本文主要是介绍数据库系统概论(超详解!!!) 第三节 关系数据库标准语言SQL(Ⅳ),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1.集合查询
集合操作的种类
并操作UNION
交操作INTERSECT
差操作EXCEPT
参加集合操作的各查询结果的列数必须相同;对应项的数据类型也必须相同
查询计算机科学系的学生及年龄不大于19岁的学生。SELECT *FROM StudentWHERE Sdept= 'CS'UNIONSELECT *FROM StudentWHERE Sage<=19;
UNION:将多个查询结果合并起来时,系统自动去掉重复元组
UNION ALL:将多个查询结果合并起来时,保留重复元组
查询选修了课程1或者选修了课程2的学生。SELECT SnoFROM SCWHERE Cno=' 1 'UNIONSELECT SnoFROM SCWHERE Cno= ' 2 ';查询计算机科学系的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生的交集。SELECT *
FROM Student
WHERE Sdept='CS'
INTERSECT
SELECT *
FROM Student
WHERE Sage<=19 实际上就是查询计算机科学系中年龄不大于19岁的学生。SELECT *FROM StudentWHERE Sdept= 'CS' AND Sage<=19;查询既选修了课程1又选修了课程2的学生。SELECT SnoFROM SCWHERE Cno=' 1 ' INTERSECTSELECT SnoFROM SCWHERE Cno='2 ';也可以表示为:SELECT SnoFROM SCWHERE Cno=' 1 ' AND Sno IN(SELECT SnoFROM SCWHERE Cno=' 2 ');查询计算机科学系的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生的差集。SELECT *FROM StudentWHERE Sdept='CS'EXCEPTSELECT *FROM StudentWHERE Sage <=19;实际上是查询计算机科学系中年龄大于19岁的学生SELECT *FROM StudentWHERE Sdept= 'CS' AND Sage>19;2.于派生表的查询
子查询不仅可以出现在WHERE子句中,还可以出现在FROM子句中。
这时子查询生成的临时派生表(Derived Table)成为主查询的查询对象
找出每个学生超过他自己选修课程平均成绩的课程号SELECT Sno, CnoFROM SC, (SELECTSno, Avg(Grade) FROM SCGROUP BY Sno)AS Avg_sc(avg_sno,avg_grade)WHERE SC.Sno = Avg_sc.avg_snoand SC.Grade >=Avg_sc.avg_grade
如果子查询中没有聚集函数,派生表可以不指定属性列,子查询SELECT子句后面的列名为其缺省属性。
查询所有选修了1号课程的学生姓名,可以用如下查询完成:SELECT SnameFROM Student, (SELECT Sno FROM SC WHERE Cno=' 1 ') AS SC1WHERE Student.Sno=SC1.Sno;
3.Select语句的一般形式
SELECT [ALL|DISTINCT]
<目标列表达式> [别名] [ ,<目标列表达式> [别名]] …
FROM <表名或视图名> [别名]
[ ,<表名或视图名> [别名]] …
|(<SELECT语句>)[AS]<别名>
[WHERE <条件表达式>]
[GROUP BY <列名1>[HAVING<条件表达式>]]
[ORDER BY <列名2> [ASC|DESC]];
1. 目标列表达式的可选格式
目标列表达式格式
(1) *
(2) <表名>.*
(3) COUNT([DISTINCT|ALL]* )
(4) [<表名>.]<属性列名表达式>[,<表名>.]<属性列名表达式>]…
其中<属性列名表达式>可以是由属性列、作用于属性列 的聚集函数和常量的任意算术运算(+,-,*,/)组成的 运算公式
2. 聚集函数的一般格式
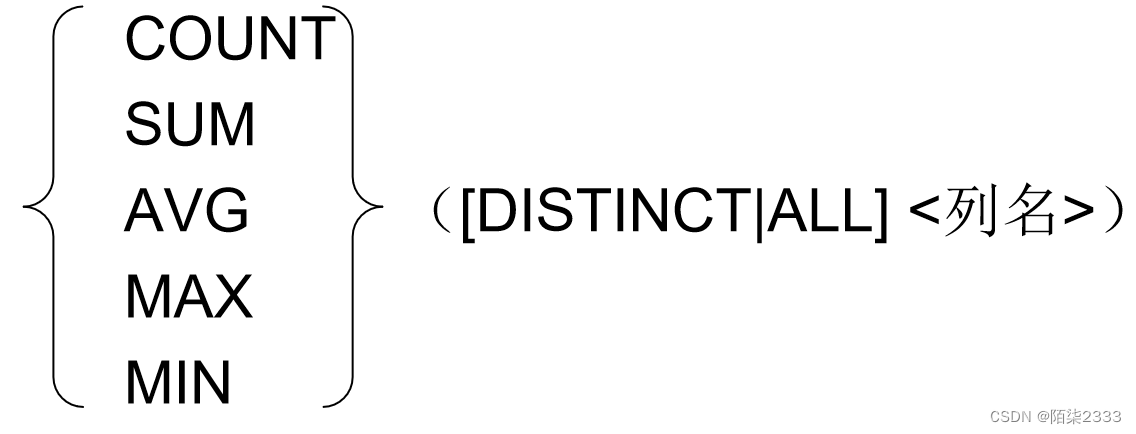
3. WHERE子句的条件表达式的可选格式
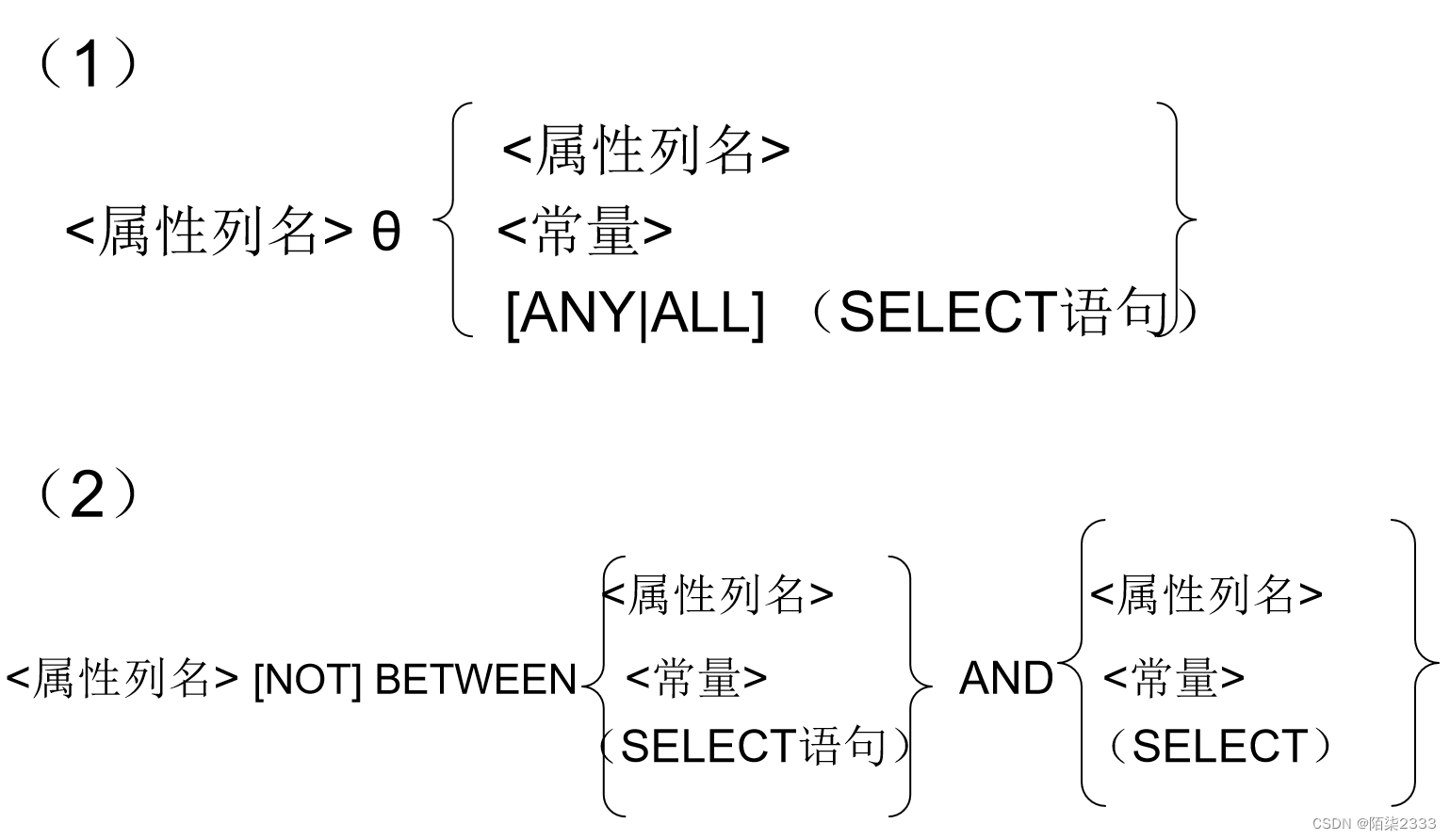

