本文主要是介绍Redis Pipelining 底层原理分析及实践,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
作者:vivo 互联网服务器团队-Wang Fei
Redis是一种基于客户端-服务端模型以及请求/响应的TCP服务。在遇到批处理命令执行时,Redis提供了Pipelining(管道)来提升批处理性能。本文结合实践分析了Spring Boot框架下Redis的Lettuce客户端和Redisson客户端对Pipeline特性的支持原理,并针对实践过程中遇到的问题进行了分析,可以帮助开发者了解不同客户端对Pipeline支持原理及避免实际使用中出现问题。
一、前言
Redis 已经提供了像 mget 、mset 这种批量的命令,但是某些操作根本就不支持或没有批量的操作,从而与 Redis 高性能背道而驰。为此, Redis基于管道机制,提供Redis Pipeline新特性。Redis Pipeline是一种通过一次性发送多条命令并在执行完后一次性将结果返回,从而减少客户端与redis的通信次数来实现降低往返延时时间提升操作性能的技术。目前,Redis Pipeline是被很多个版本的Redis 客户端所支持的。
二、Pipeline 底层原理分析
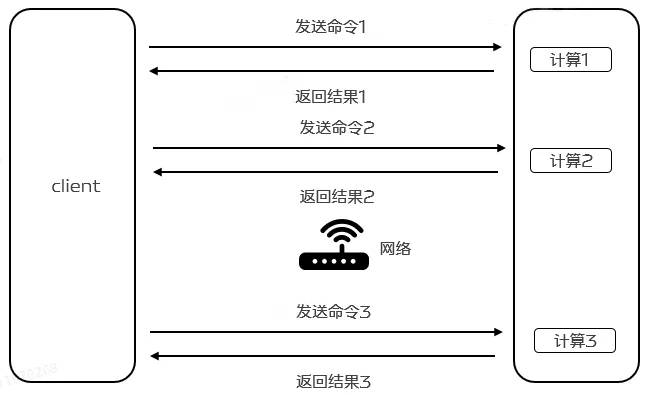
2.1 Redis单个命令执行基本步骤
Redis是一种基于客户端-服务端模型以及请求/响应的TCP服务。一次Redis客户端发起的请求,经过服务端的响应后,大致会经历如下的步骤:
-
客户端发起一个(查询/插入)请求,并监听socket返回,通常情况都是阻塞模式等待Redis服务器的响应。
-
服务端处理命令,并且返回处理结果给客户端。
-
客户端接收到服务的返回结果,程序从阻塞代码处返回。
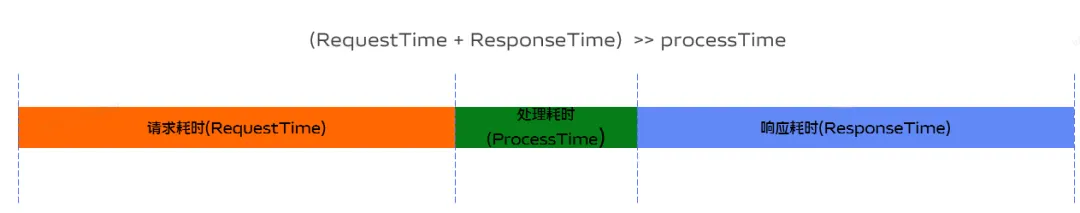
2.2 RTT 时间
Redis客户端和服务端之间通过网络连接进行数据传输,数据包从客户端到达服务器,并从服务器返回数据回复客户端的时间被称之为RTT(Round Trip Time - 往返时间)。我们可以很容易就意识到,Redis在连续请求服务端时,如果RTT时间为250ms, 即使Redis每秒能处理100k请求,但也会因为网络传输花费大量时间,导致每秒最多也只能处理4个请求,导致整体性能的下降。
2.3 Redis Pipeline
为了提升效率,这时候Pipeline出现了。Pipelining不仅仅能够降低RRT,实际上它极大的提升了单次执行的操作数。这是因为如果不使用Pipelining,那么每次执行单个命令,从访问数据的结构和服务端产生应答的角度,它的成本是很低的。但是从执行网络IO的角度,它的成本其实是很高的。其中涉及到read()和write()的系统调用,这意味着需要从用户态切换到内核态,而这个上下文的切换成本是巨大的。
当使用Pipeline时,它允许多个命令的读通过一次read()操作,多个命令的应答使用一次write()操作,它允许客户端可以一次发送多条命令,而不等待上一条命令执行的结果。不仅减少了RTT,同时也减少了IO调用次数(IO调用涉及到用户态到内核态之间的切换),最终提升程序的执行效率与性能。如下图:
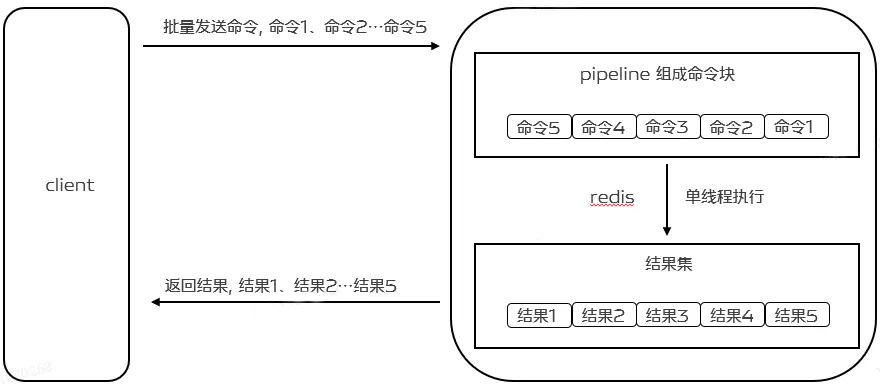
要支持Pipeline,其实既要服务端的支持,也要客户端支持。对于服务端来说,所需要的是能够处理一个客户端通过同一个TCP连接发来的多个命令,可以理解为,这里将多个命令切分,和处理单个命令一样,Redis就是这样处理的。而客户端,则是要将多个命令缓存起来,缓冲区满了就发送,然后再写缓冲,最后才处理Redis的应答。
三、Pipeline 基本使用及性能比较
下面我们以给10w个set结构分别插入一个整数值为例,分别使用jedis单个命令插入、jedis使用Pipeline模式进行插入和redisson使用Pipeline模式进行插入以及测试其耗时。
@Slf4j
public class RedisPipelineTestDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//连接redisJedis jedis = new Jedis("10.101.17.180", 6379);//jedis逐一给每个set新增一个valueString zSetKey = "Pipeline-test-set";int size = 100000;long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {jedis.sadd(zSetKey + i, "aaa");}log.info("Jedis逐一给每个set新增一个value耗时:{}ms", (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));//Jedis使用Pipeline模式 Pipeline Pipeline = jedis.Pipelined();begin = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { Pipeline.sadd(zSetKey + i, "bbb");} Pipeline.sync();log.info("Jedis Pipeline模式耗时:{}ms", (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));//Redisson使用Pipeline模式Config config = new Config();config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://10.101.17.180:6379");RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);RBatch redisBatch = redisson.createBatch();begin = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {redisBatch.getSet(zSetKey + i).addAsync("ccc");}redisBatch.execute();log.info("Redisson Pipeline模式耗时:{}ms", (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));//关闭 Pipeline.close();jedis.close();redisson.shutdown();}
}测试结果如下:
Jedis逐一给每个set新增一个value耗时:162655ms
Jedis Pipeline模式耗时:504ms
Redisson Pipeline模式耗时:1399ms
我们发现使用Pipeline模式对应的性能会明显好于单个命令执行的情况。
四、项目中实际应用
在实际使用过程中有这样一个场景,很多应用在节假日的时候需要更新应用图标样式,在运营进行后台配置的时候, 可以根据圈选的用户标签预先计算出单个用户需要下发的图标样式并存储在Redis里面,从而提升性能,这里就涉及Redis的批量操作问题,业务流程如下:
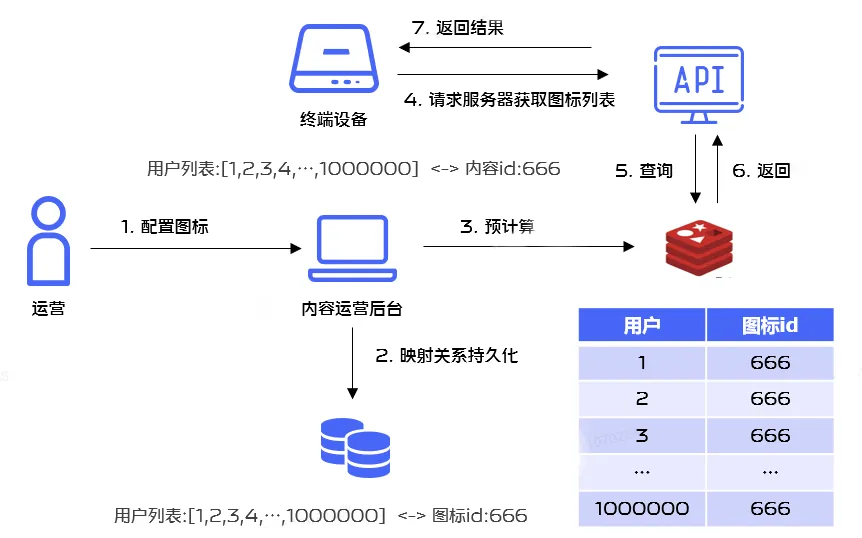
为了提升Redis操作性能,我们决定使用Redis Pipelining机制进行批量执行。
4.1 Redis 客户端对比
针对Java技术栈而言,目前Redis使用较多的客户端为Jedis、Lettuce和Redisson。
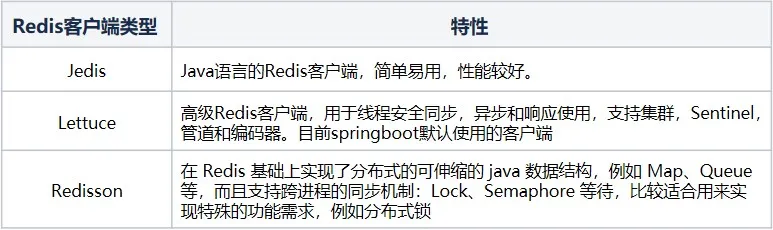
目前项目主要是基于SpringBoot开发,针对Redis,其默认的客户端为Lettuce,所以我们基于Lettuce客户端进行分析。
4.2 Spring环境下Lettuce客户端对Pipeline的实现
在Spring环境下,使用Redis的Pipeline也是很简单的。spring-data-redis提供了StringRedisTemplate简化了对Redis的操作, 只需要调用StringRedisTemplate的executePipelined方法就可以了,但是在参数中提供了两种回调方式:SessionCallback和RedisCallback。
两种使用方式如下(这里以操作set结构为例):
