本文主要是介绍目标检测-锚框概念和代码实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言
经历过图像分类后,进一步的就是更复杂的目标检测了,从这一章开始,将会不断记录图像目标检测中的学习经历,其中大多数思路以及代码来源,来自于李沐的动手学深度学习课程,不过在这里,我会尽可能不用d2l的库,而是把里面方法提取出来,或者重写,以便理解和单独使用。
锚框概念
在目标检测中,我们需要去框选出目标所在位置的坐标,这个时候,在初始的深度学习方案中,提出了锚框的概念,即预先对每个像素绘制5个左右的虚拟框,例如:
假设输入一张500x500的图片,那么它应该得到的锚框数为:
500x500x5个
代码实现如下:
def multibox_prior(data, sizes, ratios):in_height, in_width = data.shape[-2:]device = data.devicenum_sizes, num_ratios = len(sizes), len(ratios)boxes_per_pixel = num_sizes + num_ratios - 1 # 每个像素的anchor数量size_tensor = torch.tensor(sizes, device=device)ratio_tensor = torch.tensor(ratios, device=device)offset_h, offset_w = 0.5, 0.5# 归一化steps_h = 1.0 / in_heightsteps_w = 1.0 / in_width# 计算中心偏移center_h = (torch.arange(in_height, device=device) + offset_h) * steps_hcenter_w = (torch.arange(in_width, device=device) + offset_w) * steps_wshift_y, shift_x = torch.meshgrid(center_h, center_w)shift_y, shift_x = shift_y.reshape(-1), shift_x.reshape(-1)# 由于一个像素对应boxes_per_pixel个anchor,交叉重复boxes_per_pixel次out_grid = torch.stack([shift_x, shift_y, shift_x, shift_y], dim=1).repeat_interleave(boxes_per_pixel, dim=0)# 计算在一个像素处,anchor左上、右下坐标相对于像素中心的偏移# 下面在计算w时,为了处理矩形的情况,需要* in_height / in_widthw = torch.cat((size_tensor * torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[0]), sizes[0] * torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[1:]))) * in_height / in_widthh = torch.cat((size_tensor / torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[0]), sizes[0] / torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[1:])))anchor_manipulations = torch.stack((-w, -h, w, h)).T.repeat(in_height * in_width, 1) / 2output = out_grid + anchor_manipulationsreturn output.unsqueeze(0)
img_get = Image.open("../img/1.jpeg") # 读取图片
plt.imshow(img_get , cmap=plt.cm.binary)
# plt.show()
print(img_get)
trans = transforms.Compose([ # 将所有的transform操作合并在一起执行
transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
])
img = img_get.convert("RGB")
img =trans(img)
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
print(img.shape)
h, w = img.shape[-2:]
print(h, w)
# 构建与图像大小一直的锚框模板
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 3, h, w))print("X.shape",X.shape)
print("X",X)
# 生成锚框 每个坐标生成5个框
Y = multibox_prior(X, sizes=[0.75, 0.5, 0.25], ratios=[1, 2, 0.5])
print("Y",Y)
print(Y.shape)
这里输入了1979x2968的图片

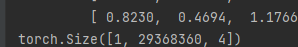
获取到了29368360个锚框,每个锚框的坐标为4个数据
然后利用锚框坐标进行绘制
#来自d2l的函数
def bbox_to_rect(bbox, color):# 将边界框(左上x, 左上y, 右下x, 右下y)格式转换成matplotlib格式:# ((左上x, 左上y), 宽, 高)return plt.Rectangle(xy=(bbox[0], bbox[1]), width=bbox[2] - bbox[0], height=bbox[3] - bbox[1],fill=False, edgecolor=color, linewidth=2)
# 绘制锚框
def show_bboxes(axes, bboxes, labels=None, colors=None):"""Show bounding boxes."""def make_list(obj, default_values=None):if obj is None:obj = default_valueselif not isinstance(obj, (list, tuple)):obj = [obj]return objlabels = make_list(labels)colors = make_list(colors, ['b', 'g', 'r', 'm', 'c'])for i, bbox in enumerate(bboxes):color = colors[i % len(colors)]# rect = d2l.bbox_to_rect(bbox.detach().numpy(), color)rect = bbox_to_rect(bbox.detach().numpy(), color)axes.add_patch(rect)if labels and len(labels) > i:text_color = 'k' if color == 'w' else 'w'axes.text(rect.xy[0], rect.xy[1], labels[i], va='center',ha='center', fontsize=9, color=text_color,bbox=dict(facecolor=color, lw=0))# 将锚框数据reshape成方便绘制的格式
boxes = Y.reshape(h, w, 5, 4)
print("boxes",boxes)
print(boxes.shape)
# boxes[250, 250, 0, :]
# d2l.set_figsize(figsize=(10, 10))
bbox_scale = torch.tensor((w, h, w, h))
fig =plt.imshow(img_get)
#fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
show_bboxes(fig.axes, boxes[1000, 1000, :, :] * bbox_scale, ['s=0.75, r=1', 's=0.5, r=1', 's=0.25, r=1', 's=0.75, r=2', 's=0.75, r=0.5'
])
plt.show()

