本文主要是介绍【Android AMS】startActivity流程分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- AMS
- ActivityStack
- startActivity流程
- startActivityMayWait
- startActivityUncheckedLocked
- startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask, boolean doResume, boolean keepCurTransition)
- resumeTopActivityLocked
- 参考
AMS是个用于管理Activity和其它组件运行状态的系统进程。
AMS
AMS在系统启动的时候,创建一个线程循环处理客户端的请求。AMS会向ServiceManager注册多种Binder Server:“activity”、“meminfo”、“cpuinfo”等。
AMS启动过程:
/*frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java*/public static void main(String[] args) {...// This used to be its own separate thread, but now it is// just the loop we run on the main thread.ServerThread thr = new ServerThread();thr.initAndLoop();}
/*frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java*/
public void run() {…Slog.i(TAG, "Activity Manager");context = ActivityManagerService.main(factoryTest); //启动AMS…ActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess(); //向Service Manager注册…
}
AMS提供了一个static main函数,通过它可以轻松启动AMS,通过setSystemProcess把这个重要系统服务注册到ServiceManager。
//frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.javapublic static final Context main(int factoryTest) {AThread thr = new AThread();//AMS线程thr.start();//启动//这个线程执行在system server上,通过thr.mService判断AMS启动是否成功。如果成功,返回system server,否则一直等待。如果出错,就无力回天,空处理。synchronized (thr) {while (thr.mService == null) {try {thr.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {}}}ActivityManagerService m = thr.mService;mSelf = m;ActivityThread at = ActivityThread.systemMain();mSystemThread = at;Context context = at.getSystemContext();context.setTheme(android.R.style.Theme_Holo);m.mContext = context;m.mFactoryTest = factoryTest;m.mIntentFirewall = new IntentFirewall(m.new IntentFirewallInterface());m.mStackSupervisor = new ActivityStackSupervisor(m, context, thr.mLooper);m.mBatteryStatsService.publish(context);m.mUsageStatsService.publish(context);m.mAppOpsService.publish(context);//唤醒synchronized (thr) {thr.mReady = true;thr.notifyAll();}m.startRunning(null, null, null, null);return context;}
这里一个wait & notify配对使用,让system server确保AMS启动成功,它自己再接着执行。这么做的原因无它,就是system server需要依赖于AMS。
将AMS注册到ServiceManager之后,它还注册了一系列和进程管理相关的服务:
public static void setSystemProcess() {try {ActivityManagerService m = mSelf; ServiceManager.addService("activity", m, true);//AMS的主业ServiceManager.addService("meminfo", new MemBinder(m));//内存使用情况…//其他服务省略}
要了解AMS提供的所有功能,可以查看IActivityManager.java文件。
可以把这些接口进行分类:
- 组件状态管理:例如startActivity、startService
- 组件状态查询:例如getServices
- Task相关:例如removeSubTask
- 其它:查询运行时信息,例如getMemoryInfo
ActivityStack
/*frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java*/
public static final Context main(int factoryTest) {/*main()函数是启动AMS的入口*/…ActivityManagerService m = thr.mService;…m.mMainStack = new ActivityStack(m, context, true, thr.mLooper);/*生成ActivityStack对象*/…
}
ActivityStack是管理当前系统所有activity状态的一个数据结构。
它里面有个enum 叫做ActivityState :
enum ActivityState {INITIALIZING, //正在初始化RESUMED, //恢复PAUSING, //正在暂停PAUSED, //已经暂停STOPPING, //正在停止STOPPED, //已经停止FINISHING, //正在完成DESTROYING, //正在销毁DESTROYED //已经销毁}
ActivityStack除了管理状态,还有一系列不同功能的ArrayList成员变量,它们都是ActivityRecord,用来记录每个activity的runtime信息:
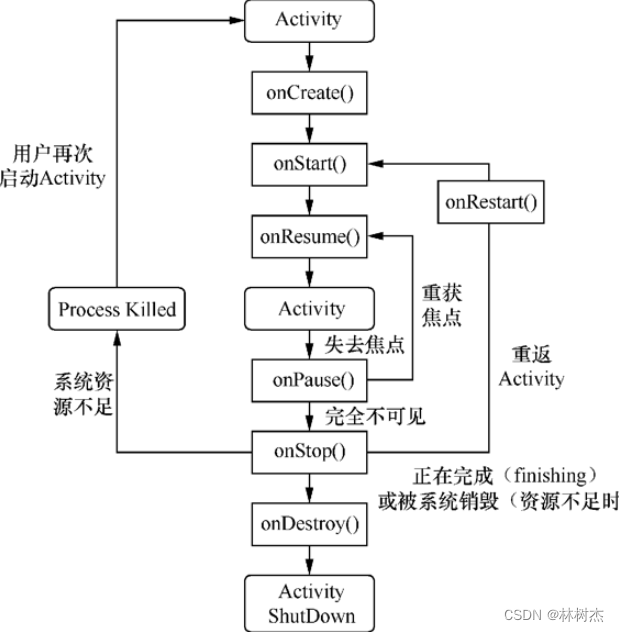
startActivity流程
startActivity()用来启动一个Activity,它有可能启动当前进程的Activity,也有可能启动其它进程的Activity。当通过Intent匹配到目标对象,如果目标对象的进程已经启动,那么AMS就会通知这个进程加载并运行这个activity。如果进程没有启动,AMS就会先启动进程,再让进程运行目标activity。
