本文主要是介绍最前沿・量子退火建模方法(1) : subQUBO讲解和python实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言
量子退火机在小规模问题上的效果得到了有效验证,但是由于物理量子比特的大规模制备以及噪声的影响,还没有办法再大规模的场景下应用。
这时候就需要我们思考,如何通过软件的方法怎么样把大的问题分解成小的问题,以便通过现在小规模的量子退火机解决。主要思路就是,同样的QUBO建模,怎么使用更少的量子比特。
下面的文章中,量子退火机和伊辛机会混用。
一、subQUBO的创新点
先行的研究中,使用启发式方法将大型问题划分为较小的问题,并使用伊辛机进行求解,但划分后的问题的答案与原始大型问题的答案并不相同。达成协议的理论条件仍不清楚。早稻田大学的研究者开发出了subQUBO算法在保证分解后的小问题也能保证在原始大问题上的理论上做出了突破。
Atobe, Yuta, Masashi Tawada, and Nozomu Togawa. "Hybrid annealing method based on subQUBO model extraction with multiple solution instances." IEEE Transactions on Computers 71.10 (2021): 2606-2619.
subQUBO的创新点:
- 首先研究将大规模组合优化问题划分为较小问题而不失去最优性的条件。该条件成立的话就证明,如果用伊辛机来解决一个满足条件的小问题,它就会和原来的大规模问题的答案相匹配。
- 还提出了一种新算法,成功地从大规模问题中提取出此类条件,将原始大规模问题缩小到伊辛机可以解决的问题规模,并迭代求解。所提出的算法通过基于理论支持将大规模问题分解为更小的问题来解决它,使得以比传统技术更高的精度解决原始大规模问题成为可能。
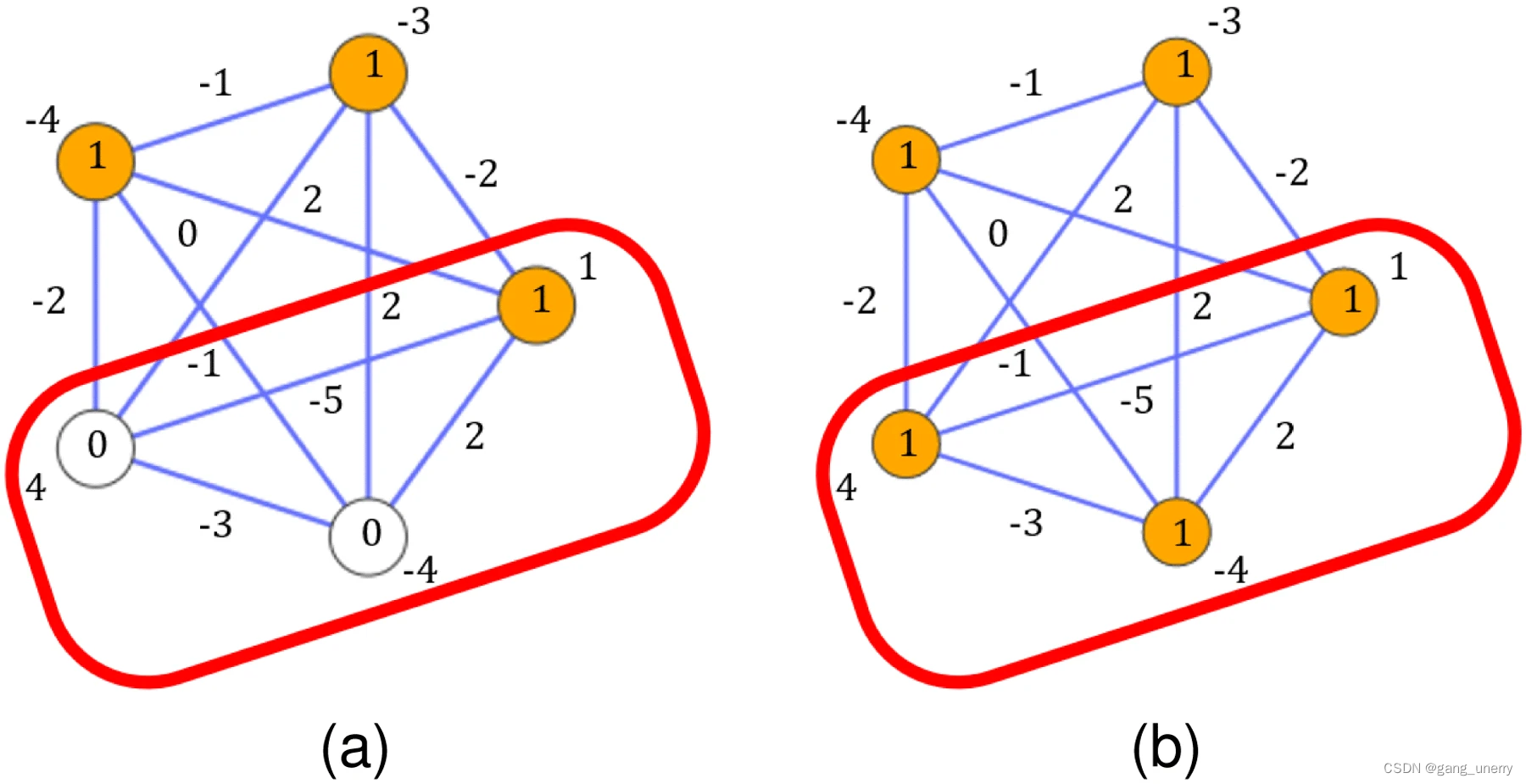
二、subQUBO的详细思路
1. 怎么把大规模问题分解成小问题
1.1 逻辑前提:挑出错误后,回炉重造
- 大规模组合优化问题的QUBO建模中,最终的答案由多个量子比特集合组成。
- 如果你创建一个小规模问题,其中包括最终解的量子比特集合中的,所有不正确的量子比特集合,
- 并使用伊辛机解决该问题,则所有最终解的不正确的量子比特集合都将被纠正为正确的量子比特集合作为解。
1.2 具体实现:
实现方法: 可以创建一个大致包含所有不正确的量子比特集合的小问题,并使用伊辛机重复解决它。
-
不正确的量子比特集合创建:
– 我们使用传统的经典计算器来准备问题的多个候选答案。这些候选答案不一定是正确的,但在比较经典计算器求解得到的多个答案的量子比特集合的最终值。
– 多个候选中匹配一致的就是正确的量子比特集合;
– 答案不匹配且不同的就是不正确的量子比特集合。 -
通过仅提取不正确的量子比特集合,并使用真实的伊辛机进行求解,最终可以获得整体的正确答案。
1.3 业界影响:
传统上,伊辛机很难解决大规模问题,因为可用位数受到硬件限制,但通过使用这种方法,可以使用伊辛机进行计算。因此,人们认为可以使用伊辛机(包括量子退火机)扩展现实世界组合优化问题的用例。此外,本研究尝试将经典计算机与伊辛机相结合来解决问题,这将大大扩展伊辛机的使用范围。
最新成果,参考以下新闻:
Quanmatic Co., Ltd.利用量子计算技术解决方案规模突破1亿比特
https://prtimes.jp/main/html/rd/p/000000015.000117406.html
三、subQUBO的python实现
- 导入库
import random
import itertools
import numpy as np
from dataclasses import dataclass
- 设置subQUBO所需参数
N_I = 20 # instance池
N_E = 10 # subQUBO的抽取次数
N_S = 10 # N_I个instance池中抽取的解的个数
sub_qubo_size = 5 # subQUBO的量子比特数
- QUBO建模
# 为了简单,使用TSP作为例子
NUM_CITY = 4
ALPHA = 1
np.random.seed(0)
num_spin = NUM_CITY ** 2distance_mtx = np.random.randint(1, 100, (NUM_CITY, NUM_CITY))
distance_mtx = np.tril(distance_mtx) + np.tril(distance_mtx).T - 2 * np.diag(distance_mtx.diagonal())# <<< Objective term >>>