-
RedisCallback的使用方式:
public void testRedisCallback() {List<Integer> ids= Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);Integer contentId = 1;redisTemplate.executePipelined(new InsertPipelineExecutionA(ids, contentId));}@AllArgsConstructorprivate static class InsertPipelineExecutionA implements RedisCallback<Void> {private final List<Integer> ids;private final Integer contentId;@Overridepublic Void doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) DataAccessException {RedisSetCommands redisSetCommands = connection.setCommands();ids.forEach(id-> {String redisKey = "aaa:" + id;String value = String.valueOf(contentId);redisSetCommands.sAdd(redisKey.getBytes(), value.getBytes());});return null;}}- SessionCallback的使用方式:
public void testSessionCallback() {List<Integer> ids= Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);Integer contentId = 1;redisTemplate.executePipelined(new InsertPipelineExecutionB(ids, contentId));}@AllArgsConstructorprivate static class InsertPipelineExecutionB implements SessionCallback<Void> {private final List<Integer> ids;private final Integer contentId;@Overridepublic <K, V> Void execute(RedisOperations<K, V> operations) throws DataAccessException {SetOperations<String, String> setOperations = (SetOperations<String, String>) operations.opsForSet();ids.forEach(id-> {String redisKey = "aaa:" + id;String value = String.valueOf(contentId);setOperations.add(redisKey, value);});return null;}}4.3 RedisCallBack和SessionCallback之间的比较
1、RedisCallBack和SessionCallback都可以实现回调,通过它们可以在同一条连接中一次执行多个redis命令。
2、RedisCallback使用的是原生RedisConnection,用起来比较麻烦,比如上面执行set的add操作,key和value需要进行转换,可读性差,但原生api提供的功能比较齐全。
3、SessionCalback提供了良好的封装,可以优先选择使用这种回调方式。
最终的代码实现如下:
public void executeB(List<Integer> userIds, Integer iconId) {redisTemplate.executePipelined(new InsertPipelineExecution(userIds, iconId));
}@AllArgsConstructor
private static class InsertPipelineExecution implements SessionCallback<Void> {private final List<Integer> userIds;private final Integer iconId;@Overridepublic <K, V> Void execute(RedisOperations<K, V> operations) throws DataAccessException {SetOperations<String, String> setOperations = (SetOperations<String, String>) operations.opsForSet();userIds.forEach(userId -> {String redisKey = "aaa:" + userId;String value = String.valueOf(iconId);setOperations.add(redisKey, value);});return null;}
}4.4 源码分析
那么为什么使用Pipeline方式会对性能有较大提升呢,我们现在从源码入手着重分析一下:
4.4.1 Pipeline方式下获取连接相关原理分析:
@Overridepublic List<Object> executePipelined(SessionCallback<?> session, @Nullable RedisSerializer<?> resultSerializer) {Assert.isTrue(initialized, "template not initialized; call afterPropertiesSet() before using it");Assert.notNull(session, "Callback object must not be null");//1. 获取对应的Redis连接工厂RedisConnectionFactory factory = getRequiredConnectionFactory();//2. 绑定连接过程RedisConnectionUtils.bindConnection(factory, enableTransactionSupport);try {//3. 执行命令流程, 这里请求参数为RedisCallback, 里面有对应的回调操作return execute((RedisCallback<List<Object>>) connection -> {//具体的回调逻辑connection.openPipeline();boolean PipelinedClosed = false;try {//执行命令Object result = executeSession(session);if (result != null) {throw new InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException("Callback cannot return a non-null value as it gets overwritten by the Pipeline");}List<Object> closePipeline = connection.closePipeline(); PipelinedClosed = true;return deserializeMixedResults(closePipeline, resultSerializer, hashKeySerializer, hashValueSerializer);} finally {if (!PipelinedClosed) {connection.closePipeline();}}});} finally {RedisConnectionUtils.unbindConnection(factory);}}① 获取对应的Redis连接工厂,这里要使用Pipeline特性需要使用LettuceConnectionFactory方式,这里获取的连接工厂就是LettuceConnectionFactory。
