本文主要是介绍G2D图像处理硬件调用和测试-基于米尔-全志T113-i开发板,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本篇测评由电子工程世界的优秀测评者“jf_99374259”提供。
本文将介绍基于米尔电子MYD-YT113i开发板的G2D图像处理硬件调用和测试。
MYC-YT113i核心板及开发板
真正的国产核心板,100%国产物料认证
-
国产T113-i处理器配备2*Cortex-A7@1.2GHz ,RISC-V
-
外置DDR3接口、支持视频编解码器、HiFi4 DSP
-
接口丰富:视频采集接口、显示器接口、USB2.0 接口、CAN 接口、千兆以太网接口
-
工业级:-40℃~+85℃、尺寸37mm*39mm
-
邮票孔+LGA,140+50PIN


全志 T113-i 2D图形加速硬件支持情况
-
Supports layer size up to 2048 x 2048 pixels
-
Supports pre-multiply alpha image data
-
Supports color key
-
Supports two pipes Porter-Duff alpha blending
-
Supports multiple video formats 4:2:0, 4:2:2, 4:1:1 and multiple pixel formats (8/16/24/32 bits graphics layer)
-
Supports memory scan order option
-
Supports any format convert function
-
Supports 1/16× to 32× resize ratio
-
Supports 32-phase 8-tap horizontal anti-alias filter and 32-phase 4-tap vertical anti-alias filter
-
Supports window clip
-
Supports FillRectangle, BitBlit, StretchBlit and MaskBlit
-
Supports horizontal and vertical flip, clockwise 0/90/180/270 degree rotate for normal buffer
-
Supports horizontal flip, clockwise 0/90/270 degree rotate for LBC buffer
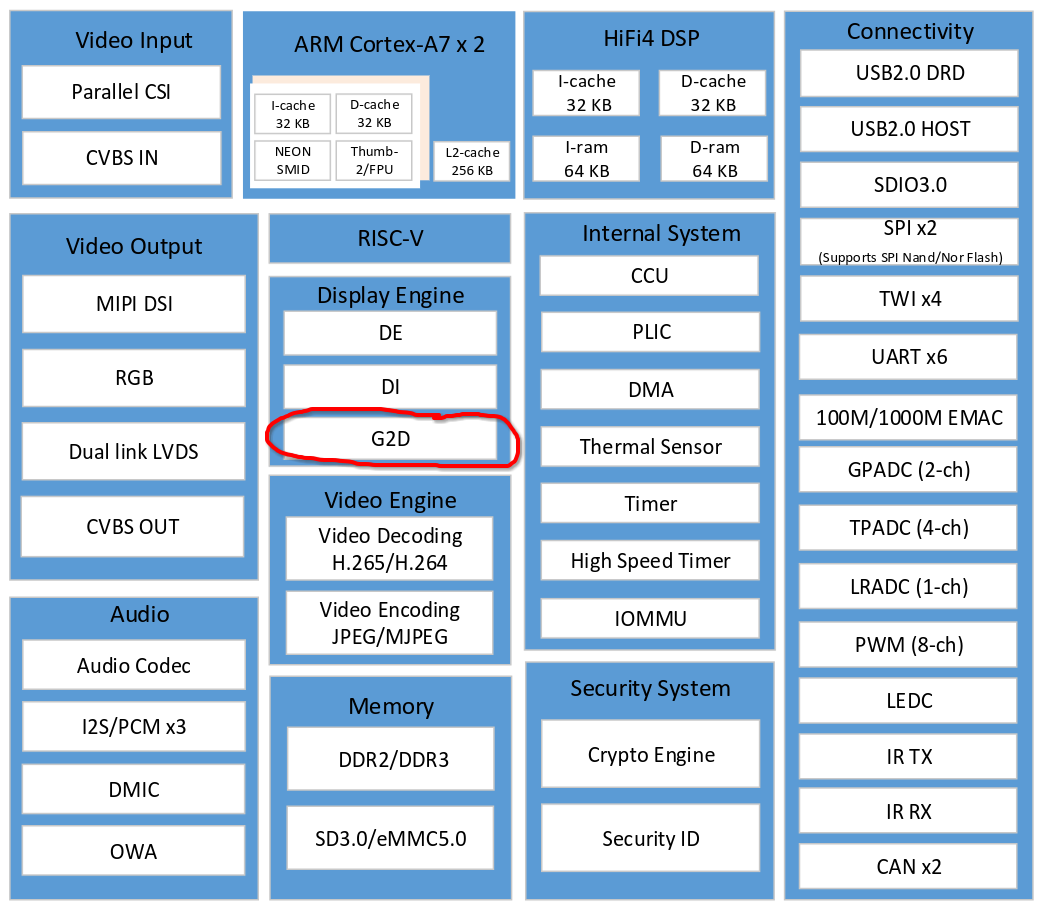
可以看到 g2d 硬件支持相当多的2D图像处理,包括颜色空间转换,分辨率缩放,图层叠加,旋转等
开发环境配置
基础开发环境搭建参考上上上一篇
【米尔-全志T113-i开发板试用】基础开发环境配置和opencv-mobile移植测试 - 米尔电子 - 电子技术论坛 - 广受欢迎的专业电子论坛!