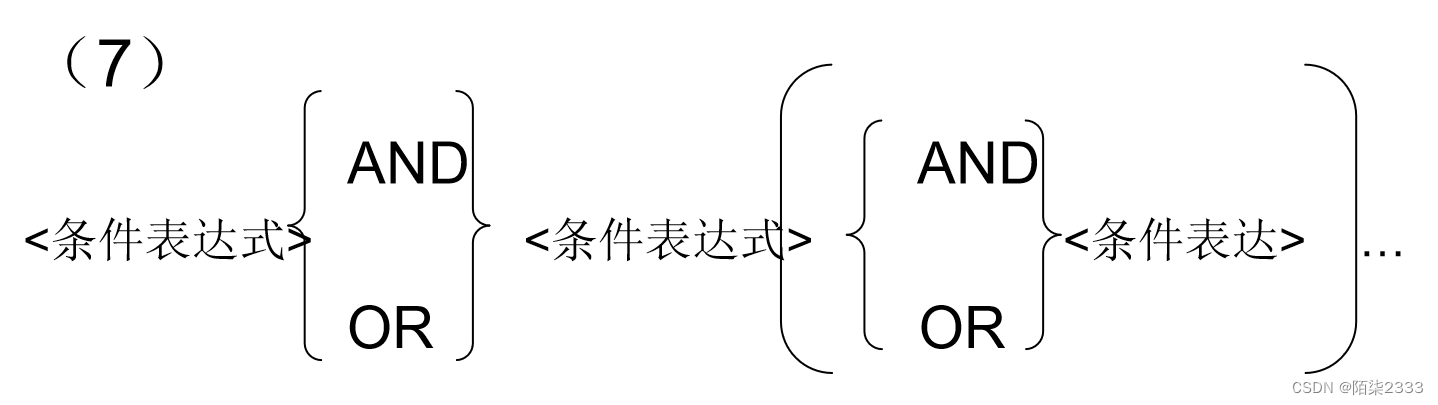
4.练习
/*(1)查询选修了81003号课程的学生姓名;*//*方法1:连接查询*/select snamefrom Student,SCwhere Student.Sno=SC.Sno and SC.Cno='81003';/*方法2:嵌套in*/select snamefrom Student where Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Cno='81003');/*方法3:嵌套exists*/select snamefrom Student where exists (select *from SCwhere Sno=Student.Sno and Cno='81003');/*(2)查询选修了学分为3的课程的学生学号和姓名;*//*方法1:连接查询*/select Student.Sno ,student.snamefrom Student,SC,Coursewhere Student.Sno=SC.Sno and SC.Cno=Course.Cno and Ccredit='3';/*方法2:嵌套in*/select Sno ,snamefrom Student where Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Cno in (select Cnofrom Coursewhere Ccredit='3'));/*(3)找出每个超过其所在专业平均年龄的学号,姓名和年龄*//*方法1:嵌套相关查询*/select sno,sname,YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate)as'年龄'from Studentwhere YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate)> any(select AVG(YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate))from Studentgroup by Smajor);/*方法2:派生表*/select distinct sno,sname,YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate)as'年龄'from Student x,(select AVG(YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate))from Student ygroup by y.Smajor) as avg_sex(sex)where YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate)>avg_sex.sex;/*(4)查询学分大于“操作系统”的所有课程名称;*//*方法1:嵌套>*/select Cnamefrom Course where Ccredit >(select Ccreditfrom Coursewhere Cname='操作系统');/*方法2:嵌套exists*/select Cnamefrom Course xwhere exists(select *from Course ywhere x.Ccredit>y.Ccredit and y.Cname='操作系统');/*(5)查询没有选“数据库”的学生学号;*//*方法1:嵌套exists*/select distinct Snofrom SC x where not exists(select *from SC ywhere y.Sno=x.Sno and exists(select * from Coursewhere Cno=y.Cno and Cname='数据库系统概论') );/*方法2:集合差*/select distinct snofrom SCexceptselect Snofrom Course,SCwhere Course.Cno=SC.Cno and Cname='数据库系统概论';/*方法3:not in*/select distinct Snofrom SC where Sno not in (select Snofrom SC where Cno in (select Cno from Coursewhere