② 绑定连接过程,具体指的是将当前连接绑定到当前线程上面, 核心方法为:doGetConnection。
public static RedisConnection doGetConnection(RedisConnectionFactory factory, boolean allowCreate, boolean bind,boolean enableTransactionSupport) {Assert.notNull(factory, "No RedisConnectionFactory specified");//核心类,有缓存作用,下次可以从这里获取已经存在的连接RedisConnectionHolder connHolder = (RedisConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(factory);//如果connHolder不为null, 则获取已经存在的连接, 提升性能if (connHolder != null) {if (enableTransactionSupport) {potentiallyRegisterTransactionSynchronisation(connHolder, factory);}return connHolder.getConnection();}......//第一次获取连接,需要从Redis连接工厂获取连接RedisConnection conn = factory.getConnection();//bind = true 执行绑定if (bind) {RedisConnection connectionToBind = conn;......connHolder = new RedisConnectionHolder(connectionToBind);//绑定核心代码: 将获取的连接和当前线程绑定起来TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(factory, connHolder);......return connHolder.getConnection();}return conn;}里面有个核心类RedisConnectionHolder,我们看一下RedisConnectionHolder connHolder =
(RedisConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(factory);
@Nullablepublic static Object getResource(Object key) {Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);Object value = doGetResource(actualKey);if (value != null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Retrieved value [" + value + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread [" +Thread.currentThread().getName() + "]");}return value;}里面有一个核心方法doGetResource(actualKey),大家很容易猜测这里涉及到一个map结构,如果我们看源码,也确实是这样一个结构。
@Nullableprivate static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) {Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();if (map == null) {return null;}Object value = map.get(actualKey);// Transparently remove ResourceHolder that was marked as void...if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {map.remove(actualKey);// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...if (map.isEmpty()) {resources.remove();}value = null;}return value;}resources是一个ThreadLocal类型,这里会涉及到根据RedisConnectionFactory获取到连接connection的逻辑,如果下一次是同一个actualKey,那么就直接使用已经存在的连接,而不需要新建一个连接。第一次这里map为null,就直接返回了,然后回到doGetConnection方法,由于这里bind为true,我们会执行TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(factory, connHolder);,也就是将连接和当前线程绑定了起来。
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException {Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);Assert.notNull(value, "Value must not be null");Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();// set ThreadLocal Map if none foundif (map == null) {map = new HashMap<>();resources.set(map);}Object oldValue = map.put(actualKey, value);......}③ 我们回到executePipelined,在获取到连接工厂,将连接和当前线程绑定起来以后,就开始需要正式去执行命令了, 这里会调用execute方法
@Override
@Nullable
public <T> T execute(RedisCallback<T> action) {return execute(action, isExposeConnection());
}这里我们注意到execute方法的入参为RedisCallback<T>action,RedisCallback对应的doInRedis操作如下,这里在后面的调用过程中会涉及到回调。
connection.openPipeline();
boolean PipelinedClosed = false;
try {Object result = executeSession(session);if (result != null) {throw new InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException("Callback cannot return a non-null value as it gets overwritten by the Pipeline");}List<Object> closePipeline = connection.closePipeline(); PipelinedClosed = true;return deserializeMixedResults(closePipeline, resultSerializer, hashKeySerializer, hashValueSerializer);
} finally {if (!PipelinedClosed) {connection.closePipeline();}
}我们再来看execute(action, isExposeConnection())方法,这里最终会调用<T>execute(RedisCallback<T>action, boolean exposeConnection, boolean Pipeline)方法。
@Nullable
