本文主要是介绍c 语言 无处不在的二分搜索,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
我们知道二分查找算法。二分查找是最容易正确的算法。我提出了一些我在二分搜索中收集的有趣问题。有一些关于二分搜索的请求。我请求您遵守准则:“我真诚地尝试解决问题并确保不存在极端情况”。阅读完每个问题后,最小化浏览器并尝试解决它。
问题陈述:给定一个由 N 个不同元素组成的排序数组,使用最少的比较次数在数组中找到一个键。 (您认为二分搜索是在排序数组中搜索键的最佳选择吗?)无需太多理论,这里是典型的二分搜索算法。
// Returns location of key, or -1 if not found
int BinarySearch(int A[], int l, int r, int key)
{
int m;
while( l <= r )
{
m = l + (r-l)/2;
if( A[m] == key ) // first comparison
return m;
if( A[m] < key ) // second comparison
l = m + 1;
else
r = m - 1;
}
return -1;
}
理论上,最坏情况下我们需要进行log N + 1次比较。如果我们观察的话,我们会在每次迭代中使用两次比较,除非最终成功匹配(如果有)。在实践中,比较将是昂贵的操作,它不仅仅是原始类型比较。尽量减少与理论极限的比较更为经济。请参阅下图,了解下一个实现中索引的初始化。

以下实现使用较少的比较次数。
// Invariant: A[l] <= key and A[r] > key
// Boundary: |r - l| = 1
// Input: A[l .... r-1]
int BinarySearch(int A[], int l, int r, int key)
{
int m;
while( r - l > 1 )
{
m = l + (r-l)/2;
if( A[m] <= key )
l = m;
else
r = m;
}
if( A[l] == key )
return l;
if( A[r] == key )
return r;
else
return -1;
}
在 while 循环中,我们仅依赖于一次比较。搜索空间收敛到将l和r指向两个不同的连续元素。我们需要再进行一次比较来跟踪搜索状态。您可以查看示例测试用例 http://ideone.com/76bad0。 (C++11 代码)。
问题陈述:给定一个由 N 个不同整数组成的数组,找到输入“key”的下限值。假设 A = {-1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10} 且 key = 7,我们应该返回 6 作为结果。我们可以使用上面的优化实现来找到键的下限值。只要不变量成立,我们就不断地将左指针移到最右边。最终左指针指向小于或等于 key 的元素(根据定义下限值)。以下是可能的极端情况, —> 如果数组中的所有元素都小于 key,则左指针移动到最后一个元素。 —> 如果数组中的所有元素都大于 key,则为错误情况。 —> 如果数组中的所有元素都相等且 <= key,则这是我们实现的最坏情况输入。
这是示例:
// largest value <= key
// Invariant: A[l] <= key and A[r] > key
// Boundary: |r - l| = 1
// Input: A[l .... r-1]
// Precondition: A[l] <= key <= A[r]
int Floor(int A[], int l, int r, int key)
{
int m;
while( r - l > 1 )
{
m = l + (r - l)/2;
if( A[m] <= key )
l = m;
else
r = m;
}
return A[l];
}
// Initial call
int Floor(int A[], int size, int key)
{
// Add error checking if key < A[0]
if( key < A[0] )
return -1;
// Observe boundaries
return Floor(A, 0, size, key);
}
您可以看到一些测试用例 http://ideone.com/z0Kx4a。
问题陈述:给定一个可能有重复元素的排序数组。查找log N时间内输入“key”出现的次数。这里的想法是使用二分搜索查找数组中最左边和最右边出现的键。我们可以修改底函数来跟踪最右边的出现和最左边的出现。
这是示例:
// Input: Indices Range [l ... r)
// Invariant: A[l] <= key and A[r] > key
int GetRightPosition(int A[], int l, int r, int key)
{
int m;
while( r - l > 1 )
{
m = l + (r - l)/2;
if( A[m] <= key )
l = m;
else
r = m;
}
return l;
}
// Input: Indices Range (l ... r]
// Invariant: A[r] >= key and A[l] > key
int GetLeftPosition(int A[], int l, int r, int key)
{
int m;
while( r - l > 1 )
{
m = l + (r - l)/2;
if( A[m] >= key )
r = m;
else
l = m;
}
return r;
}
int CountOccurrences(int A[], int size, int key)
{
// Observe boundary conditions
int left = GetLeftPosition(A, -1, size-1, key);
int right = GetRightPosition(A, 0, size, key);
// What if the element doesn't exists in the array?