Cname='数据库系统概论') );/*(6)查询与“数据库”、“数学”学分不同的所有课程名称;*//*方法1:not in*/select Cnamefrom Course where Ccredit not in (select Ccreditfrom Course where Cname in (select Cname from Coursewhere Cname in('数据库系统概论','离散数学') ));/*方法3:<> all或者any*/select Cnamefrom Course where Ccredit <> any(select Ccreditfrom Course where Cname in (select Cname from Coursewhere Cname in('数据库系统概论','离散数学') )); /*(7)查询平均分大于等于80分的所有课程号和课程名称;*//*方法1:连接查询*/select Course.Cno,Cnamefrom Course,SCwhere Course.Cno=SC.Cnogroup by Course.Cno,Cnamehaving AVG(Grade)>='80';/*方法2:派生表*/select Course.Cno,Cnamefrom Course,(select cnofrom SCgroup by Cnohaving AVG(Grade)>='80')as avg_sc(avg_cno)where Course.Cno=avg_sc.avg_cnogroup by Course.Cno,Cname/*(8)查询同时选修了‘81001’和‘81002’号课程的学生学号和姓名;*//*方法1:自身连接*/select student.Sno,Snamefrom Student ,SC s1,SC s2where Student.Sno=s1.Sno and s1.Sno=s2.Sno and s1.Cno='81001' and s2.Cno='81002'group by Student.Sno,Sname;/*方法2:嵌套in*/select Sno,Snamefrom Student where Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Cno = '81001'and Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Cno='81002'));/*方法3:集合*/select student.Sno,Snamefrom Student ,SC where Student.Sno=sc.Sno and Cno='81001' INTERSECTselect student.Sno,Snamefrom Student ,SC where Student.Sno=SC.Sno and Cno='81002';/*(9)查询同时选修了‘数据库系统概论’和‘数据结构’的学生学号和姓名;*//*方法1:嵌套in*/select Sno,Snamefrom Student where Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Cno in (select Cnofrom Coursewhere Cname = '数据库系统概论') and Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Cno in (select Cnofrom Coursewhere Cname='数据结构')));/*方法2:集合*/select Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,(select Snofrom SCwhere Cno in (select Cnofrom Coursewhere Cname = '数据库系统概论'))as x_sc(sno)where Student.Sno=x_sc.snointersectselect Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,(select Snofrom SCwhere Cno in (select Cnofrom Coursewhere Cname='数据结构'))as y_sc(sno)where Student.Sno=y_sc.sno /*(10)查询所有学生都选了的课程号;*/ /*嵌套exists,不存在一个学生没选的课程*/