/*frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java*/public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,String profileFile, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, Bundle options) {return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType,result To, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profileFile, profileFd, options,UserHandle.getCallingUserId());}
startActivityAsUser比startActivity多了一个userId参数,用来表示调用者的用户ID,通过Binder机制的getCallingUid获得。
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String calling Package,Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags, String profileFile,ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, Bundle options, int userId ){enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");userId = handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId,false, true, "startActivity", null);return mMainStack.startActivityMayWait(caller,-1,callingPackage,intent, resolvedType,resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profileFile, profileFd,null, null, options, userId);/*这个函数是ActivityStack提供的*/}
startActivityAsUser的重点是做权限检查。
startActivityMayWait
startActivityMayWait的工作:
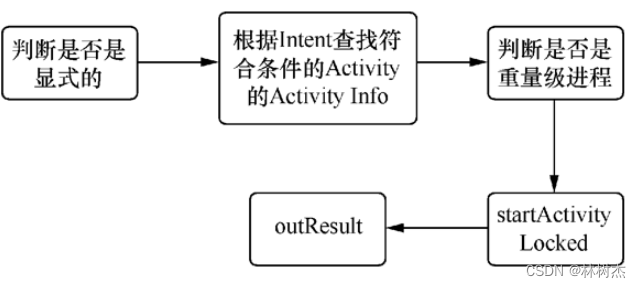
这个过程中,可能会“wait”,具体如流程图:
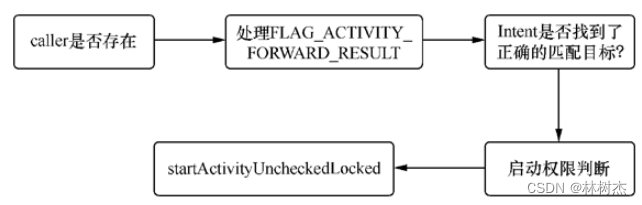
接着调用的是startActivityLocked,它有两个重载函数:
final int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller,Intent intent, String resolvedType,Uri[] grantedUriPermissions,int grantedMode, ActivityInfo aInfo, IBinder resultTo,String resultWho, int requestCode,int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean onlyIfNeeded,boolean componentSpecified, ActivityRecord[] outActivity) {int err = START_SUCCESS;ProcessRecord callerApp = null;if (caller != null) {callerApp = mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);if (callerApp != null) {callingPid = callerApp.pid;callingUid = callerApp.info.uid;} else {Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to find app for caller " + caller+ " (pid=" + callingPid + ") when starting: "+ intent.toString());err = START_PERMISSION_DENIED;}}if (err == START_SUCCESS) {Slog.i(TAG, "START {" + intent.toShortString(true, true, true, false)+ "} from pid " + (callerApp != null ? callerApp.pid : callingPid));}ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null;ActivityRecord resultRecord = null;if (resultTo != null) {int index = indexOfTokenLocked(resultTo);if (DEBUG_RESULTS) Slog.v(TAG, "Will send result to " + resultTo + " (index " + index + ")");if (index >= 0) {sourceRecord = mHistory.get(index);if (requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing) {resultRecord = sourceRecord;}}}int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();if ((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT) != 0&& sourceRecord != null) {// Transfer the result target from the source activity to the new// one being started, including any failures.if (requestCode >= 0) {return START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT;}resultRecord = sourceRecord.resultTo;resultWho = sourceRecord.resultWho;requestCode = sourceRecord.requestCode;sourceRecord.resultTo = null;if (resultRecord != null) {resultRecord.removeResultsLocked(sourceRecord, resultWho, requestCode);}}if (err == START_SUCCESS && intent.getComponent() == null) {// We couldn't find a class that can handle the given Intent.