;cin >> s1 >> s2 >> s3;Solution solution;cout << boolalpha << solution.isInterleave(s1, s2, s3);return 0;
}98. 验证二叉搜索树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
- 节点的左
子树
只包含 小于 当前节点的数。 - 节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
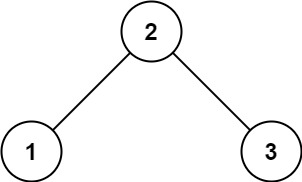
输入:root = [2,1,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
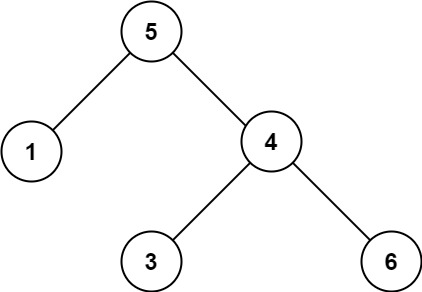
输入:root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6] 输出:false 解释:根节点的值是 5 ,但是右子节点的值是 4 。
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[1, 104]内 -2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
#include<climits>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode* right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> st;TreeNode* prev = NULL;while(root != NULL || !st.empty()) {while(root != NULL) {st.push(root);root = root->left;}root = st.top();st.pop();if(prev != NULL && prev->val >= root->val) {return false;}prev = root;root = root->right;}return true;}
};TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;cout << boolalpha << solution.isValidBST(root);return 0;
}99. 恢复二叉搜索树
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,该树中的 恰好 两个节点的值被错误地交换。请在不改变其结构的情况下,恢复这棵树 。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,3,null,null,2] 输出:[3,1,null,null,2] 解释:3 不能是 1 的左孩子,因为 3 > 1 。交换 1 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
示例 2:
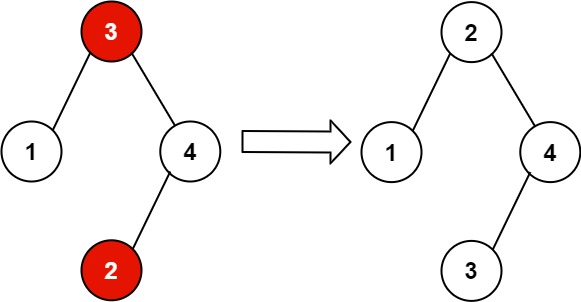
输入:root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] 输出:[2,1,4,null,null,3] 解释:2 不能在 3 的右子树中,因为 2 < 3 。交换 2 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
提示:
- 树上节点的数目在范围
[2, 1000]内 -2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
进阶:使用 O(n) 空间复杂度的解法很容易实现。你能想出一个只使用 O(1) 空间的解决方案吗?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode* right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {TreeNode* first = NULL;TreeNode* second = NULL;TreeNode* prev = NULL;stack<TreeNode*> s;TreeNode* curr = root;while(curr != NULL || !s.empty()) {while(curr != NULL) {s.push(curr);curr = curr->left;}curr = s.top();s.pop();if(prev != NULL && prev->val > curr->val) {if(first == NULL) {first = prev;}second = curr;}prev = curr;curr = curr->right;}// 交换两个错误的节点的值int temp = first->val;first->val = second->val;second->val = temp; }
};TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}void printTree(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {return;}cout << root->val << " ";printTree(root->left);printTree(root->right);
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;solution.recoverTree(root);printTree(root);return 0;
}100. 相同的树
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
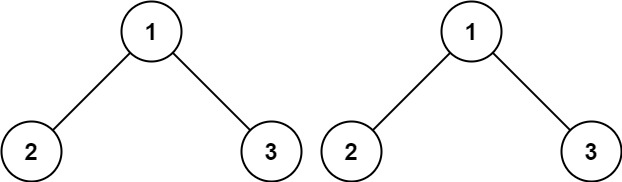
输入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
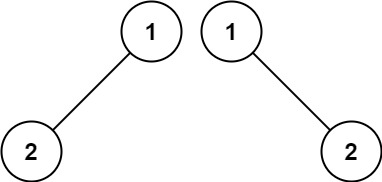
输入:p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2] 输出:false
示例 3:
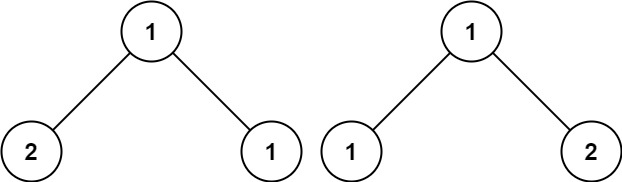
输入:p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2] 输出:false
提示:
- 两棵树上的节点数目都在范围
[0, 100]内 -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {
public:bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if(p == NULL && q == NULL) return true;if(p == NULL || q == NULL) return false;if(p->val != q->val) return false;return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);}
};// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* p = createBinaryTree();TreeNode* q = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;int result = solution.isSameTree(p, q);if(result)cout << "true";elsecout << "false";return 0;
}101. 对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
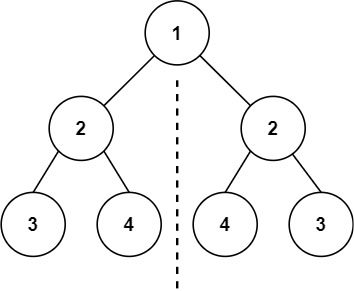
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true
示例 2:
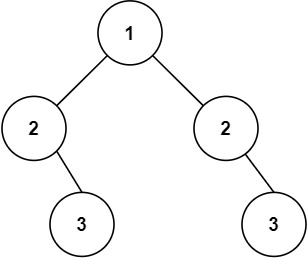
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 输出:false