除了工具链外,我们使用 opencv-mobile 加载输入图片和保存结果,用来查看颜色转换是否正常
g2d硬件直接采用标准的 Linux ioctl 操纵,只需要引入相关结构体定义即可,无需链接so
framework/auto/sdk_lib/include/g2d_driver.h at develop-yt113-framework · MYIR-ALLWINNER/framework · GitHub
此外,g2d的输入和输出数据必须在dmaion buffer上,因此还需要dmaion.h头文件,用来分配和释放dmaion buffer
framework/auto/sdk_lib/include/DmaIon.h at develop-yt113-framework · MYIR-ALLWINNER/framework · GitHub
基于C语言实现的YUV转RGB
这里复用之前T113-i JPG解码的函数
void yuv420sp2rgb(const unsigned char* yuv420sp, int w, int h, unsigned char* rgb)
{const unsigned char* yptr = yuv420sp;const unsigned char* vuptr = yuv420sp + w * h;for (int y = 0; y < h; y += 2){const unsigned char* yptr0 = yptr;const unsigned char* yptr1 = yptr + w;unsigned char* rgb0 = rgb;unsigned char* rgb1 = rgb + w * 3;int remain = w;#define SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR(X) (unsigned char)::std::min(::std::max((int)(X), 0), 255);for (; remain > 0; remain -= 2){// R = 1.164 * yy + 1.596 * vv// G = 1.164 * yy - 0.813 * vv - 0.391 * uu// B = 1.164 * yy + 2.018 * uu// R = Y + (1.370705 * (V-128))// G = Y - (0.698001 * (V-128)) - (0.337633 * (U-128))// B = Y + (1.732446 * (U-128))// R = ((Y << 6) + 87.72512 * (V-128)) >> 6// G = ((Y << 6) - 44.672064 * (V-128) - 21.608512 * (U-128)) >> 6// B = ((Y << 6) + 110.876544 * (U-128)) >> 6// R = ((Y << 6) + 90 * (V-128)) >> 6// G = ((Y << 6) - 46 * (V-128) - 22 * (U-128)) >> 6// B = ((Y << 6) + 113 * (U-128)) >> 6// R = (yy + 90 * vv) >> 6// G = (yy - 46 * vv - 22 * uu) >> 6// B = (yy + 113 * uu) >> 6int v = vuptr[0] - 128;int u = vuptr[1] - 128;int ruv = 90 * v;int guv = -46 * v + -22 * u;int buv = 113 * u;int y00 = yptr0[0] << 6;rgb0[0] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y00 + ruv) >> 6);rgb0[1] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y00 + guv) >> 6);rgb0[2] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y00 + buv) >> 6);int y01 = yptr0[1] << 6;rgb0[3] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y01 + ruv) >> 6);rgb0[4] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y01 + guv) >> 6);rgb0[5] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y01 + buv) >> 6);int y10 = yptr1[0] << 6;rgb1[0] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y10 + ruv) >> 6);rgb1[1] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y10 + guv) >> 6);rgb1[2] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y10 + buv) >> 6);int y11 = yptr1[1] << 6;rgb1[3] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y11 + ruv) >> 6);rgb1[4] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y11 + guv) >> 6);rgb1[5] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y11 + buv) >> 6);yptr0 += 2;yptr1 += 2;vuptr += 2;rgb0 += 6;rgb1 += 6;}
#undef SATURATE_CAST_UCHARyptr += 2 * w;rgb += 2 * 3 * w;}
}基于ARM neon指令集优化的YUV转RGB
考虑到armv7编译器的自动neon优化能力较差,这里针对性的编写 arm neon inline assembly 实现YUV2RGB内核部分,达到最优化的性能,榨干cpu性能
void yuv420sp2rgb_neon(const unsigned char* yuv420sp, int w, int h, unsigned char* rgb)
