本文主要是介绍二分图、匈牙利算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
一,二分图
CodeForces 687A NP-Hard Problem
力扣 785. 判断二分图
二,完全二分图
1,完全二分图
2,K2,3
3,K3,3
三,匈牙利算法
1,二分图最大匹配
2,其他图论问题
一,二分图
一般我们研究二分图默认指的是无向图。
二分图是指,可以把图中的顶点分成两个集合,使得每个集合中的所有点之间都是互不相连的。
//判断是不是二分图, 节点编号是0到n-1static bool isTwoDivGraph(int n, UndirectedGraphData<int> &g) {UnionDif unions(n);for (auto e : g.edges) {unions.find(e.a);unions.find(e.b);if (unions.inSame(e.a, e.b)) {if (int(unions.getDif(e.a) + unions.getDif(e.b)) % 2)return false;}else {unions.merge(e.a, e.b,1);}}return true;}CodeForces 687A NP-Hard Problem
题目:
Description
Recently, Pari and Arya did some research about NP-Hard problems and they found the minimum vertex cover problem very interesting.
Suppose the graph G is given. Subset A of its vertices is called a vertex cover of this graph, if for each edge uv there is at least one endpoint of it in this set, i.e. or (or both).
Pari and Arya have won a great undirected graph as an award in a team contest. Now they have to split it in two parts, but both of them want their parts of the graph to be a vertex cover.
They have agreed to give you their graph and you need to find two disjoint subsets of its vertices A and B, such that both A and B are vertex cover or claim it's impossible. Each vertex should be given to no more than one of the friends (or you can even keep it for yourself).
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100 000) — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the prize graph, respectively.
Each of the next m lines contains a pair of integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n), denoting an undirected edge between ui and vi. It's guaranteed the graph won't contain any self-loops or multiple edges.
Output
If it's impossible to split the graph between Pari and Arya as they expect, print "-1" (without quotes).
If there are two disjoint sets of vertices, such that both sets are vertex cover, print their descriptions. Each description must contain two lines. The first line contains a single integer k denoting the number of vertices in that vertex cover, and the second line contains kintegers — the indices of vertices. Note that because of m ≥ 1, vertex cover cannot be empty.
Sample Input
Input
4 2
1 2
2 3
Output
1
2
2
1 3
Input
3 3
1 2
2 3
1 3
Output
-1
题目大意就是把图分成二分图,如果不能的话,输出-1,如果能的话,分别输出2个部分的点的数量和点的标号。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;int list[100005];
int fenzu[100005];int main()
{int n, m;cin >> n >> m;int fx, fy;memset(list, 0, sizeof(list));memset(fenzu, 0, sizeof(fenzu));int x, y;int zu = 1;while (m--){cin >> x >> y; if (list[x] == 0){if (list[y] == 0){fenzu[x] = zu;fenzu[y] = zu;list[x] = 1;list[y] = 2;zu++;}else{fenzu[x] = fenzu[y];list[x] = 3 - list[y];}}else{if (list[y] == 0){fenzu[y] = fenzu[x];list[y] = 3 - list[x];}else{fx = fenzu[x];fy = fenzu[y];if (fx == fy){if (list[x] == list[y]){cout << "-1";return 0;}}else{ if (list[x] == list[y]){for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (fenzu[i] == fy){fenzu[i] = fx;list[i] = 3 - list[i];}} else for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (fenzu[i] == fy)fenzu[i] = fx;}}}}int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (list[i] == 1)sum++;cout << sum << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (list[i] == 1)cout << i<<" ";cout << endl << n - sum << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (list[i] != 1)cout << i << " ";return 0;
}可惜超时了,在test14超时了,test14估计是n和m非常大的了。
前面13个test都过了,想必这个代码是没有问题的,就是效率的问题。
很显然,主要的效率问题就是,在唯一的while循环里面,有1个从1到n的循环,只为了检索一些特定的目标出来。
所以很显然,我应该使用队列。
抛弃这个思想,用队列来做,其实很简单,只要记录每个点的所有邻居即可。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;vector<int>v[100005];
queue<int>q;
int list[100005];int main()
{int n, m;cin >> n >> m;int x, y;while (m--){cin >> x >> y; v[x].insert(v[x].end(),y);v[y].insert(v[y].end(),x);}int k, key = 1;memset(list, 0, sizeof(list));vector< int >::iterator p;while (1){while (list[key])key++;if (key > n)break;q.push(key);list[key] = 1;while (!q.empty()){k = q.front();q.pop();for (p = v[k].begin(); p != v[k].end(); p++){if (list[*p] == list[k]){cout << "-1";return 0;}if (list[*p] == 0){q.push(*p);list[*p] = 3 - list[k];}}}}int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (list[i] == 1)sum++;cout << sum << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (list[i] == 1)cout << i<<" ";cout << endl << n - sum << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (list[i] != 1)cout << i << " ";return 0;
}表面上有3层循环,实际上外面的2层while循环是有限制的,合起来也就是大约n而已。
里面的循环就更不用说了,3层循环合起来也就是大约n而已。
所以这个算法还是很快的,果然AC了。
力扣 785. 判断二分图
存在一个 无向图 ,图中有 n 个节点。其中每个节点都有一个介于 0 到 n - 1 之间的唯一编号。给你一个二维数组 graph ,其中 graph[u] 是一个节点数组,由节点 u 的邻接节点组成。形式上,对于 graph[u] 中的每个 v ,都存在一条位于节点 u 和节点 v 之间的无向边。该无向图同时具有以下属性:
- 不存在自环(
graph[u]不包含u)。 - 不存在平行边(
graph[u]不包含重复值)。 - 如果
v在graph[u]内,那么u也应该在graph[v]内(该图是无向图) - 这个图可能不是连通图,也就是说两个节点
u和v之间可能不存在一条连通彼此的路径。
二分图 定义:如果能将一个图的节点集合分割成两个独立的子集 A 和 B ,并使图中的每一条边的两个节点一个来自 A 集合,一个来自 B 集合,就将这个图称为 二分图 。
如果图是二分图,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
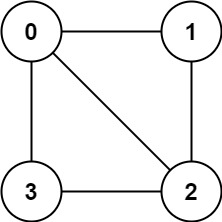
输入:graph = [[1,2,3],[0,2],[0,1,3],[0,2]]
输出:false
解释:不能将节点分割成两个独立的子集,以使每条边都连通一个子集中的一个节点与另一个子集中的一个节点。
示例 2:

输入:graph = [[1,3],[0,2],[1,3],[0,2]]
输出:true
解释:可以将节点分成两组: {0, 2} 和 {1, 3} 。
提示:
graph.length == n1 <= n <= 1000 <= graph[u].length < n0 <= graph[u][i] <= n - 1graph[u]不会包含ugraph[u]的所有值 互不相同- 如果
graph[u]包含v,那么graph[v]也会包含u
c++代码:
class Solution {
public:bool isBipartite(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {map<int, vector<int>>m;for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++)m[i] = graph[i];UndirectedGraphData<int> g(m);return UndirectedGraph::isTwoDivGraph(m.size(), g);}
};rust代码:
struct Union{fa:Vec<usize>,dif:Vec<i32>,
}
impl Union{fn find(& mut self,x:usize)->usize{if self.fa[x] == x{return x;}Union::find(self,self.fa[x]);self.dif[x] += self.dif[self.fa[x]];self.fa[x] = self.fa[self.fa[x]];return self.fa[x];}fn in_same(& mut self,x:usize,y:usize)->bool{return Union::find(self,x) == Union::find(self,y);}fn merge(& mut self,x:usize,y:usize,x_sub_y:i32)->(){Union::find(self,x);let fax = self.fa[x];self.dif[fax] = x_sub_y - self.dif[x];self.fa[fax] = y;}
}impl Solution {pub fn is_bipartite(graph: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> bool {let mut fa=Vec::new();let mut dif=Vec::new();for i in 0..graph.len(){fa.push(i);dif.push(0);}let mut opt = Union{fa:fa,dif:dif};for x in 0..graph.len(){for y in graph[x].clone(){let y = y as usize;if opt.in_same(x, y){if (opt.dif[x]+opt.dif[y])%2 == 0{return false;}}else{opt.merge(x, y, 1);}}}return true;}
}二,完全二分图
1,完全二分图
完全二分图是一种特殊的二分图,可以把图中的顶点分成两个集合,使得第一个集合中的所有顶点都与第二个集合中的所有顶点相连。
2,K2,3

3,K3,3

三,匈牙利算法
1,二分图最大匹配
思路:
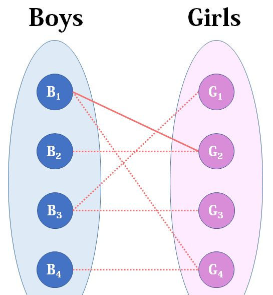
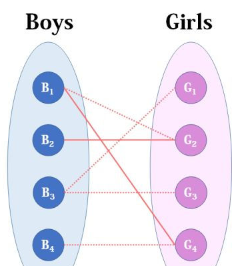
从0开始,逐步扩展。
扩展方法:寻找类似于0-1-2-3-4-5的路径,把匹配“1-2 3-4”调整成匹配“0-1 2-3 4-5”,匹配数加1。
示例:
调整前:
寻找路径:

调整后:
模板代码:
参考ACM模板
2,其他图论问题
待更新
这篇关于二分图、匈牙利算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