public <T> T execute(RedisCallback<T> action, boolean exposeConnection, boolean Pipeline) {Assert.isTrue(initialized, "template not initialized; call afterPropertiesSet() before using it");Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");//获取对应的连接工厂RedisConnectionFactory factory = getRequiredConnectionFactory();RedisConnection conn = null;try {if (enableTransactionSupport) {// only bind resources in case of potential transaction synchronizationconn = RedisConnectionUtils.bindConnection(factory, enableTransactionSupport);} else {//获取对应的连接(enableTransactionSupport=false) conn = RedisConnectionUtils.getConnection(factory);}boolean existingConnection = TransactionSynchronizationManager.hasResource(factory);RedisConnection connToUse = preProcessConnection(conn, existingConnection);boolean PipelineStatus = connToUse.isPipelined();if (Pipeline && !PipelineStatus) {connToUse.openPipeline();}RedisConnection connToExpose = (exposeConnection ? connToUse : createRedisConnectionProxy(connToUse));//核心方法,这里就开始执行回调操作T result = action.doInRedis(connToExpose);// close Pipelineif (Pipeline && !PipelineStatus) {connToUse.closePipeline();}// TODO: any other connection processing?return postProcessResult(result, connToUse, existingConnection);} finally {RedisConnectionUtils.releaseConnection(conn, factory, enableTransactionSupport);}
}我们看到这里最开始也是获取对应的连接工厂,然后获取对应的连接(enableTransactionSupport=false),具体调用是RedisConnectionUtils.getConnection(factory)方法,最终会调用RedisConnection doGetConnection(RedisConnectionFactory factory, booleanallowCreate, boolean bind, boolean enableTransactionSupport),此时bind为false
public static RedisConnection doGetConnection(RedisConnectionFactory factory, boolean allowCreate, boolean bind,boolean enableTransactionSupport) {Assert.notNull(factory, "No RedisConnectionFactory specified");//直接获取与当前线程绑定的Redis连接RedisConnectionHolder connHolder = (RedisConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(factory);if (connHolder != null) {if (enableTransactionSupport) {potentiallyRegisterTransactionSynchronisation(connHolder, factory);}return connHolder.getConnection();}......return conn;
}前面我们分析过一次,这里调用RedisConnectionHolder connHolder = (RedisConnectionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(factory);会获取到之前和当前线程绑定的Redis,而不会新创建一个连接。
然后会去执行T result = action.doInRedis(connToExpose),这里的action为RedisCallback,执行doInRedis为:
//开启Pipeline功能
connection.openPipeline();
boolean PipelinedClosed = false;
try {//执行Redis命令Object result = executeSession(session);if (result != null) {throw new InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException("Callback cannot return a non-null value as it gets overwritten by the Pipeline");}List<Object> closePipeline = connection.closePipeline(); PipelinedClosed = true;return deserializeMixedResults(closePipeline, resultSerializer, hashKeySerializer, hashValueSerializer);
} finally {if (!PipelinedClosed) {connection.closePipeline();}
}这里最开始会开启Pipeline功能,然后执行Object result = executeSession(session);
private Object executeSession(SessionCallback<?> session) {return session.execute(this);
}这里会调用我们自定义的execute方法
@AllArgsConstructor
private static class InsertPipelineExecution implements SessionCallback<Void> {private final List<Integer> userIds;private final Integer iconId;@Overridepublic <K, V> Void execute(RedisOperations<K, V> operations) throws DataAccessException {SetOperations<String, String> setOperations = (SetOperations<String, String>) operations.opsForSet();userIds.forEach(userId -> {String redisKey = "aaa:" + userId;String value = String.valueOf(iconId);setOperations.add(redisKey, value);});return null;}
}进入到foreach循环,执行DefaultSetOperations的add方法。
@Override
public Long add(K key, V... values) {byte[] rawKey = rawKey(key);byte[][] rawValues = rawValues((Object[]) values);//这里的connection.sAdd是后续回调要执行的方法return execute(connection -> connection.sAdd(rawKey, rawValues), true);