{const unsigned char* yptr = yuv420sp;const unsigned char* vuptr = yuv420sp + w * h;#if __ARM_NEONuint8x8_t _v128 = vdup_n_u8(128);int8x8_t _v90 = vdup_n_s8(90);int8x8_t _v46 = vdup_n_s8(46);int8x8_t _v22 = vdup_n_s8(22);int8x8_t _v113 = vdup_n_s8(113);
#endif // __ARM_NEONfor (int y = 0; y < h; y += 2){const unsigned char* yptr0 = yptr;const unsigned char* yptr1 = yptr + w;unsigned char* rgb0 = rgb;unsigned char* rgb1 = rgb + w * 3;#if __ARM_NEONint nn = w >> 3;int remain = w - (nn << 3);#elseint remain = w;
#endif // __ARM_NEON#if __ARM_NEON
#if __aarch64__for (; nn > 0; nn--){int16x8_t _yy0 = vreinterpretq_s16_u16(vshll_n_u8(vld1_u8(yptr0), 6));int16x8_t _yy1 = vreinterpretq_s16_u16(vshll_n_u8(vld1_u8(yptr1), 6));int8x8_t _vvuu = vreinterpret_s8_u8(vsub_u8(vld1_u8(vuptr), _v128));int8x8x2_t _vvvvuuuu = vtrn_s8(_vvuu, _vvuu);int8x8_t _vv = _vvvvuuuu.val[0];int8x8_t _uu = _vvvvuuuu.val[1];int16x8_t _r0 = vmlal_s8(_yy0, _vv, _v90);int16x8_t _g0 = vmlsl_s8(_yy0, _vv, _v46);_g0 = vmlsl_s8(_g0, _uu, _v22);int16x8_t _b0 = vmlal_s8(_yy0, _uu, _v113);int16x8_t _r1 = vmlal_s8(_yy1, _vv, _v90);int16x8_t _g1 = vmlsl_s8(_yy1, _vv, _v46);_g1 = vmlsl_s8(_g1, _uu, _v22);int16x8_t _b1 = vmlal_s8(_yy1, _uu, _v113);uint8x8x3_t _rgb0;_rgb0.val[0] = vqshrun_n_s16(_r0, 6);_rgb0.val[1] = vqshrun_n_s16(_g0, 6);_rgb0.val[2] = vqshrun_n_s16(_b0, 6);uint8x8x3_t _rgb1;_rgb1.val[0] = vqshrun_n_s16(_r1, 6);_rgb1.val[1] = vqshrun_n_s16(_g1, 6);_rgb1.val[2] = vqshrun_n_s16(_b1, 6);vst3_u8(rgb0, _rgb0);vst3_u8(rgb1, _rgb1);yptr0 += 8;yptr1 += 8;vuptr += 8;rgb0 += 24;rgb1 += 24;}
#elseif (nn > 0){asm volatile("0: n""pld [%3, #128] n""vld1.u8 {d2}, [%3]! n""vsub.s8 d2, d2, %12 n""pld [%1, #128] n""vld1.u8 {d0}, [%1]! n""pld [%2, #128] n""vld1.u8 {d1}, [%2]! n""vshll.u8 q2, d0, #6 n""vorr d3, d2, d2 n""vshll.u8 q3, d1, #6 n""vorr q9, q2, q2 n""vtrn.s8 d2, d3 n""vorr q11, q3, q3 n""vmlsl.s8 q9, d2, %14 n""vorr q8, q2, q2 n""vmlsl.s8 q11, d2, %14 n""vorr q10, q3, q3 n""vmlal.s8 q8, d2, %13 n""vmlal.s8 q2, d3, %16 n""vmlal.s8 q10, d2, %13 n""vmlsl.s8 q9, d3, %15 n""vmlal.s8 q3, d3, %16 n""vmlsl.s8 q11, d3, %15 n""vqshrun.s16 d24, q8, #6 n""vqshrun.s16 d26, q2, #6 n""vqshrun.s16 d4, q10, #6 n""vqshrun.s16 d25, q9, #6 n""vqshrun.s16 d6, q3, #6 n""vqshrun.s16 d5, q11, #6 n""subs %0, #1 n""vst3.u8 {d24-d26}, [%4]! n""vst3.u8 {d4-d6}, [%5]! n""bne 0b n": "=r"(nn), // %0"=r"(yptr0), // %1"=r"(yptr1), // %2"=r"(vuptr), // %3"=r"(rgb0), // %4"=r"(rgb1) // %5: "0"(nn),"1"(yptr0),"2"(yptr1),"3"(vuptr),"4"(rgb0),"5"(rgb1),"w"(_v128), // %12"w"(_v90), // %13"w"(_v46), // %14"w"(_v22), // %15"w"(_v113) // %16: "cc", "memory", "q0", "q1", "q2", "q3", "q8", "q9", "q10", "q11", "q12", "d26");}#endif // __aarch64__
