本文主要是介绍Mark : Spark RDD 内部结构(二) RDD分区,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
RDD 分区
分区
先回答第一个问题:RDD 内部,如何表示并行计算的一个计算单元。答案是使用分区(Partition)。
RDD 内部的数据集合在逻辑上和物理上被划分成多个小子集合,这样的每一个子集合我们将其称为分区,分区的个数会决定并行计算的粒度,而每一个分区数值的计算都是在一个单独的任务中进行,因此并行任务的个数,也是由 RDD(实际上是一个阶段的末 RDD,调度章节会介绍)分区的个数决定的,我会在 1.2 小节以及第二章中,具体说明分区与并行计算的关系。
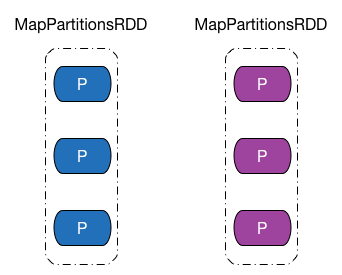
在后文中,我会用下图所示图形来表示 RDD 以及 RDD 内部的分区,RDD 上方文字表示该 RDD 的类型或者名字,分区颜色为紫红色表示该 RDD 内数据被缓存到存储介质中,蓝色表示该 RDD 为普通 RDD。 —— 话说这配色真的很丑么……
分区实现
分区的源码实现为 Partition 类。
/*** An identifier for a partition in an RDD.*/
trait Partition extends Serializable {/*** Get the partition's index within its parent RDD*/def index: Int// A better default implementation of HashCodeoverride def hashCode(): Int = index
}
RDD 只是数据集的抽象,分区内部并不会存储具体的数据。Partition 类内包含一个 index 成员,表示该分区在 RDD 内的编号,通过 RDD 编号 + 分区编号可以唯一确定该分区对应的块编号,利用底层数据存储层提供的接口,就能从存储介质(如:HDFS、Memory)中提取出分区对应的数据。
RDD 抽象类中定义了 _partitions 数组成员和 partitions 方法,partitions 方法提供给外部开发者调用,用于获取 RDD 的所有分区。partitions 方法会调用内部 getPartitions 接口,RDD 的子类需要自行实现 getPartitions 接口。
@transient private var partitions_ : Array[Partition] = null/*** Implemented by subclasses to return the set of partitions in this RDD. This method will only* be called once, so it is safe to implement a time-consuming computation in it.*/protected def getPartitions: Array[Partition]/*** Get the array of partitions of this RDD, taking into account whether the* RDD is checkpointed or not.*/final def partitions: Array[Partition] = {checkpointRDD.map(_.partitions).getOrElse {if (partitions_ == null) {partitions_ = getPartitions}partitions_}}
以 map 转换操作生成 MapPartitionsRDD 类中的 getPartitions 方法为例。
override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = firstParent[T].partitions
可以看到,MapPartitionsRDD 的分区实际上与父 RDD 的分区完全一致,这也符合我们对 map 转换操作的认知。
分区个数
RDD 分区的一个分配原则是:尽可能使得分区的个数,等于集群核心数目。
RDD 可以通过创建操作或者转换操作得到。转换操作中,分区的个数会根据转换操作对应多个 RDD 之间的依赖关系确定,窄依赖子 RDD 由父 RDD 分区个数决定,Shuffle 依赖由子 RDD 分区器决定。
创建操作中,程序开发者可以手动指定分区的个数,例如 sc.parallelize (Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5), 2) 表示创建得到的 RDD 分区个数为 2,在没有指定分区个数的情况下,Spark 会根据集群部署模式,来确定一个分区个数默认值。
分别讨论 parallelize 和textFile 两种通过外部数据创建生成RDD的方法。
对于 parallelize 方法,默认情况下,分区的个数会受 Apache Spark 配置参数 spark.default.parallelism 的影响,官方对该参数的解释是用于控制 Shuffle 过程中默认使用的任务数量,这也符合我们之间对分区个数与任务个数之间关系的理解。
/** Distribute a local Scala collection to form an RDD.** @note Parallelize acts lazily. If `seq` is a mutable collection and is altered after the call* to parallelize and before the first action on the RDD, the resultant RDD will reflect the* modified collection. Pass a copy of the argument to avoid this.* @note avoid using `parallelize(Seq())` to create an empty `RDD`. Consider `emptyRDD` for an* RDD with no partitions, or `parallelize(Seq[T]())` for an RDD of `T` with empty partitions.*/def parallelize[T: ClassTag](seq: Seq[T],numSlices: Int = defaultParallelism): RDD[T] = withScope {assertNotStopped()new ParallelCollectionRDD[T](this, seq, numSlices, Map[Int, Seq[String]]())}
无论是以本地模式、Standalone 模式、Yarn 模式或者是 Mesos 模式来运行 Apache Spark,分区的默认个数等于对 spark.default.parallelism 的指定值,若该值未设置,则 Apache Spark 会根据不同集群模式的特征,来确定这个值。
对于本地模式,默认分区个数等于本地机器的 CPU 核心总数(或者是用户通过 local[N] 参数指定分配给 Apache Spark 的核心数目,见 LocalBackend 类),显然这样设置是合理的,因为把每个分区的计算任务交付给单个核心执行,能够保证最大的计算效率。
override def defaultParallelism() =scheduler.conf.getInt("spark.default.parallelism", totalCores)
若使用 Apache Mesos 作为集群的资源管理系统,默认分区个数等于 8(对 Apache Mesos 不是很了解,根据这个 TODO,个人猜测 Apache Spark 暂时还无法获取 Mesos 集群的核心总数)(见 MesosSchedulerBackend 类)。
// TODO: query Mesos for number of coresoverride def defaultParallelism(): Int = sc.conf.getInt("spark.default.parallelism", 8)