}这里会继续执行redisTemplate的execute方法,里面最终会调用我们之前分析过的
<T>T execute(RedisCallback<T>action, boolean exposeConnection, boolean Pipeline)方法。
@Nullable
public <T> T execute(RedisCallback<T> action, boolean exposeConnection, boolean Pipeline) {Assert.isTrue(initialized, "template not initialized; call afterPropertiesSet() before using it");Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");RedisConnectionFactory factory = getRequiredConnectionFactory();RedisConnection conn = null;try {......//再次执行回调方法,这里执行的Redis基本数据结构对应的操作命令T result = action.doInRedis(connToExpose);......// TODO: any other connection processing?return postProcessResult(result, connToUse, existingConnection);} finally {RedisConnectionUtils.releaseConnection(conn, factory, enableTransactionSupport);}
}这里会继续执行T result = action.doInRedis(connToExpose);,这里其实执行的doInRedis方法为:
connection -> connection.sAdd(rawKey, rawValues)4.4.2 Pipeline方式下执行命令的流程分析:
① 接着上面的流程分析,这里的sAdd方法实际调用的是DefaultStringRedisConnection的sAdd方法
@Override
public Long sAdd(byte[] key, byte[]... values) {return convertAndReturn(delegate.sAdd(key, values), identityConverter);
}② 这里会进一步调用DefaultedRedisConnection的sAdd方法
@Override
@Deprecated
default Long sAdd(byte[] key, byte[]... values) {return setCommands().sAdd(key, values);
}③ 接着调用LettuceSetCommands的sAdd方法
@Override
public Long sAdd(byte[] key, byte[]... values) {Assert.notNull(key, "Key must not be null!");Assert.notNull(values, "Values must not be null!");Assert.noNullElements(values, "Values must not contain null elements!");try {// 如果开启了 Pipelined 模式,获取的是 异步连接,进行异步操作if (isPipelined()) { Pipeline(connection.newLettuceResult(getAsyncConnection().sadd(key, values)));return null;}if (isQueueing()) {transaction(connection.newLettuceResult(getAsyncConnection().sadd(key, values)));return null;}//常规模式下,使用的是同步操作return getConnection().sadd(key, values);} catch (Exception ex) {throw convertLettuceAccessException(ex);}
}这里我们开启了Pipeline, 实际会调用Pipeline(connection.newLettuceResult(getAsyncConnection().sadd(key, values))); 也就是获取异步连接getAsyncConnection,然后进行异步操作sadd,而常规模式下,使用的是同步操作,所以在Pipeline模式下,执行效率更高。
从上面的获取连接和具体命令执行相关源码分析可以得出使用Lettuce客户端Pipeline模式高效的根本原因:
-
普通模式下,每执行一个命令都需要先打开一个连接,命令执行完毕以后又需要关闭这个连接,执行下一个命令时,又需要经过连接打开和关闭的流程;而Pipeline的所有命令的执行只需要经过一次连接打开和关闭。
-
普通模式下命令的执行是同步阻塞模式,而Pipeline模式下命令的执行是异步非阻塞模式。
五、项目中遇到的坑
前面介绍了涉及到批量操作,可以使用Redis Pipelining机制,那是不是任何批量操作相关的场景都可以使用呢,比如list类型数据的批量移除操作,我们的代码最开始是这么写的:
public void deleteSet(String updateKey, Set<Integer> userIds) {if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(userIds)) {return;}redisTemplate.executePipelined(new DeleteListCallBack(userIds, updateKey));}@AllArgsConstructor
private static class DeleteListCallBack implements SessionCallback<Object> {private Set<Integer> userIds;private String updateKey;@Overridepublic <K, V> Object execute(RedisOperations<K, V> operations) throws DataAccessException {ListOperations<String, String> listOperations = (ListOperations<String, String>) operations.opsForList();userIds.forEach(userId -> listOperations.remove(updateKey, 1, userId.toString()));return null;}
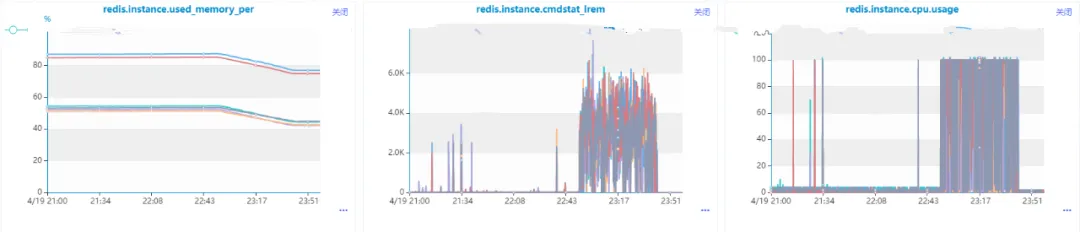
}在数据量比较小的时候没有出现问题,直到有一条收到了Redis的内存和cpu利用率的告警消息,我们发现这么使用是有问题的,核心原因在于list的lrem操作的时间复杂度是O(N+M),其中N是list的长度, M是要移除的元素的个数,而我们这里还是一个一个移除的,当然会导致Redis数据积压和cpu每秒ops升高导致cpu利用率飚高。也就是说,即使使用Pipeline进行批量操作,但是由于单次操作很耗时,是会导致整个Redis出现问题的。
后面我们进行了优化,选用了list的ltrim命令,一次命令执行批量remove操作:
public void deleteSet(String updateKey, Set<Integer> deviceIds) {if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(deviceIds)) {return;}int maxSize = 10000;redisTemplate.opsForList().trim(updateKey, maxSize + 1, -1);}由于ltrim本身的时间复杂度为O(M), 其中M要移除的元素的个数,相比于原始方案的lrem,效率提升很多,可以不需要使用Redis Pipeline,优化结果使得Redis内存利用率和cpu利用率都极大程度得到缓解。