SELECT CnoFROM CourseWHERE NOT EXISTS(SELECT *FROM StudentWHERE NOT EXISTS(SELECT *FROM SCWHERE Sno= Student.SnoAND Cno= Course.Cno));/*(11)查询与“数据结构”具有相同先修课的课程号和课程名;*//*方法1:自身连接*/select c1.Cno,c1.Cnamefrom Course c1,Course c2where c1.Cpno=c2.Cpno and c2.Cname='数据结构' and c1.Cname<>'数据结构';/*方法2:嵌套in*/select Cno,Cnamefrom Course where Cname<>'数据结构' and Cpno in (select Cpnofrom Coursewhere Cname='数据结构');/*方法3:嵌套exists*/select Cno,Cnamefrom Course xwhere Cname<>'数据结构' and exists (select *from Course ywhere y.Cpno=x.Cpno and Cname='数据结构');/*方法4:派生表*/select Cno,Cnamefrom Course,(select Cpnofrom Coursewhere Cname='数据结构')as xcourse(scpno)where Cname<>'数据结构'and Cpno=xcourse.scpno;/*(12)查询所有具有不及格记录的学生学号和姓名*//*方法1:连接查询*/select Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,SCwhere Student.Sno=SC.Snogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Gradehaving Grade<'60';/*方法3:嵌套in*/select Sno,Snamefrom Studentwhere Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Grade<'60');/*方法3:嵌套exists*/select Sno,Snamefrom Studentwhere exists(select *from SCwhere sno=Student.Sno and Grade<'60');/*方法4:派生表*/select Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,(select Snofrom SCwhere Grade<'60')as xsc(sno)where Student.Sno=xsc.snogroup by Student.Sno,Sname/*(13)查询计算机科学与技术专业学生选修的所有课程号;*//*方法1:连接查询*/select SC.Cnofrom Student,SCwhere Student.Sno=SC.Snogroup by SC.Cno,Smajorhaving Smajor='计算机科学与技术';/*方法2:嵌套in*/select distinct Cnofrom SCwhere Sno in (select Snofrom Studentwhere Smajor='计算机科学与技术');/*方法3:嵌套exists*/select distinct Cnofrom SCwhere exists(select *from Studentwhere Sno=SC.Sno and Smajor='计算机科学与技术');/*方法4:派生表*/select Cnofrom SC,(select Snofrom Studentwhere Smajor='计算机科学与技术')as xstudent(sno)where xstudent.sno=SC.Snogroup by Cno;/*(14)查询所有计算机科学与技术专业学生都选的课程号;*/