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL)return true;else {return dfs(root->left, root->right);}}bool dfs(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {if(left == NULL && right == NULL)return true;if(left == NULL || right == NULL)return false;return (left->val == right->val) && dfs(left->left, right->right) && dfs(left->right, right->left);}
};// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;int result = solution.isSymmetric(root);if(result)cout << "true";elsecout << "false";return 0;
}102. 二叉树的层序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例 1:
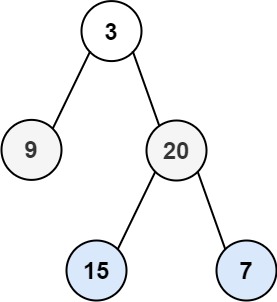
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 2000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> result;if(root == NULL) {return result;}queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while(!q.empty()) {int size = q.size();vector<int> level;for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode *node = q.front();q.pop();level.push_back(node->val);if(node->left != NULL) {q.push(node->left);}if(node->right != NULL) {q.push(node->right);}}result.push_back(level);}return result;}
};TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode *root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.levelOrder(root);for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {cout << result[i][j];} else {cout << result[i][j] << ", ";}}if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "], ";}}return 0;
}103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[3],[20,9],[15,7]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 2000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> result;if(root == NULL) {return result;}queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);bool leftToRight = true; // 记录是从左到右还是从右到左 while(!q.empty()) {int size = q.size();vector<int> level;stack<int> s;for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode *node = q.front();q.pop();if(leftToRight) {level.push_back(node->val);} else {s.push(node->val);}if(node->left != NULL) {q.push(node->left);}if(node->right != NULL) {q.push(node->right);}}while(!s.empty()) {level.push_back(s.top());s.pop();}result.push_back(level);leftToRight = !leftToRight;}return result;}
};TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode *root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.zigzagLevelOrder(root);for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {cout << result[i][j];} else {cout << result[i][j] << ", ";}}if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "], ";}}return 0;
}104. 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
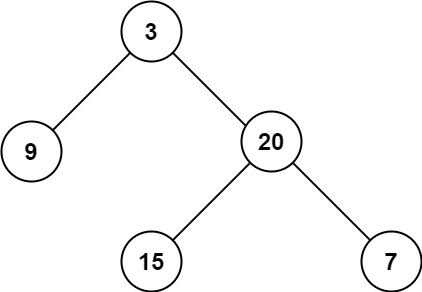
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2] 输出:2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 10^4]区间内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解法一:递归
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { // 递归 if(root == NULL) {return 0;} else {return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;}}
};// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;cout << solution.maxDepth(root);return 0;
}解法二:迭代
#include<iostream>
//#include<math.h>
#include <queue>
#include<stack>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:
// int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { // 递归
// if(root == NULL) {
// return 0;
// } else {
// return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
// }
// }int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { // 迭代 if(root == NULL) {return 0;}stack<pair<TreeNode*, int> > s;s.push(make_pair(root, 1));int maxDepth = 0;while(!s.empty()) {pair<TreeNode*, int> current = s.top();s.pop();TreeNode* node = current.first;int depth = current.second;maxDepth = max(maxDepth, depth);if(node->left != NULL) {s.push(make_pair(node->left, depth + 1));}if(node->right != NULL) {s.push(make_pair(node->right, depth + 1));}}return maxDepth;}
};// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;cout << solution.maxDepth(root);return 0;