六、Redisson 对 Redis Pipeline 特性支持
在redisson官方文档中额外特性介绍中有说到批量命令执行这个特性, 也就是多个命令在一次网络调用中集中发送,该特性是RBatch这个类支持的,从这个类的描述来看,主要是为Redis Pipeline这个特性服务的,并且主要是通过队列和异步实现的。
/*** Interface for using Redis Pipeline feature.* <p>* All method invocations on objects got through this interface* are batched to separate queue and could be executed later* with <code>execute()</code> or <code>executeAsync()</code> methods.*** @author Nikita Koksharov**/
public interface RBatch {/*** Returns stream instance by <code>name</code>** @param <K> type of key* @param <V> type of value* @param name of stream* @return RStream object*/<K, V> RStreamAsync<K, V> getStream(String name);/*** Returns stream instance by <code>name</code>* using provided <code>codec</code> for entries.** @param <K> type of key* @param <V> type of value* @param name - name of stream* @param codec - codec for entry* @return RStream object*/<K, V> RStreamAsync<K, V> getStream(String name, Codec codec);....../*** Returns list instance by name.** @param <V> type of object* @param name - name of object* @return List object*/<V> RListAsync<V> getList(String name);<V> RListAsync<V> getList(String name, Codec codec);....../*** Executes all operations accumulated during async methods invocations.* <p>* If cluster configuration used then operations are grouped by slot ids* and may be executed on different servers. Thus command execution order could be changed** @return List with result object for each command* @throws RedisException in case of any error**/BatchResult<?> execute() throws RedisException;/*** Executes all operations accumulated during async methods invocations asynchronously.* <p>* In cluster configurations operations grouped by slot ids* so may be executed on different servers. Thus command execution order could be changed** @return List with result object for each command*/RFuture<BatchResult<?>> executeAsync();/*** Discard batched commands and release allocated buffers used for parameters encoding.*/void discard();/*** Discard batched commands and release allocated buffers used for parameters encoding.** @return void*/RFuture<Void> discardAsync();}简单的测试代码如下:
@Slf4j
public class RedisPipelineTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//Redisson使用Pipeline模式Config config = new Config();config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://xx.xx.xx.xx:6379");RedissonClient redisson = Redisson.create(config);RBatch redisBatch = redisson.createBatch();int size = 100000;String zSetKey = "Pipeline-test-set";long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();//将命令放入队列中for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {redisBatch.getSet(zSetKey + i).addAsync("ccc");}//批量执行命令redisBatch.execute();log.info("Redisson Pipeline模式耗时:{}ms", (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));//关闭redisson.shutdown();}
}核心方法分析:
1.建Redisson客户端RedissonClient redisson = redisson.create(config), 该方法最终会调用Reddison的构造方法Redisson(Config config)。
protected Redisson(Config config) {this.config = config;Config configCopy = new Config(config);connectionManager = ConfigSupport.createConnectionManager(configCopy);RedissonObjectBuilder objectBuilder = null;if (config.isReferenceEnabled()) {objectBuilder = new RedissonObjectBuilder(this);}//新建异步命令执行器commandExecutor = new CommandSyncService(connectionManager, objectBuilder);//执行删除超时任务的定时器evictionScheduler = new EvictionScheduler(commandExecutor);writeBehindService = new WriteBehindService(commandExecutor);
}该构造方法中会新建异步命名执行器CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor和用户删除超时任务的EvictionScheduler evictionScheduler。
2.创建RBatch实例RBatch redisBatch = redisson.createBatch(), 该方法会使用到步骤1中的commandExecutor和evictionScheduler实例对象。