SELECT CnoFROM CourseWHERE NOT EXISTS(SELECT *FROM StudentWHERE NOT EXISTS(SELECT *FROM SCWHERE Sno= Student.SnoAND Cno= Course.Cno )and Smajor='计算机科学与技术');/*(15)查询选修了81003号课程并且不及格的学生姓名*//*方法1:多表连接法*/select Snamefrom Student,SCwhere Student.Sno=SC.Snogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Grade,Cnohaving Grade<'60'and Cno='81003';/*方法2:嵌套in*/select Snamefrom Studentwhere Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Grade<'60'and Cno='81003');/*方法3:交集*/select Snamefrom Student,SCwhere Student.Sno=SC.Snogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Grade,Cnohaving Grade<'60'intersectselect Snamefrom Student,SCwhere Student.Sno=SC.Snogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Grade,Cnohaving Cno='81003';/*方法4:派生表*/select Snamefrom Student,(select Snofrom SCwhere Grade<'60'and Cno='81003')as xsc(sno)where Student.Sno=xsc.snogroup by Sname;/*方法5:嵌套exists*/select Snamefrom Studentwhere exists(select *from SCwhere Sno=Student.Sno and Grade<'60'and Cno='81003'); /*(16)查询选修了“数据库系统概论”并且不及格的学生姓名*//*方法1:多表连接法*/select Snamefrom Student,SC,Coursewhere Student.Sno=SC.Sno and SC.Cno=Course.Cnogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Grade,Cnamehaving Grade<'60'and Cname='数据库系统概论';/*方法2:嵌套in*/select Snamefrom Studentwhere Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Grade<'60'and Cno in (select Cnofrom Coursewhere Cname='数据库系统概论'));/*方法3:交集*/select Snamefrom Student,SCwhere Student.Sno=SC.Snogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Gradehaving Grade<'60'intersectselect Snamefrom Student,SC,Coursewhere Student.Sno=SC.Sno and SC.Cno=Course.Cnogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Cnamehaving Cname='数据库系统概论';/*方法4:派生表*/select Snamefrom Student,(select Sno,Cnofrom SCwhere Grade<'60')as xsc(sno,cno),(select Cnofrom Coursewhere Cname='数据库系统概论')as xcourse(cno)where Student.Sno=xsc.sno and xsc.cno=xcourse.cnogroup by Sname; /*(17)查询计算机科学与技术专业选修了“数据库系统概论”课且成绩及格的所有学生的学号和姓名;*//*方法1:多表连接法*/select Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,SC,Coursewhere Student.Sno=SC.Sno and SC.Cno=Course.Cnogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Grade,Cname,Smajorhaving Grade>'60'and