}105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
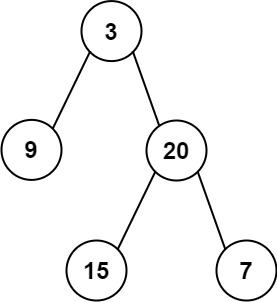
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] 输出: [-1]
提示:
1 <= preorder.length <= 3000inorder.length == preorder.length-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000preorder和inorder均 无重复 元素inorder均出现在preorderpreorder保证 为二叉树的前序遍历序列inorder保证 为二叉树的中序遍历序列
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {unordered_map<int, int> indexMap;for(int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++) {indexMap[inorder[i]] = i;}return buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, 0, preorder.size() - 1, 0, inorder.size() - 1, indexMap);}TreeNode* buildTreeHelper(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int inStart, int inEnd, unordered_map<int, int>& indexMap) {if(preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) {return NULL;}int rootVal = preorder[preStart];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);int inIndex = indexMap[rootVal];int leftSubtreeSize = inIndex - inStart;root->left = buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftSubtreeSize, inStart, inIndex - 1, indexMap);root->right = buildTreeHelper(preorder, inorder, preStart + leftSubtreeSize + 1, preEnd, inIndex + 1, inEnd, indexMap);return root;}
};vector<int> Create() {string input;getline(cin, input);stringstream stream(input);vector<int> order;int num;while(stream >> num) {order.push_back(num);}return order;
}
void printTree(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL) {return;}cout << root->val << " ";printTree(root->left);printTree(root->right);
}int main() {vector<int> preorder = Create();vector<int> inorder = Create();Solution solution;TreeNode* root = solution.buildTree(preorder, inorder);printTree(root);return 0;
}106. 从中序与后序遍历构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:

输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1] 输出:[-1]
提示:
1 <= inorder.length <= 3000postorder.length == inorder.length-3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000inorder和postorder都由 不同 的值组成postorder中每一个值都在inorder中inorder保证是树的中序遍历postorder保证是树的后序遍历
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {unordered_map<int, int> indexMap;for(int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++) {indexMap[inorder[i]] = i;}return buildTreeHelper(inorder, postorder, 0, inorder.size() - 1, 0, postorder.size() - 1, indexMap);}TreeNode* buildTreeHelper(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int postStart, int postEnd, unordered_map<int, int>& indexMap) {if(inStart > inEnd || postStart > postEnd) {return NULL;}int rootVal = postorder[postEnd];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);int inIndex = indexMap[rootVal];int rightSubtreeSize = inEnd - inIndex;root->left = buildTreeHelper(inorder, postorder, inStart, inIndex - 1, postStart, postEnd - rightSubtreeSize - 1, indexMap);root->right = buildTreeHelper(inorder, postorder, inIndex + 1, inEnd, postEnd - rightSubtreeSize, postEnd - 1, indexMap);return root;}
};vector<int> Create() {string input;getline(cin, input);stringstream stream(input);vector<int> order;int num;while(stream >> num) {order.push_back(num);}return order;
}
void printTree(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL) {return;}cout << root->val << " ";printTree(root->left);printTree(root->right);
}int main() {vector<int> inorder = Create();vector<int> postorder = Create();Solution solution;TreeNode* root = solution.buildTree(inorder, postorder);printTree(root);return 0;
}107. 二叉树的层序遍历Ⅱ
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值 自底向上的层序遍历 。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[15,7],[9,20],[3]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 2000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> result;if(root == NULL) {return result;}queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while(!q.empty()) {int size = q.size();vector<int> levelValues;for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode* node = q.front();q.pop();levelValues.push_back(node->val);if(node->left) {q.push(node->left);}if(node->right) {q.push(node->right); }}result.push_back(levelValues);}reverse(result.begin(), result.end());return result;}
};TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode *root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.levelOrderBottom(root);for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {cout << result[i][j];} else {cout << result[i][j] << ", ";}}if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "], ";}}return 0;
}108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 高度平衡 二叉搜索树。
高度平衡 二叉树是一棵满足「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 」的二叉树。
示例 1:
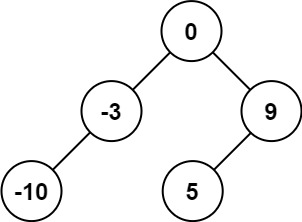
输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] 输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5] 解释:[0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] 也将被视为正确答案:
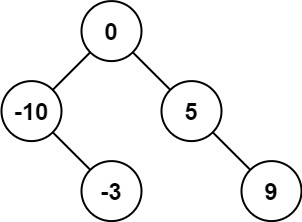
示例 2:
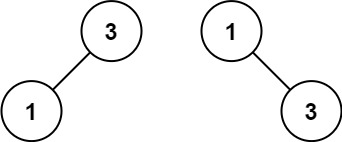
输入:nums = [1,3] 输出:[3,1] 解释:[1,null,3] 和 [3,1] 都是高度平衡二叉搜索树。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104nums按 严格递增 顺序排列
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {if(nums.empty()) {return NULL;}return helper(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);}TreeNode* helper(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end) {if(start > end) {return NULL;}int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);root->left = helper(nums, start, mid - 1);root->right = helper(nums, mid + 1, end);return root;}
};// 层序遍历
void printTree(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL) {cout << "null ";return;}cout << root->val << " ";if(root->left != NULL || root->right != NULL) {printTree(root->left);printTree(root->right);}
}int main() {vector<int> nums;int temp;while(cin >> temp) {nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n') break;}Solution solution;TreeNode* root = solution.sortedArrayToBST(nums);printTree(root);return 0;
}109.有序链表转换为二叉搜索树
给定一个单链表的头节点 head ,其中的元素 按升序排序 ,将其转换为平衡二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
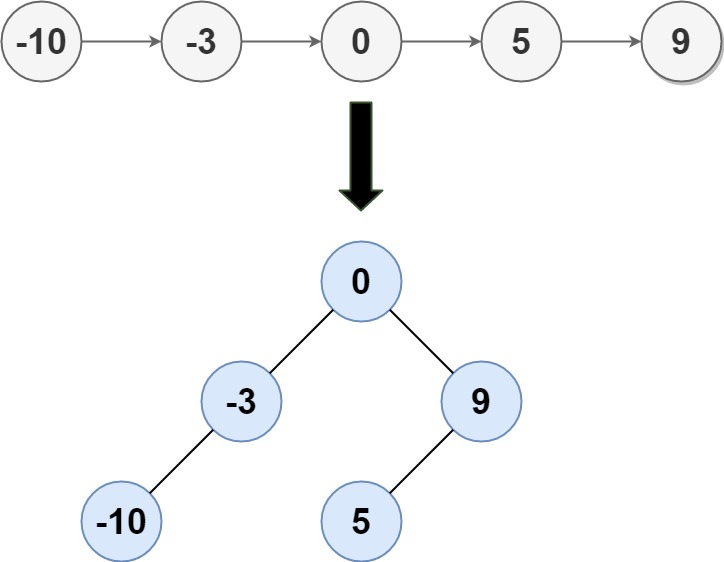
输入: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9] 输出: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] 解释: 一个可能的答案是[0,-3,9,-10,null,5],它表示所示的高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
示例 2:
输入: head = [] 输出: []
提示:
head中的节点数在[0, 2 * 104]范围内-105 <= Node.val <= 105
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};// Defintion for a singly-linked list
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {if(head == NULL) {return NULL;}if(head->next == NULL) {return new TreeNode(head->val);}ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head;ListNode* prev = NULL;while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {prev = slow;slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(slow->val);if(prev != NULL) {prev->next = NULL;root->left = sortedListToBST(head);}root->right = sortedListToBST(slow->next);return root;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode *head = NULL;ListNode *current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = current->next;}if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}return head;
}void printTree(TreeNode* root) {TreeNode *Q[1000], *q = NULL;int front = -1, rear = -1;if(root == NULL) return;Q[++rear] = root;while(front != rear) {q = Q[++front];cout << q->val << " ";if(q->left != NULL) Q[++rear] = q->left;if(q->right != NULL) Q[++rear] = q->right;}
}int main() {ListNode *head = createList();Solution solution;TreeNode* root = solution.sortedListToBST(head);printTree(root);return 0;
}110. 平衡二叉树
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
示例 1:
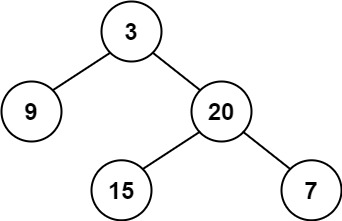