@Override
public RBatch createBatch(BatchOptions options) {return new RedissonBatch(evictionScheduler, commandExecutor, options);
}public RedissonBatch(EvictionScheduler evictionScheduler, CommandAsyncExecutor executor, BatchOptions options) {this.executorService = new CommandBatchService(executor, options);this.evictionScheduler = evictionScheduler;
}其中的options对象会影响后面批量执行命令的流程。
3. 异步给set集合添加元素的操作addAsync,这里会具体调用RedissonSet的addAsync方法
@Override
public RFuture<Boolean> addAsync(V e) {String name = getRawName(e);return commandExecutor.writeAsync(name, codec, RedisCommands.SADD_SINGLE, name, encode(e));
}(1)接着调用CommandAsyncExecutor的异步写入方法writeAsync。
@Override
public <T, R> RFuture<R> writeAsync(String key, Codec codec, RedisCommand<T> command, Object... params) {RPromise<R> mainPromise = createPromise();NodeSource source = getNodeSource(key);async(false, source, codec, command, params, mainPromise, false);return mainPromise;
}(2) 接着调用批量命令执行器CommandBatchService的异步发送命令。
@Override
public <V, R> void async(boolean readOnlyMode, NodeSource nodeSource,Codec codec, RedisCommand<V> command, Object[] params, RPromise<R> mainPromise, boolean ignoreRedirect) {if (isRedisBasedQueue()) {boolean isReadOnly = options.getExecutionMode() == ExecutionMode.REDIS_READ_ATOMIC;RedisExecutor<V, R> executor = new RedisQueuedBatchExecutor<>(isReadOnly, nodeSource, codec, command, params, mainPromise,false, connectionManager, objectBuilder, commands, connections, options, index, executed, latch, referenceType);executor.execute();} else {//执行分支RedisExecutor<V, R> executor = new RedisBatchExecutor<>(readOnlyMode, nodeSource, codec, command, params, mainPromise,false, connectionManager, objectBuilder, commands, options, index, executed, referenceType);executor.execute();}}(3) 接着调用了RedisBatchExecutor.execute方法和BaseRedisBatchExecutor.addBatchCommandData方法。
@Override
public void execute() {addBatchCommandData(params);
}protected final void addBatchCommandData(Object[] batchParams) {MasterSlaveEntry msEntry = getEntry(source);Entry entry = commands.get(msEntry);if (entry == null) {entry = new Entry();Entry oldEntry = commands.putIfAbsent(msEntry, entry);if (oldEntry != null) {entry = oldEntry;}}if (!readOnlyMode) {entry.setReadOnlyMode(false);}Codec codecToUse = getCodec(codec);BatchCommandData<V, R> commandData = new BatchCommandData<V, R>(mainPromise, codecToUse, command, batchParams, index.incrementAndGet());entry.getCommands().add(commandData);
}这里的commands以主节点为KEY,以待发送命令队列列表为VALUE(Entry),保存一个MAP.然后会把命令都添加到entry的commands命令队列中, Entry结构如下面代码所示。
public static class Entry {Deque<BatchCommandData<?, ?>> commands = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>();volatile boolean readOnlyMode = true;public Deque<BatchCommandData<?, ?>> getCommands() {return commands;}public void setReadOnlyMode(boolean readOnlyMode) {this.readOnlyMode = readOnlyMode;}public boolean isReadOnlyMode() {return readOnlyMode;}public void clearErrors() {for (BatchCommandData<?, ?> commandEntry : commands) {commandEntry.clearError();}}}4. 批量执行命令redisBatch.execute(),这里会最终调用CommandBatchService的executeAsync方法,该方法完整代码如下,我们下面来逐一进行拆解。
public RFuture<BatchResult<?>> executeAsync() {......RPromise<BatchResult<?>> promise = new RedissonPromise<>();RPromise<Void> voidPromise = new RedissonPromise<Void>();if (this.options.isSkipResult()&& this.options.getSyncSlaves() == 0) {......} else {//这里是对异步执行结果进行处理,可以先忽略, 后面会详细讲,先关注批量执行命令的逻辑voidPromise.onComplete((res, ex) -> {......});}AtomicInteger slots = new AtomicInteger(commands.size());......//真正执行的代码入口,批量执行命令for (Map.Entry<MasterSlaveEntry, Entry> e : commands.entrySet()) {RedisCommonBatchExecutor executor = new RedisCommonBatchExecutor(new NodeSource(e.getKey()), voidPromise,connectionManager, this.options, e.getValue(), slots, referenceType);executor.execute();}return promise;}里面会用到我们在3.3步骤所生成的commands实例。