到这里我们完成了锚框的设计和绘制。但是存在一个问题,锚框实在太多了,这是很浪费的表现,这时需要用到nms极大值抑制的方法,去获取与真实标记框的iou,从而删掉一部分无关的背景框。
现在我们去将每个锚框与真实框进行对比:
def assign_anchor_to_bbox(ground_truth, anchors, device, iou_threshold=0.5):num_anchors, num_gt_boxes = anchors.shape[0], ground_truth.shape[0]#这里计算出了所有锚框与真实框的iou值jaccard = box_iou(anchors, ground_truth)anchors_bbox_map = torch.full((num_anchors,), -1, dtype=torch.long,device=device)max_ious, indices = torch.max(jaccard, dim=1)anc_i = torch.nonzero(max_ious >= 0.5).reshape(-1)box_j = indices[max_ious >= 0.5]anchors_bbox_map[anc_i] = box_jcol_discard = torch.full((num_anchors,), -1)row_discard = torch.full((num_gt_boxes,), -1)for _ in range(num_gt_boxes):max_idx = torch.argmax(jaccard) # Find the largest IoUbox_idx = (max_idx % num_gt_boxes).long()anc_idx = (max_idx / num_gt_boxes).long()anchors_bbox_map[anc_idx] = box_idxjaccard[:, box_idx] = col_discardjaccard[anc_idx, :] = row_discardreturn anchors_bbox_map最后返回得到的map会包含和真实框近似的所有锚框,这个锚框数量和准确度取决于我们设置的iou_threshold,到此我们实现了上万的锚框的有效缩减.
其中的IOU值计算如下:
# 计算IOUdef box_iou(boxes1, boxes2):box_area = lambda boxes: ((boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]))areas1 = box_area(boxes1)areas2 = box_area(boxes2)# 此处利用了broadcast机制,最终的shape为(no. of boxes1, no. of boxes2, 2)inter_upperlefts = torch.max(boxes1[:, None, :2], boxes2[:, :2])inter_lowerrights = torch.min(boxes1[:, None, 2:], boxes2[:, 2:])inters = (inter_lowerrights - inter_upperlefts).clamp(min=0)inter_areas = inters[:, :, 0] * inters[:, :, 1]union_areas = areas1[:, None] + areas2 - inter_areas # 此处利用broadcast机制return inter_areas / union_areas
在得到了有效缩减后的锚框后,计算了一个偏移量,主要功能是让其中的数据分得更加广,用以让真实框和锚框之间更好地去匹配预测
# 为了让offset更容易拟合,要使offset更加均匀的分布。
def offset_boxes(anchors, assigned_bb, eps=1e-6):c_anc = box_corner_to_center(anchors)c_assigned_bb = box_corner_to_center(assigned_bb)offset_xy = 10 * (c_assigned_bb[:, :2] - c_anc[:, :2]) / c_anc[:, 2:]offset_wh = 5 * torch.log(eps + c_assigned_bb[:, 2:] / c_anc[:, 2:])offset = torch.cat([offset_xy, offset_wh], axis=1)return offset#真实坐标往中心点计算
def box_corner_to_center(boxes):x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3]cx = (x1 + x2) / 2cy = (y1 + y2) / 2w = x2 - x1h = y2 - y1boxes = torch.stack((cx, cy, w, h), axis=-1)return boxes
#中心点偏移坐标往真实坐标转换
def box_center_to_corner(boxes):cx, cy, w, h = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3]x1 = cx - 0.5 * wy1 = cy - 0.5 * hx2 = cx + 0.5 * wy2 = cy + 0.5 * hboxes = torch.stack((x1, y1, x2, y2), axis=-1)return boxes这里在很多数据标注中也采用了这种方式,这里举个例子,在之前我标注了一张图,如下:

当时标注得到的label信息为

代表了两个飞机的位置
但当你实际去测量它的图片位置信息,会发现它并不是直接的坐标,需要通过上述的公式转换,得到如下坐标:
[ 0.3188, 0.0448, 0.4058, 0.2239], [ 0.6594, 0.2388, 0.7246, 0.3552]
而这才是它在图中的真实坐标,这里有所偏差,因为是我手动测量的.
最后便是真实框和锚框的对比计算了
def multibox_detection(cls_probs, offset_preds, anchors, nms_threshold=0.5,pos_threshold=0.009999999):device, batch_size = cls_probs.device, cls_probs.shape[0]anchors = anchors.squeeze(0) # ???????????????????print('anchors', anchors.shape)num_classes, num_anchors = cls_probs.shape[1], cls_probs.shape[2]out = []for i in range(batch_size):cls_prob, offset_pred, anchor = cls_probs[i], offset_preds[i].reshape(-1, 4), anchors[i]# print('cls_prob', cls_prob.shape)# print('offset_pred', offset_pred.shape)conf, class_id = torch.max(cls_prob[1:], 0) # 获得的class id 从0 开始predicted_bb = offset_inverse(anchor, offset_pred) # 经offset修正后的bboxkeep = nms(predicted_bb, conf, nms_threshold) # 经nms后保留下来的bbox# 寻找non-keep, 并将类别设为backgroundall_idx = torch.arange(num_anchors, dtype=torch.long, device=device)combined = torch.cat((keep, all_idx))uniques, counts = combined.unique(return_counts=True)non_keep = uniques[counts == 1]class_id[non_keep] = -1# 将keep的放在前面,将non_keep的放在后面all_id_sorted = torch.cat((keep, non_keep))class_id = class_id[all_id_sorted]conf, predicted_bb = conf[all_id_sorted], predicted_bb[all_id_sorted]# 将conf < pos_threshold的bbox,设置为背景,-1below_min_idx = (conf < pos_threshold)class_id[below_min_idx] = -1conf[below_min_idx] = 1 - conf[below_min_idx]pred_info = torch.cat((class_id.unsqueeze(1), conf.unsqueeze(1), predicted_bb), dim=1) # 在anchor的那一维度catout.append(pred_info)return torch.stack(out)假设我们不适用nms,得到的图将会是这样:

其中黑色的是真实框,然后其他颜色的分别是包含了真实框且iou值大于0.5的锚框.
然后让我们使用nms试试:
# 构造4个锚框anchors = torch.tensor([[0.31, 0.04, 0.42, 0.22], [0.3, 0.044, 0.40, 0.22],[0.61, 0.21, 0.71, 0.33], [0.3188, 0.0448, 0.4058, 0.2239]])# 假设预测的偏移量都是零offset_preds = torch.tensor([0] * anchors.numel())# 预测概率cls_probs = torch.tensor([[0] * 4, # 背景的预测概率[0.1, 0.1, 0.85, 0], # plane1的预测概率[0.88, 0.2, 0.3, 0.9]]) # plane2的预测概率# 为输入增加样本维度output = multibox_detection(cls_probs.unsqueeze(dim=0).repeat(2, 1, 1),offset_preds.unsqueeze(dim=0).repeat(2, 1),anchors.unsqueeze(dim=0).repeat(2, 1, 1), nms_threshold=0.5)print(output)for i in output[0].detach().numpy():if i[0] == -1:continuelabel = ('plane1=', 'plane2=')[int(i[0])] + str(i[1])show_bboxes(fig.axes, [torch.tensor(i[2:]) * bbox_scale], label)plt.show()

可以看到它将较低的锚框都删掉了.
打印一下数据:

可以看到第二列分别为他们的nms的置信度,如果小于了0.5则不认为这是一个包含真实框的锚框,设为-1,如果大于0.5,则认为它预测对了.
这篇关于目标检测-锚框概念和代码实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