Cname='数据库系统概论'and Smajor='计算机科学与技术';/*方法2:嵌套in*/select Sno,Snamefrom Studentwhere Smajor='计算机科学与技术' and Sno in (select Snofrom SCwhere Grade>'60'and Cno in (select Cnofrom Coursewhere Cname='数据库系统概论') );/*方法3:交集*/select Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,SCwhere Student.Sno=SC.Sno group by Student.Sno,Sname,Gradehaving Grade>'60'intersectselect Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,SC,Coursewhere Student.Sno=SC.Sno and SC.Cno=Course.Cnogroup by Student.Sno,Sname,Grade,Cname,Smajorhaving Cname='数据库系统概论'intersectselect Sno,Snamefrom Studentwhere Smajor='计算机科学与技术';/*方法4:派生表*/select Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,(select Sno,Cnofrom SCwhere Grade>'60')as xsc(sno,cno),(select Cnofrom Coursewhere Cname='数据库系统概论')as xcourse(cno)where Student.Sno=xsc.sno and xsc.cno=xcourse.cno and Smajor='计算机科学与技术'group by Student.Sno,Sname; /*(18)查询与“刘晨”同岁且不与“刘晨”在同一个系的学生学号与姓名;*//*方法1:嵌套in*/select Sno,Snamefrom Studentwhere Sname<>'刘晨' and YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate)in (select YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate)from Studentwhere Sname='刘晨')and Smajor not in (select Smajorfrom Studentwhere Sname='刘晨');/*方法2:嵌套exists*/select Sno,Snamefrom Student xwhere Sname<>'刘晨' and exists(select *from Student ywhere YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(y.sbirthdate)=YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(x.sbirthdate)and y.Sname='刘晨')and not exists(select *from Student zwhere z.Smajor=x.Smajor and z.Sname='刘晨');/*方法3:派生表*/ select Student.Sno,Snamefrom Student,(select Sno,YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate)from Studentwhere Sname='刘晨')as ystudent(sno,sex),(select Sno,Smajorfrom Studentwhere Sname='刘晨')as zstudent(sno,smajor)where Sname<>'刘晨'and YEAR(GETDATE())-YEAR(sbirthdate)=ystudent.sex and Student.Smajor<>zstudent.smajor这篇关于数据库系统概论(超详解!!!) 第三节 关系数据库标准语言SQL(Ⅳ)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