qubo_obj = np.zeros((NUM_CITY**2, NUM_CITY**2), dtype=np.int32)
for t_u_v in itertools.product(range(NUM_CITY), repeat=3):t, u, v = t_u_v[0], t_u_v[1], t_u_v[2]idx_i = NUM_CITY * t + uif t < NUM_CITY - 1:idx_j = NUM_CITY * (t + 1) + velif t == NUM_CITY - 1:idx_j = vqubo_obj[idx_i, idx_j] += distance_mtx[u, v]
qubo_obj = np.triu(qubo_obj) + np.tril(qubo_obj).T - np.diag(np.diag(qubo_obj))# <<< Constraint term >>>
qubo_constraint = np.zeros((NUM_CITY**2, NUM_CITY**2), dtype=np.int32)
# Calculate constraint term1 : 1-hot of horizontal line
for t in range(NUM_CITY):for u in range(NUM_CITY - 1):for v in range(u + 1, NUM_CITY):qubo_constraint[NUM_CITY*t+u, NUM_CITY*t+v] += ALPHA * 2
# Linear term
for t_u in itertools.product(range(NUM_CITY), repeat=2):qubo_constraint[NUM_CITY*t_u[0]+t_u[1], NUM_CITY*t_u[0]+t_u[1]] += ALPHA * (-1)
const_constraint = ALPHA * NUM_CITY# Calculate constraint term2 : 1-hot of vertical line
# Quadratic term
for u in range(NUM_CITY):for t1 in range(NUM_CITY - 1):for t2 in range(t1+1, NUM_CITY):qubo_constraint[NUM_CITY*t1+u, NUM_CITY*t2+u] += ALPHA * 2
# Linear term
for u_t in itertools.product(range(NUM_CITY), repeat=2):qubo_constraint[NUM_CITY*u_t[1]+u_t[0], NUM_CITY*u_t[1]+u_t[0]] += ALPHA * (-1)
const_constraint += ALPHA * NUM_CITY
- 创建instance池
@dataclass
class Solution():"""Solution information.Attributes:x (np.ndarray): n-sized solution composed of binary variablesenergy_all (float): energy value obtained from QUBO-matrix of all termenergy_obj (float): energy value obtained from QUBO-matrix of objective termenergy_constraint (float): energy value obtained from QUBO-matrix of constraint termconstraint (bool): flag whether the solution satisfies the given constraint"""x: np.ndarrayenergy_all: float = 0energy_obj: float = 0energy_constraint: float = 0constraint: bool = True@classmethoddef energy(cls, qubo:np.ndarray, x: np.ndarray, const=0) -> float:"""Calculate the enrgy from the QUBO-matrix & solution xArgs:qubo (np.ndarray): n-by-n QUBO-matrixx (np.ndarray): n-sized solution composed of binary variablesconst (int, optional): _description_. Defaults