本文主要是介绍Java基础入门day24,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
day24
abstract
抽象:似是而非,像又不是,具备某种对象的特征,但不完整
生活中的抽象:动物,并不真实存在的事物
程序中的抽象:不应该被创建的对象,动物近视一种会吃会睡的对象,再无其他行为,不够具体,不够完整
package com.saas.oo01; public class Animal { String breed; int age; public void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");} public void sleep(){System.out.println("sleeping...");System.out.println("zzzzzzzzzZZZZZZZZZZZ");} }package com.saas.oo01; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) {Animal animal = new Animal(); animal.breed = "taidi";animal.age = 5; animal.eat();System.out.println("------------------");animal.sleep();} }以上程序设计,我们说让程序员自觉地不进行创建对象,但是一旦使用new关键字调用,还是可以执行的,但是这样没有意义,所以这种方式没有办法从根本上杜绝问题存在。
我们在程序中不能对这种不够具体的事物创建其对象,可以使用abstract关键字来实现这种限制
package com.saas.oo02; public abstract class Animal { String breed; int age; public void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");} public void sleep(){System.out.println("sleeping...");System.out.println("zzzzzzzzzZZZZZZZZZZZ");} }package com.saas.oo02; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) {Animal animal = new Animal(); animal.breed = "taidi";animal.age = 5; animal.eat();System.out.println("------------------");animal.sleep();} }将Animal类使用abstract抽象关键字来修饰,一旦一个类用abstract修饰,那么该类就是抽象类,抽象类是无法创建对象,一旦想要直接创建对象,编译器会报错。所以可以从根本上解决创建对象的问题
一个类被abstract修饰,此类是不能new对象
被abstract修饰的类,成为抽象类
抽象类意为不够完整的类、不够具体的类,抽象类对象无法独立存在,即不能创建new对象
抽象类的作用:
可以被子类继承,提供共性的属性和方法
可声明为引用,可以更自然的使用多态
抽象方法
被abstract修饰的方法,被称之为抽象方法
抽象方法特点:只有方法声明,没有方法实现,意为不完整的方法,必须包含在抽象类中
抽象类中可以不必含有抽象方法
抽象类中是含有构造方法,之不能不能直接初始化抽象类对象本身,可以在该构造方法中初始化各个子类类型的对象
小结:
abstract修饰的类:不能new对象,但可以声明引用
abstract修饰的方法:只有方法声明,没有方法实现(需包含在抽象类中)
抽象类中不一定含有抽象方法,但是含有抽象方法的类一定是抽象类
抽象类中是含有构造方法的
子类继承抽象类后,必须重写父类的所有抽象方法,否则可以让子类继续保持抽象
static
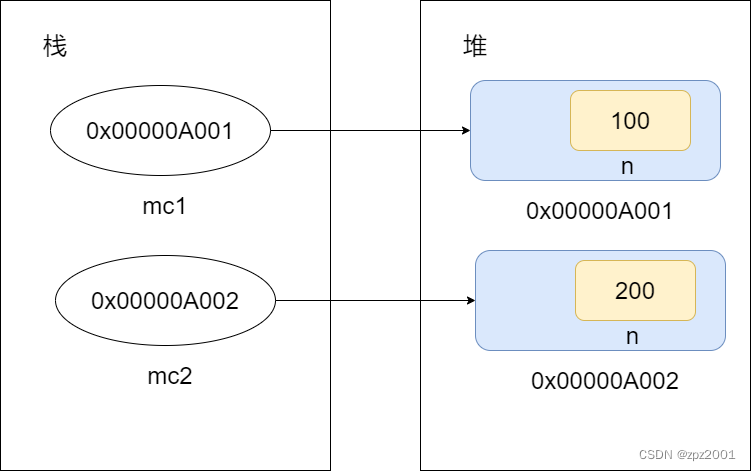
package com.saas.oo4; public class MyClass { int n; }package com.saas.oo4; public class TestStatic { public static void main(String[] args) {MyClass mc1 = new MyClass(); mc1.n = 100; System.out.println(mc1.n); System.out.println("================="); MyClass mc2 = new MyClass(); mc2.n = 200; System.out.println(mc2.n); System.out.println("=================="); System.out.println("mc1.n\t" + mc1.n +"\nmc2.n:\t" + mc2.n) ;} }运行结果如下:
100 ================= 200 ================== mc1.n 100 mc2.n: 200实例属性是每个对象各自持有的独立空间(多份),对象单方面修改,不会影响其他对象
有些时候,我们希望属性是整个类共同持有的共享空间(一份),任何对象修改,都会影响其他对象
package com.saas.oo4; public class MyClass02 { static int n; }package com.saas.oo4; public class TestStatic02 { public static void main(String[] args) {MyClass02 mc1 = new MyClass02(); mc1.n = 100; System.out.println(mc1.n); System.out.println("================="); MyClass02 mc2 = new MyClass02(); mc2.n = 200; System.out.println(mc2.n); System.out.println("=================="); System.out.println("mc1.n\t" + mc1.n +"\nmc2.n:\t" + mc2.n) ;} }运行结果如下:
100 ================= 200 ================== mc1.n 200 mc2.n: 200通过两次
的运行结果发现:
一旦属性用static修饰,那么该属性就属于静态属性,静态属性是属于整个类的,不专属于某个对象。只要有任何对象对于静态属性做了修改,由于在整个内存中是共享空间,所以后面对象得到的该属性值已经是修改过的值
概念:
static静态可以修饰属性和方法
被static修饰的属性被称之为静态属性(类属性),被static修饰的方法称之为静态方法(类方法)
静态成员是全类所有对象共享的成员
在全类中只有一份,不会因为创建多个对象而产生多份
不必创建对象,可以直接通过类名来访问
静态方法:
被static修饰的方法被称之为静态方法
静态方法与静态属性一样,也可以通过对象来调用,但是不推荐,推荐使用类直接调用
package com.saas.oo4; public class MyClass03 { public static void test01(){System.out.println("this is test01");} public static void test02(){System.out.println(" this is test02");test01();} }package com.saas.oo4; public class TestStatic04 { public static void main(String[] args) { // MyClass03 mc = new MyClass03(); // // mc.test01(); // test01是MyClass03类中的静态方法,可以通过对象来调用,但是不推荐MyClass03.test01(); // 静态方法推荐使用类来直接调用} }在同一个类当中,静态方法可以直接调用其他的静态方法,直接写方法名即可
在其他类中静态方法可以通过当前的类名来访问静态方法
之前学过的静态方法:
Arrays.copyOf();
System.arrayCopy();
Math.random();
静态的特点:
静态方法允许直接访问静态成员
静态方法不能直接访问非静态成员,必须通过对象来访问
静态方法不允许使用this或者super关键字
静态方法可以被继承,不能重写,没有多态
package com.saas.oo4; public class Father { public static void test(){System.out.println("this is test in Father class");} }package com.saas.oo4; public class Son extends Father{ public static void test(){System.out.println("this is test in Son class");} }package com.saas.oo4; public class TestStatic05 { public static void main(String[] args) {Father.test();Son.test(); Father fs = new Son();Son ss = new Son(); fs.test();ss.test();} }最终的运行结果如下:
this is test in Father class this is test in Son class this is test in Father class this is test in Son class动态代码块和静态代码块
package com.saas.oo5; public class MyClass { String field01 = "实例属性";static String filed02 = "静态实例属性"; {System.out.println("this is non-static code block01");} {System.out.println("this is non-static code block02");} public MyClass(){System.out.println("this is MyClass Constructor.");} static {System.out.println("this is static code block02");} static {System.out.println("this is static code block01");} }package com.saas.oo5; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // System.out.println(MyClass.filed02);new MyClass();System.out.println("========================");new MyClass();System.out.println("========================");new MyClass();System.out.println("========================");new MyClass();System.out.println("========================");new MyClass();} }运行结果如下:
this is static code block02 this is static code block01 this is non-static code block01 this is non-static code block02 this is MyClass Constructor. ======================== this is non-static code block01 this is non-static code block02 this is MyClass Constructor. ======================== this is non-static code block01 this is non-static code block02 this is MyClass Constructor. ======================== this is non-static code block01 this is non-static code block02 this is MyClass Constructor. ======================== this is non-static code block01 this is non-static code block02 this is MyClass Constructor.以上的运行结果可以得出如下结论
一个类中如果同时定义了静态代码块,非静态代码块和构造方法时,其执行顺序如下:
如果只是访问当前类的静态成员,则按顺序直接执行当前类的静态代码块,以及静态成员
如果要访问当前类的非静态成员,则第一步按顺序执行当前类的静态代码块,非静态代码块,构造方法再到当前类的非静态成员
如果创建多个对象,则静态代码块还是按照顺序只执行一次,而非静态代码块次数是创建几个对象,则执行几次非静态代码块以及走几次构造方法
带有继承关系的父子类之间的静态代码块和非静态代码块的运行结果:
package com.saas.oo5; public class Father { String field01 = "Father实例属性";static String filed02 = "Father静态实例属性"; {System.out.println("this is Father non-static code block01");} {System.out.println("this is Father non-static code block02");} public Father(){System.out.println("this is Father Constructor.");} static {System.out.println("this is Father static code block02");} static {System.out.println("this is Father static code block01");} }package com.saas.oo5; public class Son extends Father { String field01 = "Son实例属性";static String filed02 = "Son静态实例属性"; {System.out.println("this is Son non-static code block01");} {System.out.println("this is Son non-static code block02");} public Son(){System.out.println("this is Son Constructor.");} static {System.out.println("this is Son static code block02");} static {System.out.println("this is Son static code block01");} }package com.saas.oo5; public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Son.filed02);} }运行结果如下:
this is Father static code block02 this is Father static code block01 this is Son static code block02 this is Son static code block01 Son静态实例属性如果只是访问子类的静态成员,则执行结果为:
先顺序执行父类的静态代码块
再顺序执行子类的静态代码块
再执行子类的静态成员
package com.saas.oo5; public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) { // System.out.println(Son.filed02);System.out.println(new Son().field01);System.out.println("====================");System.out.println(new Son().field01);System.out.println("====================");System.out.println(new Son().field01);} }运行结果如下:
this is Father static code block02 this is Father static code block01 this is Son static code block02 this is Son static code block01 this is Father non-static code block01 this is Father non-static code block02 this is Father Constructor. this is Son non-static code block01 this is Son non-static code block02 this is Son Constructor. Son实例属性 ==================== this is Father non-static code block01 this is Father non-static code block02 this is Father Constructor. this is Son non-static code block01 this is Son non-static code block02 this is Son Constructor. Son实例属性 ==================== this is Father non-static code block01 this is Father non-static code block02 this is Father Constructor. this is Son non-static code block01 this is Son non-static code block02 this is Son Constructor. Son实例属性如果要访问子类的非静态成员,得创建子类对象,那么创建子类对象多次,将按照如下结果执行:
先顺序执行父类的静态代码块
再顺序执行子类的静态代码块
再顺序执行父类的非静态代码块
再执行父类的构造器
再按顺序执行子类的非静态代码块
再执行子类的构造器
再执行子类的成员
注意:创建几个子类对象,那么以上所有的非静态代码块和构造器都将分别执行几套
static小结:
static修饰的成员为静态成员,无需创建对象即可访问
静态方法不能直接访问非静态成员
静态方法中不能使用this和super
静态方法可以继承,不能被重写,没有多态
静态代码块再类加载的过程中默认被执行,而且只执行一次
非静态代码块在创建对象时默认被执行,创建几个对象,非静态代码块执行几次
final
这篇关于Java基础入门day24的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!