#endif // __ARM_NEON#define SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR(X) (unsigned char)::std::min(::std::max((int)(X), 0), 255);for (; remain > 0; remain -= 2){// R = 1.164 * yy + 1.596 * vv// G = 1.164 * yy - 0.813 * vv - 0.391 * uu// B = 1.164 * yy + 2.018 * uu// R = Y + (1.370705 * (V-128))// G = Y - (0.698001 * (V-128)) - (0.337633 * (U-128))// B = Y + (1.732446 * (U-128))// R = ((Y << 6) + 87.72512 * (V-128)) >> 6// G = ((Y << 6) - 44.672064 * (V-128) - 21.608512 * (U-128)) >> 6// B = ((Y << 6) + 110.876544 * (U-128)) >> 6// R = ((Y << 6) + 90 * (V-128)) >> 6// G = ((Y << 6) - 46 * (V-128) - 22 * (U-128)) >> 6// B = ((Y << 6) + 113 * (U-128)) >> 6// R = (yy + 90 * vv) >> 6// G = (yy - 46 * vv - 22 * uu) >> 6// B = (yy + 113 * uu) >> 6int v = vuptr[0] - 128;int u = vuptr[1] - 128;int ruv = 90 * v;int guv = -46 * v + -22 * u;int buv = 113 * u;int y00 = yptr0[0] << 6;rgb0[0] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y00 + ruv) >> 6);rgb0[1] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y00 + guv) >> 6);rgb0[2] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y00 + buv) >> 6);int y01 = yptr0[1] << 6;rgb0[3] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y01 + ruv) >> 6);rgb0[4] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y01 + guv) >> 6);rgb0[5] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y01 + buv) >> 6);int y10 = yptr1[0] << 6;rgb1[0] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y10 + ruv) >> 6);rgb1[1] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y10 + guv) >> 6);rgb1[2] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y10 + buv) >> 6);int y11 = yptr1[1] << 6;rgb1[3] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y11 + ruv) >> 6);rgb1[4] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y11 + guv) >> 6);rgb1[5] = SATURATE_CAST_UCHAR((y11 + buv) >> 6);yptr0 += 2;yptr1 += 2;vuptr += 2;rgb0 += 6;rgb1 += 6;}
#undef SATURATE_CAST_UCHARyptr += 2 * w;rgb += 2 * 3 * w;}
}基于G2D图形硬件的YUV转RGB
我们先实现 dmaion buffer 管理器,参考
framework/auto/sdk_lib/sdk_memory/DmaIon.cpp at develop-yt113-framework · MYIR-ALLWINNER/framework · GitHub
这里贴的代码省略了异常错误处理的逻辑,有个坑是 linux-4.9 和 linux-5.4 用法不一样,米尔电子的这个T113-i系统是linux-5.4,所以不兼容4.9内核的ioctl用法习惯
struct ion_memory
{size_t size;int fd;void* virt_addr;unsigned int phy_addr;
};class ion_allocator
{
public:ion_allocator();~ion_allocator();int open();void close();int alloc(size_t size, struct ion_memory* mem);int free(struct ion_memory* mem);int flush(struct ion_memory* mem);public:int ion_fd;int cedar_fd;
};ion_allocator::ion_allocator()
{ion_fd = -1;cedar_fd = -1;
}ion_allocator::~ion_allocator()
{close();
}int ion_allocator::open()
{close();ion_fd = ::open("/dev/ion", O_RDWR);cedar_fd = ::open("/dev/cedar_dev", O_RDONLY);ioctl(cedar_fd, IOCTL_ENGINE_REQ, 0);return 0;
}void ion_allocator::close()
{if (cedar_fd != -1){ioctl(cedar_fd, IOCTL_ENGINE_REL, 0);::close(cedar_fd);cedar_fd = -1;}if (ion_fd != -1){::close(ion_fd);ion_fd = -1;}
}int ion_allocator::alloc(size_t size, struct ion_memory* mem)