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:true
示例 2:
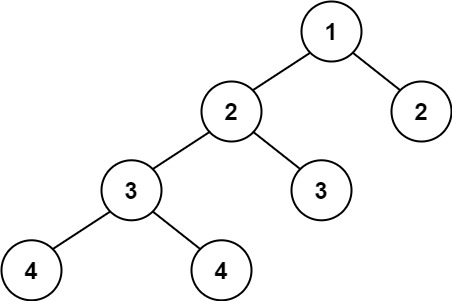
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:true
提示:
- 树中的节点数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL) {return true;}int leftHeight = getHeight(root->left);int rightHeight = getHeight(root->right);if(abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {return false;}return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);}int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {if(node == NULL) {return 0;}int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left);int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right);return 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);}};// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;int result = solution.isBalanced(root);if(result)cout << "true";else cout << "false";return 0;
}111. 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
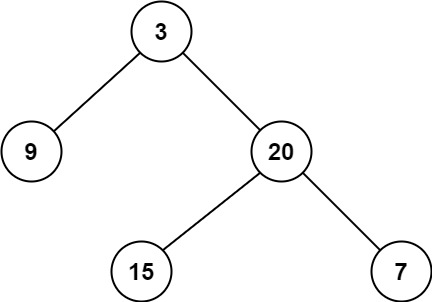
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6] 输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 10^5]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL)return 0;queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);int depth = 1;while(!q.empty()) {int size = q.size();for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode* node = q.front();q.pop();if(node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) // 根节点 return depth;if(node->left != NULL) {q.push(node->left);} if(node->right != NULL) {q.push(node->right);}}depth++; // 不符合第一个if的条件时 }return depth;}};// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;cout << solution.minDepth(root);return 0;
}112. 路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
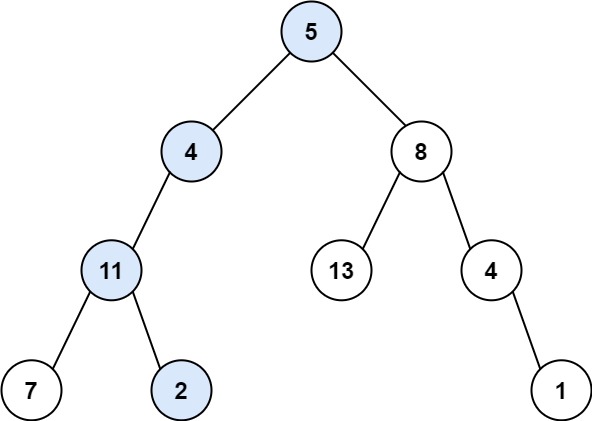
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
示例 2:
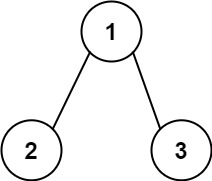
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:false 解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径: (1 --> 2): 和为 3 (1 --> 3): 和为 4 不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
示例 3:
输入:root = [], targetSum = 0 输出:false 解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
解法一:递归
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;// Defination of a bianry tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if(root == NULL) {return false;}if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && (root->val - targetSum == 0)) {return true;}return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);}
};// Function to create a binary tree from user input
TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();int targetSum;cin >> targetSum;Solution solution;int result = solution.hasPathSum(root, targetSum);if(result)cout << "true";else cout << "false";return 0;}解法二:迭代
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if(root == NULL) return false;stack<pair<TreeNode*, int> > nodes;nodes.push(make_pair(root, targetSum - root->val));while(!nodes.empty()) {TreeNode* node = nodes.top().first;int currentSum = nodes.top().second;nodes.pop();if(node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL && currentSum == 0) {return true;}if(node->right != NULL) {nodes.push(make_pair(node->right, currentSum - node->right->val));}if(node->left != NULL) {nodes.push(make_pair(node->left, currentSum - node->left->val));}}return false;
}113. 路径总和Ⅱ
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
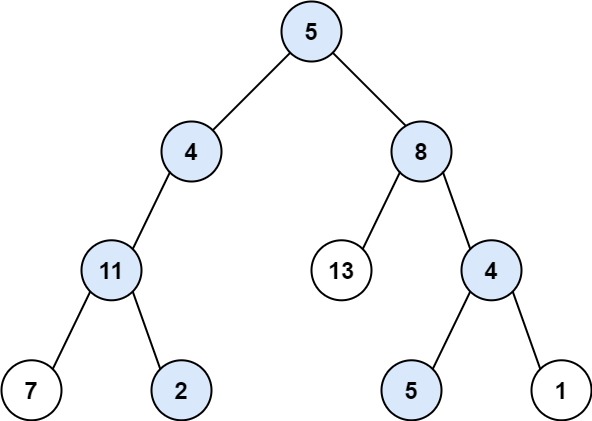
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2:
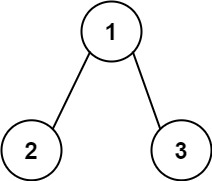
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], targetSum = 0 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点总数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {vector<vector<int>> result;vector<int> path;helper(root, targetSum, path, result);return result;}void helper(TreeNode* root, int targetSum, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int>>& result) {if(root == NULL) {return;}path.push_back(root->val);if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && root->val == targetSum) {result.push_back(path);}helper(root->left, targetSum - root->val, path, result);helper(root->right, targetSum - root->val, path, result);path.pop_back();}
};TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);} else {curr->left = NULL;}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);} else {curr->right = NULL;}}return root;
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();int targetSum;cin >> targetSum;Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.pathSum(root, targetSum);for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {cout << result[i][j];} else {cout << result[i][j] << ", ";}}if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "], ";}}return 0;
}114. 二叉树展开为链表
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
- 展开后的单链表应该同样使用
TreeNode,其中right子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为null。 - 展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。
示例 1:
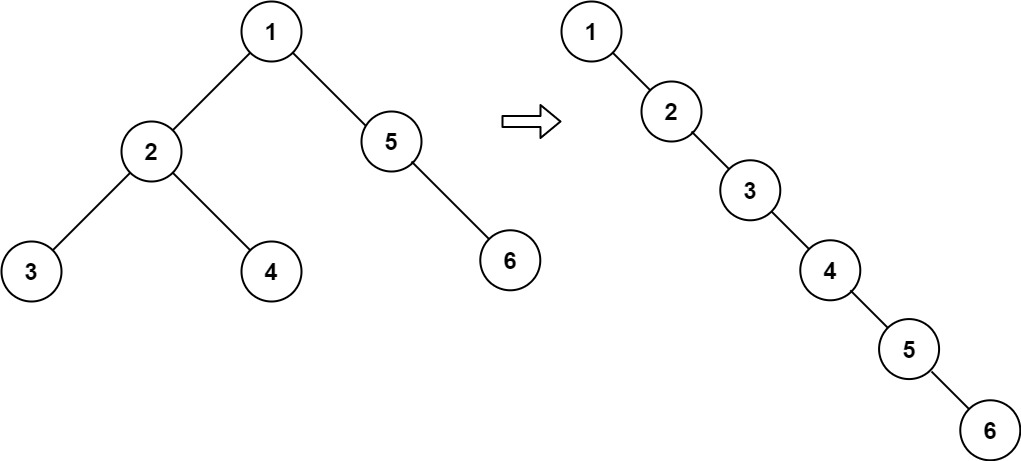
输入:root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] 输出:[1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [0] 输出:[0]
提示:
- 树中结点数在范围
[0, 2000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:你可以使用原地算法(O(1) 额外空间)展开这棵树吗?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>using namespace std;// Definition for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode *left;TreeNode *right;TreeNode() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};class Solution {public:void flatten(TreeNode* root) {if(root == NULL) {return;}stack<TreeNode*> st;st.push(root);while(!st.empty()) {TreeNode* current = st.top();st.pop();if(current->right != NULL) {st.push(current->right);}if(current->left != NULL) {st.push(current->left);}if(!st.empty()) {current->right = st.top();}current->left = NULL;}}
};TreeNode* createBinaryTree() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootVal);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {TreeNode* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new TreeNode(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);} else {curr->left = NULL;}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new TreeNode(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);} else {curr->right = NULL;}}return root;
}void printTree(TreeNode* root) {cout << "[";while(root != NULL) {if(root->right != NULL) {cout << root->val << ", ";cout << "null, ";} else {cout << root->val;}root = root->right;}cout << "]";
}int main() {TreeNode* root = createBinaryTree();Solution solution;solution.flatten(root);printTree(root);return 0;
}115. 不同的子序列
给你两个字符串 s 和 t ,统计并返回在 s 的 子序列 中 t 出现的个数,结果需要对 109 + 7 取模。
示例 1:
输入:s = "rabbbit", t = "rabbit" 输出:3 解释: 如下所示, 有 3 种可以从 s 中得到 "rabbit" 的方案。rabbbitrabbbitrabbbit
示例 2:
输入:s = "babgbag", t = "bag" 输出:5 解释: 如下所示, 有 5 种可以从 s 中得到 "bag" 的方案。babgbagbabgbagbabgbagbabgbagbabgbag
提示:
1 <= s.length, t.length <= 1000s和t由英文字母组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int numDistinct(string s, string t) {int m = s.length();int n = t.length();vector<vector<unsigned int>> dp(m + 1, vector<unsigned int>(n + 1, 0));for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {dp[i][0] = 1;}for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if(s[i - 1] == t[j - 1]) {dp[i][j] = (dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j]) % 10000000;} else {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];}}}return dp[m][n];}
};int main() {string s, t;cin >> s >> t;Solution solution;cout << solution.numDistinct(s, t) << endl;return 0;
}116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {int val;Node *left;Node *right;Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
示例 1:
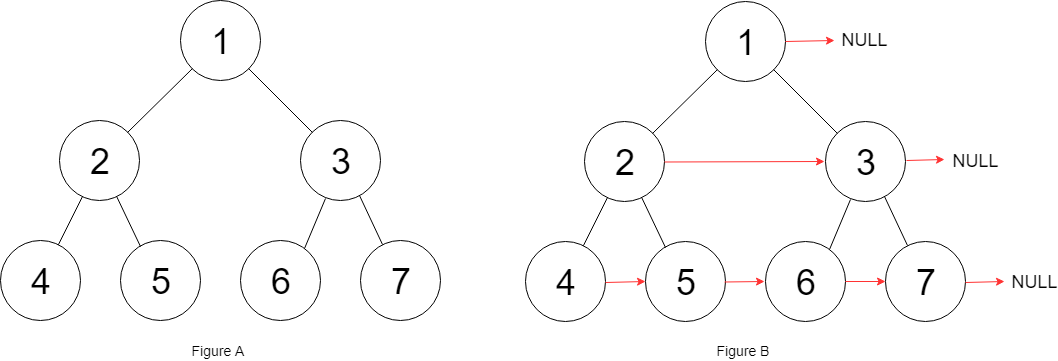