// The checks helps to trace that element exists
return (A[left] == key && key == A[right])?
(right - left + 1) : 0;
}
示例代码 zn6R6a - Online C++0x Compiler & Debugging Tool - Ideone.com。
问题陈述: 给定一个由不同元素组成的排序数组,并且该数组在未知位置旋转。找到数组中的最小元素。我们可以在下图中看到示例输入数组的图示。
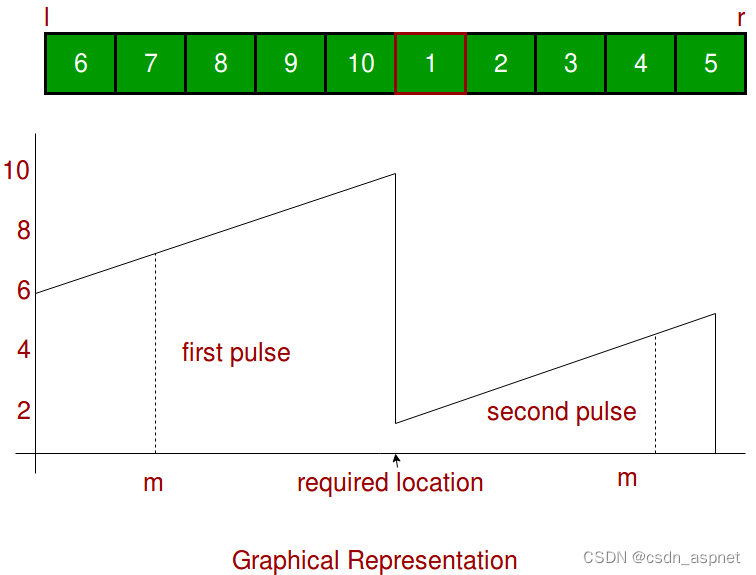
我们收敛搜索空间直到l和r 指向单个元素。如果中间位置落在第一个脉冲中,则不满足条件 A[m] < A[r],我们将搜索空间收敛到 A[m+1 … r]。如果中间位置落在第二个脉冲中,则满足条件 A[m] < A[r],我们将搜索空间收敛到 A[1 … m]。在每次迭代中,我们都会检查搜索空间大小,如果它是 1,我们就完成了。
下面给出的是算法的实现。 你能想出不同的实施方案吗?
int BinarySearchIndexOfMinimumRotatedArray(int A[], int l, int r)
{
// extreme condition, size zero or size two
int m;
// Precondition: A[l] > A[r]
if( A[l] <= A[r] )
return l;
while( l <= r )
{
// Termination condition (l will eventually falls on r, and r always
// point minimum possible value)
if( l == r )
return l;
m = l + (r-l)/2; // 'm' can fall in first pulse,
// second pulse or exactly in the middle
if( A[m] < A[r] )
// min can't be in the range
// (m < i <= r), we can exclude A[m+1 ... r]
r = m;
else
// min must be in the range (m < i <= r),
// we must search in A[m+1 ... r]
l = m+1;
}
return -1;
}
int BinarySearchIndexOfMinimumRotatedArray(int A[], int size)
{
return BinarySearchIndexOfMinimumRotatedArray(A, 0, size-1);
}
请参阅示例测试用例 KbwDrk - Online C++0x Compiler & Debugging Tool - Ideone.com。
练习:
1. 称为signum(x, y)的函数 定义为,
Signum(x, y) = -1 如果 x < y
= 0 如果 x = y
= 1 如果 x > y
您是否遇到过比较行为类似于符号函数的指令集?它能让二分搜索的第一个实现变得最优吗?
2. 实现floor函数的ceil函数复制品。
3. 与你的朋友讨论“二分查找是否是最优的(比较次数最少)?为什么不在排序数组上进行三元搜索或插值搜索?与二分搜索相比,您什么时候更喜欢三元搜索或插值搜索?”
4. 画出二分搜索的树表示(相信我,这对你理解二分搜索的内部原理有很大帮助)。
这篇关于c 语言 无处不在的二分搜索的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