其他集群模式(Standalone 或者 Yarn),默认分区个数等于集群中所有核心数目的总和,或者 2,取两者中的较大值(见 CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend 类)。
override def defaultParallelism(): Int = {conf.getInt("spark.default.parallelism", math.max(totalCoreCount.get(), 2))}
对于 textFile 方法,默认分区个数等于 min(defaultParallelism, 2)(见 SparkContext 类),而 defaultParallelism 实际上就是 parallelism 方法的默认分区值。
/*** Read a text file from HDFS, a local file system (available on all nodes), or any* Hadoop-supported file system URI, and return it as an RDD of Strings.*/def textFile(path: String,minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[String] = withScope {assertNotStopped()hadoopFile(path, classOf[TextInputFormat], classOf[LongWritable], classOf[Text],minPartitions).map(pair => pair._2.toString)}
分区内部记录个数
分区分配的另一个分配原则是:尽可能使同一 RDD 不同分区内的记录的数量一致。
对于转换操作得到的 RDD,如果是窄依赖,则分区记录数量依赖于父 RDD 中相同编号分区是如何进行数据分配的,如果是 Shuffle 依赖,则分区记录数量依赖于选择的分区器,哈希分区器无法保证数据被平均分配到各个分区,而范围分区器则能做到这一点。这部分内容我会在 1.6 小节中讨论。
parallelize 方法通过把输入的数组做一次平均分配,尝试着让每个分区的记录个数尽可能大致相同(见 ParallelCollectionRDD 类)。
private object ParallelCollectionRDD {/*** Slice a collection into numSlices sub-collections. One extra thing we do here is to treat Range* collections specially, encoding the slices as other Ranges to minimize memory cost. This makes* it efficient to run Spark over RDDs representing large sets of numbers. And if the collection* is an inclusive Range, we use inclusive range for the last slice.*/def slice[T: ClassTag](seq: Seq[T], numSlices: Int): Seq[Seq[T]] = {if (numSlices < 1) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Positive number of slices required")}// Sequences need to be sliced at the same set of index positions for operations// like RDD.zip() to behave as expecteddef positions(length: Long, numSlices: Int): Iterator[(Int, Int)] = {(0 until numSlices).iterator.map(i => {val start = ((i * length) / numSlices).toIntval end = (((i + 1) * length) / numSlices).toInt(start, end)})}seq match {case r: Range => {positions(r.length, numSlices).zipWithIndex.map({ case ((start, end), index) =>// If the range is inclusive, use inclusive range for the last sliceif (r.isInclusive && index == numSlices - 1) {new Range.Inclusive(r.start + start * r.step, r.end, r.step)}else {new Range(r.start + start * r.step, r.start + end * r.step, r.step)}}).toSeq.asInstanceOf[Seq[Seq[T]]]}case nr: NumericRange[_] => {// For ranges of Long, Double, BigInteger, etcval slices = new ArrayBuffer[Seq[T]](numSlices)var r = nrfor ((start, end) <- positions(nr.length, numSlices)) {val sliceSize = end - startslices += r.take(sliceSize).asInstanceOf[Seq[T]]r = r.drop(sliceSize)}slices}case _ => {val array = seq.toArray // To prevent O(n^2) operations for List etcpositions(array.length, numSlices).map({case (start, end) =>array.slice(start, end).toSeq}).toSeq}}}
}
textFile 方法分区内数据的大小则是由 Hadoop API 接口 FileInputFormat.getSplits 方法决定(见 HadoopRDD 类),得到的每一个分片即为 RDD 的一个分区,分片内数据的大小会受文件大小、文件是否可分割、HDFS 中块大小等因素的影响,但总体而言会是比较均衡的分配。
override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {val jobConf = getJobConf()// add the credentials here as this can be called before SparkContext initializedSparkHadoopUtil.get.addCredentials(jobConf)val inputFormat = getInputFormat(jobConf)if (inputFormat.isInstanceOf[Configurable]) {inputFormat.asInstanceOf[Configurable].setConf(jobConf)}val inputSplits = inputFormat.getSplits(jobConf, minPartitions)val array = new Array[Partition](inputSplits.size)for (i <- 0 until inputSplits.size) {array(i) = new HadoopPartition(id, i, inputSplits(i))}array}
参考资料
- Spark Configuration - Spark 1.2.0 Documentation
- FileInputFormat (Apache Hadoop Main 2.6.0 API)
- Spark:RDD 理解
这篇关于Mark : Spark RDD 内部结构(二) RDD分区的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