{struct aw_ion_new_alloc_data alloc_data;alloc_data.len = size;alloc_data.heap_id_mask = AW_ION_SYSTEM_HEAP_MASK;alloc_data.flags = AW_ION_CACHED_FLAG | AW_ION_CACHED_NEEDS_SYNC_FLAG;alloc_data.fd = 0;alloc_data.unused = 0;ioctl(ion_fd, AW_ION_IOC_NEW_ALLOC, &alloc_data);void* virt_addr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, alloc_data.fd, 0);struct aw_user_iommu_param iommu_param;iommu_param.fd = alloc_data.fd;iommu_param.iommu_addr = 0;ioctl(cedar_fd, IOCTL_GET_IOMMU_ADDR, &iommu_param);mem->size = size;mem->fd = alloc_data.fd;mem->virt_addr = virt_addr;mem->phy_addr = iommu_param.iommu_addr;return 0;
}int ion_allocator::free(struct ion_memory* mem)
{if (mem->fd == -1)return 0;struct aw_user_iommu_param iommu_param;iommu_param.fd = mem->fd;ioctl(cedar_fd, IOCTL_FREE_IOMMU_ADDR, &iommu_param);munmap(mem->virt_addr, mem->size);::close(mem->fd);mem->size = 0;mem->fd = -1;mem->virt_addr = 0;mem->phy_addr = 0;return 0;
}int ion_allocator::flush(struct ion_memory* mem)
{struct dma_buf_sync sync;sync.flags = DMA_BUF_SYNC_END | DMA_BUF_SYNC_RW;ioctl(mem->fd, DMA_BUF_IOCTL_SYNC, &sync);return 0;
}然后再实现 G2D图形硬件 YUV转RGB 的转换器
-
提前分配好YUV和RGB的dmaion buffer
-
将YUV数据拷贝到dmaion buffer,flush cache完成同步
-
配置转换参数,ioctl调用G2D_CMD_BITBLT_H完成转换
-
flush cache完成同步,从dmaion buffer拷贝出RGB数据
-
释放dmaion buffer
// 步骤1
ion_allocator ion;
ion.open();struct ion_memory yuv_ion;
ion.alloc(rgb_size, &rgb_ion);struct ion_memory rgb_ion;
ion.alloc(yuv_size, &yuv_ion);int g2d_fd = ::open("/dev/g2d", O_RDWR);// 步骤2
memcpy((unsigned char*)yuv_ion.virt_addr, yuv420sp, yuv_size);
ion.flush(&yuv_ion);// 步骤3
g2d_blt_h blit;
memset(&blit, 0, sizeof(blit));blit.flag_h = G2D_BLT_NONE_H;blit.src_image_h.format = G2D_FORMAT_YUV420UVC_V1U1V0U0;
blit.src_image_h.width = width;
blit.src_image_h.height = height;
blit.src_image_h.align[0] = 0;
blit.src_image_h.align[1] = 0;
blit.src_image_h.clip_rect.x = 0;
blit.src_image_h.clip_rect.y = 0;
blit.src_image_h.clip_rect.w = width;
blit.src_image_h.clip_rect.h = height;
blit.src_image_h.gamut = G2D_BT601;
blit.src_image_h.bpremul = 0;
blit.src_image_h.mode = G2D_PIXEL_ALPHA;
blit.src_image_h.use_phy_addr = 0;
blit.src_image_h.fd = yuv_ion.fd;blit.dst_image_h.format = G2D_FORMAT_RGB888;
blit.dst_image_h.width = width;
blit.dst_image_h.height = height;
blit.dst_image_h.align[0] = 0;
blit.dst_image_h.clip_rect.x = 0;
blit.dst_image_h.clip_rect.y = 0;
blit.dst_image_h.clip_rect.w = width;
blit.dst_image_h.clip_rect.h = height;
blit.dst_image_h.gamut = G2D_BT601;
blit.dst_image_h.bpremul = 0;
blit.dst_image_h.mode = G2D_PIXEL_ALPHA;
blit.dst_image_h.use_phy_addr = 0;
blit.dst_image_h.fd = rgb_ion.fd;ioctl(g2d_fd, G2D_CMD_BITBLT_H, &blit);// 步骤4
ion.flush(&rgb_ion);
memcpy(rgb, (const unsigned char*)rgb_ion.virt_addr, rgb_size);// 步骤5
ion.free(&rgb_ion);
ion.free(&yuv_ion);
ion.close();
::close(g2d_fd);G2D图像硬件YUV转RGB测试
考虑到dmaion buffer分配和释放都比较耗时,我们提前做好,循环调用步骤3的G2D转换,统计耗时,并在top工具中查看CPU占用率
sh-4.4# LD_LIBRARY_PATH=. ./g2dtest
INFO : cedarc <CedarPluginVDInit:84>: register mjpeg decoder success!