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] 输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#] 解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化的输出按层序遍历排列,同一层节点由 next 指针连接,'#' 标志着每一层的结束。
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 212 - 1]范围内 -1000 <= node.val <= 1000
进阶:
- 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
- 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;class Node {
public:int val;Node* left;Node* right;Node* next;Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) : val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};class Solution {
public:Node* connect(Node* root) {if(root == NULL) {return NULL;}Node* leftmost = root;while(leftmost->left != NULL) {Node* head = leftmost;while(head != NULL) {head->left->next = head->right;if(head->next != NULL) {head->right->next = head->next->left;}head= head->next;}leftmost = leftmost->left;}return root;}
};Node* Create() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;Node* root = new Node(rootVal);queue<Node*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {Node* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new Node(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);} else {curr->left = NULL;}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new Node(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);} else {curr->right = NULL;}}return root;
}void printTree(Node* root) {if(root == NULL) {return;}Node* curr = root;while(curr != NULL) {Node* temp = curr;while(temp != NULL) {cout << temp->val << " ";temp = temp->next;}cout << "# ";curr = curr->left;}
}int main() {Node* root = Create();Solution solution;solution.connect(root);printTree(root);return 0;
}117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点Ⅱ
给定一个二叉树:
struct Node {int val;Node *left;Node *right;Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL 。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL 。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7] 输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#] 解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化输出按层序遍历顺序(由 next 指针连接),'#' 表示每层的末尾。
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中的节点数在范围
[0, 6000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:
- 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
- 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序的隐式栈空间不计入额外空间复杂度。
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;class Node {public:int val;Node* left;Node* right;Node* next;Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) : val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};class Solution {public:Node* connect(Node* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return NULL;}queue<Node*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {int size = q.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {Node* node = q.front();q.pop();if (i < size - 1) {node->next = q.front();}if (node->left != nullptr) {q.push(node->left);}if (node->right != nullptr) {q.push(node->right);}}}return root;}};Node* Create() {cout << "Enter the value of the root node: ";int rootVal;cin >> rootVal;if(rootVal == -1)return NULL;Node* root = new Node(rootVal);queue<Node*> q;q.push(root);while (!q.empty()) {Node* curr = q.front();q.pop();cout << "Enter the left child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int leftVal;cin >> leftVal;if (leftVal != -1) {curr->left = new Node(leftVal);q.push(curr->left);} else {curr->left = NULL;}cout << "Enter the right child of '" << curr->val << "' (or -1 if none): ";int rightVal;cin >> rightVal;if (rightVal != -1) {curr->right = new Node(rightVal);q.push(curr->right);} else {curr->right = NULL;}}return root;
}void printTree(Node* root) {if(root == NULL) {return;}Node* curr = root;while(curr != NULL) {Node* temp = curr;while(temp != NULL) {cout << temp->val << " ";temp = temp->next;}cout << "# ";curr = curr->left;}