(1)接着调用了基类RedisExecutor的execute方法
public void execute() {......connectionFuture.onComplete((connection, e) -> {if (connectionFuture.isCancelled()) {connectionManager.getShutdownLatch().release();return;}if (!connectionFuture.isSuccess()) {connectionManager.getShutdownLatch().release();exception = convertException(connectionFuture);return;}//调用RedisCommonBatchExecutor的sendCommand方法, 里面会将多个命令放到一个List<CommandData<?, ?>> list列表里面sendCommand(attemptPromise, connection);writeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {checkWriteFuture(writeFuture, attemptPromise, connection);}});});......}(2)接着调用RedisCommonBatchExecutor的sendCommand方法,里面会将多个命令放到一个List<commanddata> list列表里面。
@Overrideprotected void sendCommand(RPromise<Void> attemptPromise, RedisConnection connection) {boolean isAtomic = options.getExecutionMode() != ExecutionMode.IN_MEMORY;boolean isQueued = options.getExecutionMode() == ExecutionMode.REDIS_READ_ATOMIC|| options.getExecutionMode() == ExecutionMode.REDIS_WRITE_ATOMIC;//将多个命令放到一个List<CommandData<?, ?>> list列表里面List<CommandData<?, ?>> list = new ArrayList<>(entry.getCommands().size());if (source.getRedirect() == Redirect.ASK) {RPromise<Void> promise = new RedissonPromise<Void>();list.add(new CommandData<Void, Void>(promise, StringCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.ASKING, new Object[] {}));}for (CommandData<?, ?> c : entry.getCommands()) {if ((c.getPromise().isCancelled() || c.getPromise().isSuccess())&& !isWaitCommand(c)&& !isAtomic) {// skip commandcontinue;}list.add(c);}......//调用RedisConnection的send方法,将命令一次性发到Redis服务器端writeFuture = connection.send(new CommandsData(attemptPromise, list, options.isSkipResult(), isAtomic, isQueued, options.getSyncSlaves() > 0));}(3)接着调用RedisConnection的send方法,通过Netty通信发送命令到Redis服务器端执行,这里也验证了Redisson客户端底层是采用Netty进行通信的。
public ChannelFuture send(CommandsData data) {return channel.writeAndFlush(data);
}5. 接收返回结果,这里主要是监听事件是否完成,然后组装返回结果, 核心方法是步骤4提到的CommandBatchService的executeAsync方法,里面会对返回结果进行监听和处理, 核心代码如下:
public RFuture<BatchResult<?>> executeAsync() {......RPromise<BatchResult<?>> promise = new RedissonPromise<>();RPromise<Void> voidPromise = new RedissonPromise<Void>();if (this.options.isSkipResult()&& this.options.getSyncSlaves() == 0) {......} else {voidPromise.onComplete((res, ex) -> {//对返回结果的处理executed.set(true);......List<Object> responses = new ArrayList<Object>(entries.size());int syncedSlaves = 0;for (BatchCommandData<?, ?> commandEntry : entries) {if (isWaitCommand(commandEntry)) {syncedSlaves = (Integer) commandEntry.getPromise().getNow();} else if (!commandEntry.getCommand().getName().equals(RedisCommands.MULTI.getName())&& !commandEntry.getCommand().getName().equals(RedisCommands.EXEC.getName())&& !this.options.isSkipResult()) {......//获取单个命令的执行结果Object entryResult = commandEntry.getPromise().getNow();......//将单个命令执行结果放到List中responses.add(entryResult);}}BatchResult<Object> result = new BatchResult<Object>(responses, syncedSlaves);promise.trySuccess(result);......});}......return promise;
}这里会把单个命令的执行结果放到responses里面,最终返回RPromise<batchresult>promise。
从上面的分析来看,Redisson客户端对Redis Pipeline的支持也是从多个命令在一次网络通信中执行和异步处理来实现的。
七、总结
Redis提供了Pipelining进行批量操作的高级特性,极大地提高了部分数据类型没有批量执行命令导致的执行耗时而引起的性能问题,但是我们在使用的过程中需要考虑Pipeline操作中单个命令执行的耗时问题,否则带来的效果可能适得其反。最后扩展分析了Redisson客户端对Redis Pipeline特性的支持原理,可以与Lettuce客户端对Redis Pipeline支持原理进行比较,加深Pipeline在不同Redis客户端实现方式的理解。
参考资料:
-
Redis Pipelining
-
RedisTemplate使用Pipeline管道命令
-
如何使用好Redis Pipeline
-
Redisson 管道批量发送命令流程分析
这篇关于Redis Pipelining 底层原理分析及实践的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!

