本文主要是介绍CF1228E. Another Filling the Grid(容斥原理+排列组合),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
You have ?×? square grid and an integer ?. Put an integer in each cell while satisfying the conditions below.
All numbers in the grid should be between 1 and ? inclusive.
Minimum number of the ?-th row is 1 (1≤?≤?).
Minimum number of the ?-th column is 1 (1≤?≤?).
Find the number of ways to put integers in the grid. Since the answer can be very large, find the answer modulo (109+7).
These are the examples of valid and invalid grid when ?=?=2.
Input
The only line contains two integers ? and ? (1≤?≤250, 1≤?≤109).
Output
Print the answer modulo (109+7).
Examples
inputCopy
2 2
outputCopy
7
inputCopy
123 456789
outputCopy
689974806
Note
In the first example, following 7 cases are possible.
In the second example, make sure you print the answer modulo (109+7).
题意: nXn的矩阵,每个格子可以填1~k的数。要求使得每行每列的数字最小值都为1.问有多少种填数方案
思路:
我是看了这篇博客
https://www.cnblogs.com/birchtree/p/11614243.html
可以有n^3的dp写法,这里是排列组合+容斥。

这里i(j)代表至少多少个最小值不为1的行(列)。
而关于为什么这样容斥,我的想法是:
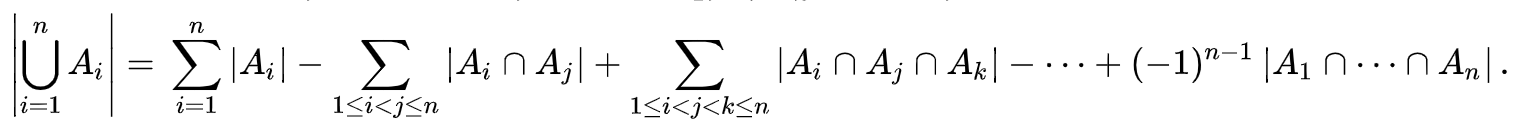
容斥原理的原始公式是划分出集和的,本题也需要划分集合。假设只有一行的情况下,你只需要考虑列。设 f [ i ] f[i] f[i]表示第 i i i列不为1。
那么 f [ 1 ] , f [ 2 ] , f [ 3 ] , . . . , f [ i ] f[1],f[2],f[3],...,f[i] f[1],f[2],f[3],...,f[i]就是集合所需的所有集合了。
答案就是 U − ( ∑ f [ i ] − ∑ f [ i ] ∩ f [ j ] + ∑ f [ i ] ∩ f [ j ] − ∑ f [ i ] ∩ f [ j ] ∩ f [ k ] . . . ) U - (∑f[i]-∑f[i]∩f[j]+∑f[i]∩f[j]-∑f[i]∩f[j]∩f[k]...) U−(∑f[i]−∑f[i]∩f[j]+∑f[i]∩f[j]−∑f[i]∩f[j]∩f[k]...)
这个式子是不是有原始公式的味道啦?
当然,行是不得不考虑的,那么就多划分出一些集合。
定义 f [ i ] f[i] f[i]为第 i i i列不存在1, g [ i ] g[i] g[i]为第 i i i行不存在1.
f [ 1 ] , f [ 2 ] , f [ 3 ] , . . . . , f [ n ] , g [ 1 ] , g [ 2 ] , g [ 3 ] , . . . , g [ n ] f[1],f[2],f[3],....,f[n],g[1],g[2],g[3],...,g[n] f[1],f[2],f[3],....,f[n],g[1],g[2],g[3],...,g[n]就是所需的所有集合。
答案就是 U − ( ∑ f [ i ] + ∑ g [ i ] − ∑ f [ i ] ∩ f [ j ] − ∑ f [ i ] ∩ g [ j ] − ∑ g [ i ] ∪ g [ j ] . . . ) U-(∑f[i]+∑g[i] - ∑f[i]∩f[j] - ∑f[i]∩g[j]-∑g[i]∪g[j] ...) U−(∑f[i]+∑g[i]−∑f[i]∩f[j]−∑f[i]∩g[j]−∑g[i]∪g[j]...)
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 7;
struct Point
{ll x,y;
}p[5005];
ll fac[maxn],inv[maxn],f[maxn];int cmp(Point a,Point b)
{if(a.x == b.x)return a.y < b.y;return a.x < b.x;
}ll qpow(ll a,ll b)
{ll res = 1;while(b){if(b & 1){res = (res * a) % mod;}a = (a * a) % mod;b = b >> 1;}return res % mod;
}ll C(ll n,ll m)
{if(m > n || m < 0)return 0;return fac[n] * ((inv[n - m] * inv[m]) % mod) % mod;
}void init()
{fac[0] = 1;inv[0] = 1;for(int i = 1;i <= maxn - 2;i++){fac[i] = (fac[i - 1] * i) % mod;inv[i] = qpow(fac[i],mod - 2);}
}int main()
{init();ll n,k;scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&k);ll ans = 0;for(int i = 0;i <= n;i++){for(int j = 0;j <= n;j++){ll cnt = n * i + n * j - i * j;ans = (ans + qpow(-1,i+j) * C(n,i) % mod * C(n,j)%mod * qpow(k - 1,cnt)%mod * qpow(k,n * n - cnt)%mod + mod * 100) % mod;}}printf("%lld\n",ans);return 0;
}DP做法
定义 f [ i ] [ j ] f[i][j] f[i][j]表示填完前 i i i行,前 i i i行都合理(最小值为1),且正好 j j j行合理。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 1000 + 7;int n,k;
ll pk[maxn],pk1[maxn];
ll f[maxn][maxn];
ll fac[maxn],inv[maxn];ll qpow(ll a,ll b)
{ll res = 1;while(b){if(b & 1){res = (res * a) % mod;}a = (a * a) % mod;b = b >> 1;}return res % mod;
}ll C(ll n,ll m)
{if(m > n || m < 0)return 0;return fac[n] * ((inv[n - m] * inv[m]) % mod) % mod;
}void init()
{fac[0] = 1;inv[0] = 1;pk[0] = 1;pk1[0] = 1;for(int i = 1;i <= maxn - 2;i++){fac[i] = (fac[i - 1] * i) % mod;inv[i] = qpow(fac[i],mod - 2);pk[i] = pk[i - 1] * k % mod;pk1[i] = pk1[i - 1] * (k - 1) % mod;}
}int main() {scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);init();for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {f[1][i] = C(n,i) * pk1[n - i] % mod;}for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++) {for(int j = 1;j <= n;j++) {for(int k = 1;k < j;k++) {f[i][j] = (f[i][j] + C(n - k,j - k) * pk[k] % mod * pk1[n - j] % mod * f[i - 1][k] % mod) % mod;}f[i][j] = (f[i][j] + (pk[j] - pk1[j] + mod) * pk1[n - j] % mod * f[i - 1][j] % mod) % mod;}}printf("%lld\n",f[n][n]);return 0;
}这篇关于CF1228E. Another Filling the Grid(容斥原理+排列组合)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