// That's the end of that!err = START_INTENT_NOT_RESOLVED;}if (err == START_SUCCESS && aInfo == null) {// We couldn't find the specific class specified in the Intent.// Also the end of the line.err = START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND;}if (err != START_SUCCESS) {if (resultRecord != null) {sendActivityResultLocked(-1,resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode,Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null);}mDismissKeyguardOnNextActivity = false;return err;}final int perm = mService.checkComponentPermission(aInfo.permission, callingPid,callingUid, aInfo.applicationInfo.uid, aInfo.exported);if (perm != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {if (resultRecord != null) {sendActivityResultLocked(-1,resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode,Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null);}mDismissKeyguardOnNextActivity = false;String msg;if (!aInfo.exported) {msg = "Permission Denial: starting " + intent.toString()+ " from " + callerApp + " (pid=" + callingPid+ ", uid=" + callingUid + ")"+ " not exported from uid " + aInfo.applicationInfo.uid;} else {msg = "Permission Denial: starting " + intent.toString()+ " from " + callerApp + " (pid=" + callingPid+ ", uid=" + callingUid + ")"+ " requires " + aInfo.permission;}Slog.w(TAG, msg);throw new SecurityException(msg);}if (mMainStack) {if (mService.mController != null) {boolean abort = false;try {// The Intent we give to the watcher has the extra data// stripped off, since it can contain private information.Intent watchIntent = intent.cloneFilter();abort = !mService.mController.activityStarting(watchIntent,aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName);} catch (RemoteException e) {mService.mController = null;}if (abort) {if (resultRecord != null) {sendActivityResultLocked(-1,resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode,Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null);}// We pretend to the caller that it was really started, but// they will just get a cancel result.mDismissKeyguardOnNextActivity = false;return START_SUCCESS;}}}ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, this, callerApp, callingUid,intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration,resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified);if (outActivity != null) {outActivity[0] = r;}if (mMainStack) {if (mResumedActivity == null|| mResumedActivity.info.applicationInfo.uid != callingUid) {if (!mService.checkAppSwitchAllowedLocked(callingPid, callingUid, "Activity start")) {PendingActivityLaunch pal = new PendingActivityLaunch();pal.r = r;pal.sourceRecord = sourceRecord;pal.grantedUriPermissions = grantedUriPermissions;pal.grantedMode = grantedMode;pal.onlyIfNeeded = onlyIfNeeded;mService.mPendingActivityLaunches.add(pal);mDismissKeyguardOnNextActivity = false;return START_SWITCHES_CANCELED;}}if (mService.mDidAppSwitch) {// This is the second allowed switch since we stopped switches,// so now just generally allow switches. Use case: user presses// home (switches disabled, switch to home, mDidAppSwitch now true);// user taps a home icon (coming from home so allowed, we hit here// and now allow anyone to switch again).mService.mAppSwitchesAllowedTime = 0;} else {mService.mDidAppSwitch = true;}mService.doPendingActivityLaunchesLocked(false);}err = startActivityUncheckedLocked(r, sourceRecord,grantedUriPermissions, grantedMode, onlyIfNeeded, true);if (mDismissKeyguardOnNextActivity && mPausingActivity == null) {// Someone asked to have the keyguard dismissed on the next// activity start, but we are not actually doing an activity// switch... just dismiss the keyguard now, because we// probably want to see whatever is behind it.mDismissKeyguardOnNextActivity = false;mService.mWindowManager.dismissKeyguard();}return err;}
