本文主要是介绍RabbitMQ消息模型之Fanout消息模型,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Fanout消息模型
* 广播模型:* 一个交换机绑定多个队列* 每个队列都有一个消费者* 每个消费者消费自己队列中的消息,每个队列的信息是一样的
生产者
package com.example.demo02.mq.fanout;import com.example.demo02.mq.util.ConnectionUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;import java.io.IOException;/*** @author Allen* 4/11/2024 8:24 AM* @version 1.0* @description: 广播模型发送者** 广播模型:* 一个交换机绑定多个队列* 每个队列都有一个消费者* 每个消费者消费自己队列中的消息,每个队列的信息是一样的*/
public class FanoutSender {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 1:获取连接Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();// 2:创建通道Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 3:声明交换机// 参数1:交换机名称 参数2:交换机类型 (fanout direct topic) 参数3:是否持久化/*fanout:广播模式绑定了这个交换机的队列都会收到消息direct:路由模式通过路由键完全匹配的队列会收到消息topic:通配符模式通过通配符匹配的队列会收到消息*/channel.exchangeDeclare("fanout.exchange", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,false);// 交换机不会存储消息,只是负责消息的转发,如果没有队列绑定到交换机上,消息会丢失// 4:发送消息到交换机:需要消费信息的消费者自己声明自己的队列绑定到当前交换机上String msg = "fanout message";channel.basicPublish("fanout.exchange", "", null, msg.getBytes());// 5:关闭通道channel.close();// 6:关闭连接connection.close();}
}
消费者1
package com.example.demo02.mq.fanout;import com.example.demo02.mq.util.ConnectionUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;import java.io.IOException;/*** @author Allen* 4/11/2024 8:55 AM* @version 1.0* @description: 广播模型接收者*/
public class FanoutReceiver1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 1:获取连接Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();// 2:创建通道Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 3:声明交换机//为什么消费者也得声明交换机?如果消费者先启动,那么交换机还没有声明,消费者就会报错,所以消费者也得声明交换机// 参数1:交换机名称 参数2:交换机类型 参数3:是否持久化channel.exchangeDeclare("fanout.exchange", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,false);// 4:声明队列// 参数1:队列名称 参数2:是否持久化 参数3:是否排他性 参数4:是否自动删除 参数5:其他参数channel.queueDeclare("fanout.queue1", false, false, false, null);// 5:绑定自己的队列到交换机channel.queueBind("fanout.queue1", "fanout.exchange", "");// 6:消费消息Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){@Override// 参数1:消费者标签 参数2:消息传递参数 参数3: 参数4:消息内容public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {// 消费消息System.out.println("Fanout1接收到的消息是:" + new String(body));// 手动确认消息channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);}};channel.basicConsume("fanout.queue1",false,consumer);}
}
消费者2
package com.example.demo02.mq.fanout;import com.example.demo02.mq.util.ConnectionUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;import java.io.IOException;/*** @author Allen* 4/11/2024 8:55 AM* @version 1.0* @description: 广播模型接收者*/
public class FanoutReceiver2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 1:获取连接Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();// 2:创建通道Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 3:声明交换机//为什么消费者也得声明交换机?如果消费者先启动,那么交换机还没有声明,消费者就会报错,所以消费者也得声明交换机channel.exchangeDeclare("fanout.exchange", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,false);// 4:声明队列// 参数1:队列名称 参数2:是否持久化 参数3:是否排他性 参数4:是否自动删除 参数5:其他参数channel.queueDeclare("fanout.queue2", false, false, false, null);// 5:绑定队列到交换机channel.queueBind("fanout.queue2", "fanout.exchange", "");// 6:消费消息Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){@Override// 参数1:消费者标签 参数2:消息传递参数 参数3: 参数4:消息内容public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {// 消费消息System.out.println("Fanout2接收到的消息是:" + new String(body));// 手动确认消息channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);}};channel.basicConsume("fanout.queue2",false,consumer);}
}
结果
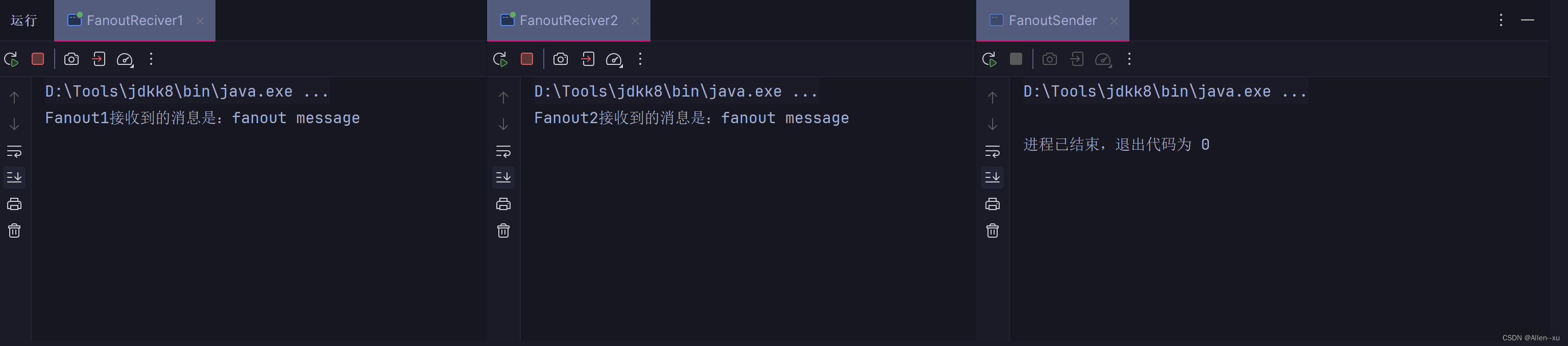
这篇关于RabbitMQ消息模型之Fanout消息模型的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