to 0.Returns:float: Energy value."""return float(np.dot(np.dot(x, qubo), x) + const)@classmethoddef check_constraint(cls, qubo: np.ndarray, x: np.ndarray, const=0) -> bool:"""Check whether the solution satisfies the constraints.Args:qubo (np.ndarray): QUBO-model of the constraint term.x (np.ndarray): solution that you want to check.const (int, optional): constant of the constraint term. Defaults to 0.Returns:bool: Return True if the solution satisfy.Return False otherwise."""return True if cls.energy(qubo, x, const) == 0 else False
- subQUBO Hybrid Annealing Algorithm
# https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9664360# <<< Line 2-4 >>>
# Initialize the Instance Pool
pool = []
for i in range(N_I):# ====================# 实验时改动此参数x = np.random.randint(0, 2, num_spin) # 生成随机解# ====================energy_obj = Solution.energy(qubo_obj, x)energy_constraint = Solution.energy(qubo=qubo_constraint, x=x, const=const_constraint)pool.append(Solution(x = x,energy_all = energy_obj + energy_constraint,energy_obj = energy_obj,energy_constraint = energy_constraint,constraint = Solution.check_constraint(qubo=qubo_constraint, x=x, const=const_constraint)))
ascending_order_idx = np.argsort(np.array(list(map(lambda sol: sol.energy_all, pool))))
pool = [pool[i] for i in ascending_order_idx]# <<< Line 5 >>>
# Find the best solution
ascending_order_idx = np.argsort(np.array(list(map(lambda sol: sol.energy_all, pool))))
x_best = pool[ascending_order_idx[0]]for _ in range(1): # <<< Line 6 >>># <<< Line 7-8 >>># Obtain a quasi-ground-state solution for every N_I solution instance by a classical QUBO solverfor solution_i in pool:# ====================# 实验时改动此参数x = np.random.randint(0, 2, num_spin) # 生成随机解# ====================# Update the solution infosolution_i.x = xenergy_obj = solution_i.energy(qubo_obj, x)energy_constraint = solution_i.energy(qubo_constraint, x, const_constraint)solution_i.energy_all = energy_obj + energy_constraintsolution_i.energy_obj = energy_objsolution_i.energy_constraint = energy_constraintsolution_i.constraint = solution_i.check_constraint(qubo=qubo_constraint, x=x, const=const_constraint)for i in range(N_E): # <<< Line 9 >>># <<< Line 10 >>># Select N_S solution instance randomly from the pooln_s_pool = random.sample(pool, N_S)# <<< Line 11-14 >>># Calculate variance of each spin x_i in N_S instance poolSolution.check_constraint(qubo_constraint, x, const_constraint)vars_of_x = np.array([sum(n_s_pool[k].x[j] for k in range(N_S)) - N_S/2 for j in range(num_spin)])# <<< Line 15 >>># Select a solution randomly from N_S solution instance pool as a tentative solutionsolution_tmp = random.choice(n_s_pool)# Extract a subQUBOextracted_spin_idx = np.argsort(vars_of_x)[:sub_qubo_size]non_extracted_spin_idx = np.argsort(vars_of_x)[sub_qubo_size:]subqubo_obj = np.array([[qubo_obj[j, k] for k in extracted_spin_idx] for j in extracted_spin_idx])subqubo_constraint = np.array([[qubo_constraint[j, k] for k in extracted_spin_idx] for j in extracted_spin_idx])for idx_i in range(sub_qubo_size):subqubo_obj[idx_i, idx_i] += sum(qubo_obj[idx_i, idx_j] * solution_tmp.x[idx_j] for idx_j in non_extracted_spin_idx)subqubo_constraint[idx_i, idx_i] += sum(qubo_constraint[idx_i, idx_j] * solution_tmp.x[idx_j] for idx_j in non_extracted_spin_idx)# <<< Line 16 >>># Optimize the subQUBO using an Ising machine# ====================# 实验时改动此参数x_sub = np.random.randint(0, 2, sub_qubo_size) # 生成随机解# ====================# Combine the quasi-ground-state solution from the subQUBO with the tentative solution X_t(solution_tmp)for idx, val in enumerate(extracted_spin_idx):solution_tmp.x[idx] = x_sub[idx]# <<< Line 17 >>># Add the solution into the poolpool.append(solution_tmp)# <<< Line 18 >>># Find the best soliutionascending_order_idx = np.argsort(np.array(list(map(lambda sol: sol.energy_all, pool))))x_best = pool[ascending_order_idx[0]]# <<< Line 19 >>># Arrange the N_I instance poolsorted_pool = [pool[i] for i in ascending_order_idx]pool = sorted_pool[:N_I]pool, x_best
总结
subQUBO思路很简单,希望大家可以看着代码,理解如果实现。这个算法已经被早稻田大学申请专利了。
这篇关于最前沿・量子退火建模方法(1) : subQUBO讲解和python实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