this device is not whitelisted for jpeg decoder cvi
this device is not whitelisted for jpeg decoder cvi
this device is not whitelisted for jpeg decoder cvi
this device is not whitelisted for jpeg encoder rkmpp
INFO : cedarc <log_set_level:43>: Set log level to 5 from /vendor/etc/cedarc.conf
ERROR : cedarc <DebugCheckConfig:316>: now cedarc log level:5
ERROR : cedarc <VideoEncCreate:241>: now cedarc log level:5
yuv420sp2rgb 46.61
yuv420sp2rgb 42.04
yuv420sp2rgb 41.32
yuv420sp2rgb 42.06
yuv420sp2rgb 41.69
yuv420sp2rgb 42.05
yuv420sp2rgb 41.29
yuv420sp2rgb 41.30
yuv420sp2rgb 42.14
yuv420sp2rgb 41.33
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 10.57
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 7.21
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 6.77
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 8.31
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 7.60
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 6.80
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 6.77
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 7.01
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 7.11
yuv420sp2rgb_neon 7.06
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.32
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.69
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.56
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.57
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.52
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.54
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.52
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.58
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.60
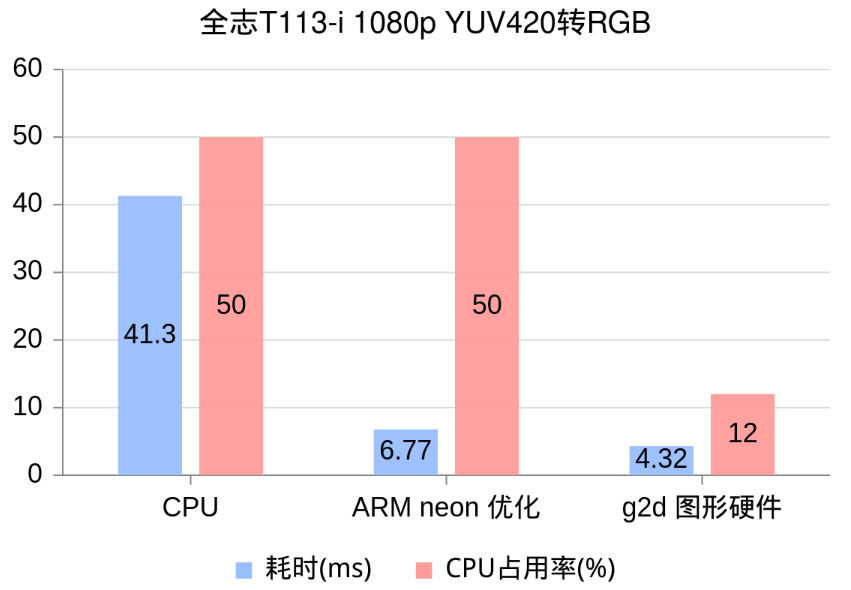
yuv420sp2rgb_g2d 4.67可以看到 ARM neon 的优化效果非常明显,而使用G2D图形硬件能获得进一步加速,并且能显著降低CPU占用率!
| 耗时(ms) | CPU占用率(%) | |
|---|---|---|
| C | 41.30 | 50 |
| neon | 6.77 | 50 |
| g2d | 4.32 | 12 |
转换结果对比和分析
C和neon的转换结果完全一致,但是g2d转换后的图片有明显的色差



G2D图形硬件只支持 G2D_BT601,G2D_BT709,G2D_BT2020 3种YUV系数,而JPG所使用的YUV系数是改版BT601,因此产生了色差
myir-t1-kernel/drivers/char/sunxi_g2d/g2d_bsp_v2.c at develop-yt113-L5.4.61 · MYIR-ALLWINNER/myir-t1-kernel · GitHub
从g2d内核驱动中也可以得知,暂时没有方法为g2d设置自定义的YUV系数,g2d不适合用于JPG的编解码,但依然适合摄像头和视频编解码的颜色空间转换
这篇关于G2D图像处理硬件调用和测试-基于米尔-全志T113-i开发板的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