这里确保调用者本身的进程是存在的,否则返回START_PERMISSION_DENIED。这种情况出现在调用者被系统杀死,crash等。
FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT这个FLAG有跨越传递的作用,比如Activity1正常启动了Activity2,而当Activity2启动Activity3时使用了这个标志,那么当Activity3调用setResult时,result并不会像一般情况中那样传递给Activity2,而是传递给最初的Activity1。
startActivityUncheckedLocked
这个方法先拿到Intent中的FLAG,然后处理FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_USER_ACTION,这个FLAG表示来电、闹钟等非用户主动触发的Activity事件。
这里处理了很多FLAG,例如LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE、LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK这些,这里暂时不展开。
startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask, boolean doResume, boolean keepCurTransition)
private final void startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask,boolean doResume, boolean keepCurTransition) {...if (doResume) {resumeTopActivityLocked(null);}}
这里是启动activity的最后一站了,是AMS启动activity的关键。如果activity不是在新task中启动,那么程序要找出目标activity位于那个已有的task中。找到之后,如果它当前对用户不可见,就将它加入mHistory中,并在WMS中注册,但是不启动它。
接着将这个activity放在stack的最顶层:
mHistory.add(addPos, r);
r.putInHistory();
r.frontOfTask = newTask;
接下来,如果不是AMS的第一个activity,即mHistory > 0,则执行切换动画。
一个activity的UI能否显示,有个关键是WMS中必须有档案可查,就是appToken,它在startActivity中添加的:
mService.mWindowManager.addAppToken(addPos, r.appToken, r.task.taskId, r.info.screenOrientation, r.fullscreen);
activity有affinity特性的,它们更亲近affinity相符的task,关键地方在于FLAG是否有FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED。
Android源码中有很多函数都有locked标志,提醒开发者必须保证它们的线程安全。
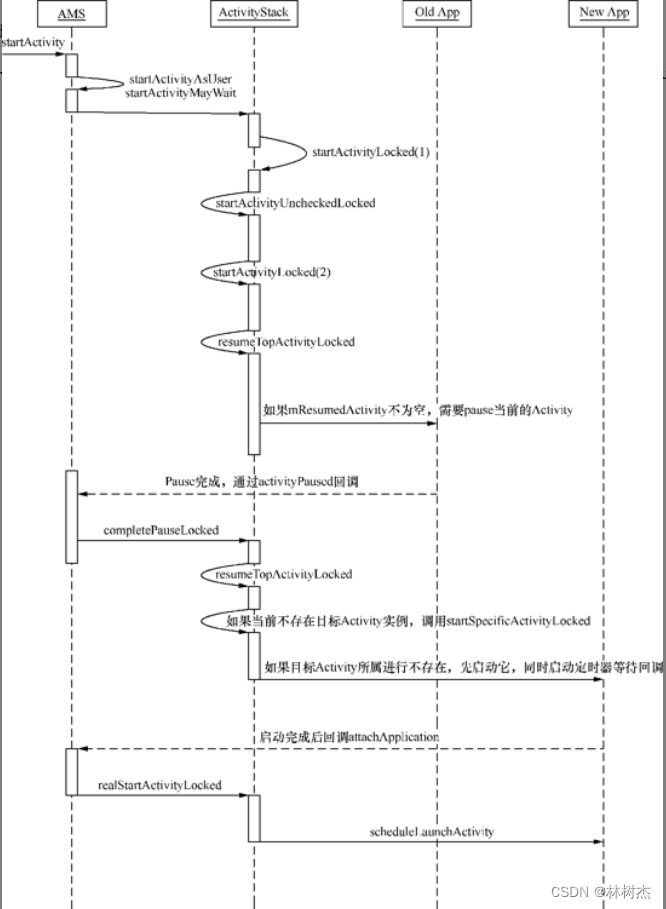
到这里startActivity分析完毕了,但是activity的启动流程还没完。
resumeTopActivityLocked
AMS会继续调用resumeTopActivityLocked来恢复最上层的Activity,并pause之前的Activity,并且在Activity切换的过程中还要首先展示切换动画,然后两个新旧Activity还会向WMS分别申请和释放Surface,最终将它们显示/不显示在屏幕上。
int i = mHistory.size()-1;//所有Activity的数量while (i >= 0) {ActivityRecord r = mHistory.get(i);if (!r.finishing && r != notTop && okToShow(r)) {return r;}i--;}return null;
这里处理ActivityRecord。
resumeTopActivityLocked执行后面的时候,可以正式启动目标activity了,但是有两种情况,一种是目标activity所属的进程已经在运行,一种是没有运行。
前者我们可以通知WMS这个Activity已经具备显示条件了:
mService.mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(next.appToken, true);
更新一系列全局变量,如果有等待启动的对象,就会通过:
next.app.thread.scheduleResumeActivity(next.appToken, mService.isNextTransitionForward());
告知目标线程要resume指定的activity。
后者的情况复杂些,会通过startSpecificActivityLocked启动进程,接着调用一系列和startActivity长得差不多的函数,最终调用zygote来fork一个新的进程:
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult =Process.start("<strong>android.app.ActivityThread</strong>", app.processName, uid, uid, gids,debugFlags,app.info.targetSdkVersion, null, null);
可以看出,一个进程启动的时候,实际上会加载ActivityThread。
那么新启动的进程什么时候启动activity呢?
进程启动后要通知AMS,AMS会预留一段时间等待回调。这个在不同设备上有所差异,有的10s,有的300s。如果进程指定时间内没有完成attachApplication回调,那么AMS就认为异常了。如果进程完成了attachApplication回调,AMS就会判断当前是不是有Activity在等待这个进程启动。是的话,调用realStartActivityLocked继续之前的任务。
接着就是activity的生命周期了,onCreate,onStart,onResume等,并且在WMS和SurfaceFlinger的配合下,目标Activity描述的UI界面会显示在屏幕。
startActivity流程才算真正完成。
参考
《深入理解Android内核设计思想》
这篇关于【Android AMS】startActivity流程分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