}int main() {Node* root = Create();Solution solution;solution.connect(root);printTree(root);return 0;
}118. 杨辉三角
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成「杨辉三角」的前 numRows 行。
在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
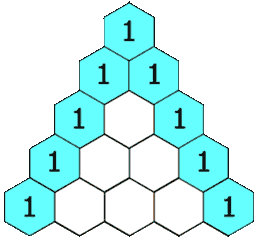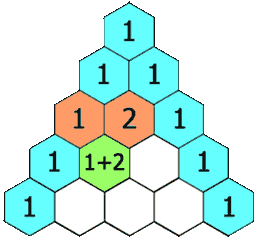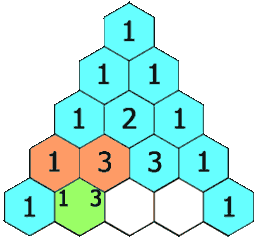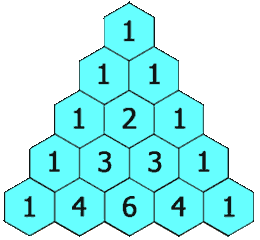
示例 1:
输入: numRows = 5 输出: [[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]]
示例 2:
输入: numRows = 1 输出: [[1]]
提示:
1 <= numRows <= 30
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<vector<int> > generate(int numRows) {vector<vector<int> > triangle(numRows);for(int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {triangle[i].resize(i + 1);triangle[i][0] = 1;triangle[i][i] = 1;for(int j = 1; j < i; j++) {triangle[i][j] = triangle[i - 1][j - 1] + triangle[i - 1][j];}}return triangle;}
};int main() {int numRows;cin >> numRows;Solution solution;vector<vector<int> > result = solution.generate(numRows);for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size() - 1; j++) {cout << result[i][j] << ", ";}cout<<result[i][result[i].size() - 1];cout << "]" << endl;}return 0;
}119. 杨辉三角Ⅱ
给定一个非负索引 rowIndex,返回「杨辉三角」的第 rowIndex 行。
在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
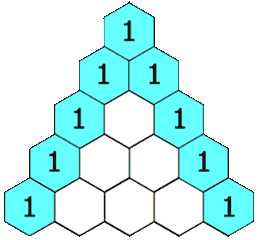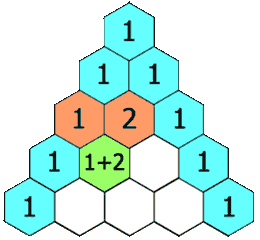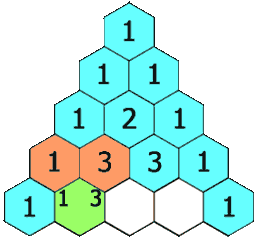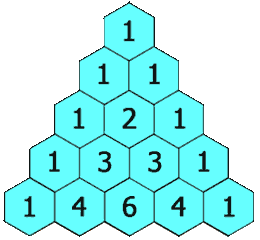
示例 1:
输入: rowIndex = 3 输出: [1,3,3,1]
示例 2:
输入: rowIndex = 0 输出: [1]
示例 3:
输入: rowIndex = 1 输出: [1,1]
提示:
0 <= rowIndex <= 33
进阶:
你可以优化你的算法到 O(rowIndex) 空间复杂度吗?
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<int> getRow(int rowIndex) {vector<int> row(rowIndex + 1, 1);for(int i = 2; i <= rowIndex; i++) {for(int j = i - 1; j > 0; j--) { // 从行 后 往 前 row[j] = row[j] + row[j - 1];}}return row;}
};int main() {int rowIndex;cin >> rowIndex;Solution solution;vector<int> result = solution.getRow(rowIndex);cout << "[";for(int i = 0; i < result.size() - 1; i++) {cout << result[i] << ", ";}cout << result[result.size() - 1] << "]";return 0;
} 解法二:
vector<int> getRow(int rowIndex) {vector<int> result;long long cur = 1;for(int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; i++) {result.push_back(cur);cur = cur * (rowIndex - i) / (i + 1);} return result;
}120. 三角形最小路径和
给定一个三角形 triangle ,找出自顶向下的最小路径和。
每一步只能移动到下一行中相邻的结点上。相邻的结点 在这里指的是 下标 与 上一层结点下标 相同或者等于 上一层结点下标 + 1 的两个结点。也就是说,如果正位于当前行的下标 i ,那么下一步可以移动到下一行的下标 i 或 i + 1 。
示例 1:
输入:triangle = [[2],[3,4],[6,5,7],[4,1,8,3]] 输出:11 解释:如下面简图所示:23 46 5 7 4 1 8 3 自顶向下的最小路径和为 11(即,2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11)。
示例 2:
输入:triangle = [[-10]] 输出:-10
提示:
1 <= triangle.length <= 200triangle[0].length == 1triangle[i].length == triangle[i - 1].length + 1-104 <= triangle[i][j] <= 104
进阶:
- 你可以只使用
O(n)的额外空间(n为三角形的总行数)来解决这个问题吗?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int minimumTotal(vector<vector<int>>& triangle) {int n = triangle.size();if(n == 0) {return 0;}vector<int> dp(n, 0);// 初始化dp数组的第一行dp[0] = triangle[0][0];// 逐行计算dp数组的值for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {// 从右到左更新dp数组,保证每一次更新时使用的时上一行的结果for(int j = i; j >= 0; j--) {if(j == 0) {// 最左边的元素dp[j] = dp[j] + triangle[i][j]; } else if(j == i) {// 最右边的元素dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + triangle[i][j]; } else {// 中间的元素dp[j] = min(dp[j - 1], dp[j]) + triangle[i][j]; }} } // 找到dp数组最后一行的最小值int minSum = dp[0];for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {minSum = min(minSum, dp[j]);} return minSum;}
};int main() {int n;cin >> n;int m = 1;vector<vector<int>> triangle;while(n--) {vector<int> nums;int temp;for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {cin >> temp;nums.push_back(temp);}m++;triangle.push_back(nums);}Solution solution;cout << solution.minimumTotal(triangle);return 0;
}这篇关于LeetCode刷题记(四):91~120题的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







